* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evidence of Evolution Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Comparative foot morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural transmission in animals wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology since 1859 wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology (through 1859) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
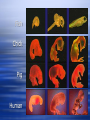
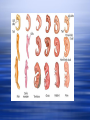
Evolution the process of change within a population that occurs over a series of generations an attempt to explain why organisms that are so similar in their molecular make-up can be so different in form and function Example: all plants have similar cells. Evidence of Evolution: Adaptations Adaptation: any variation that aids an organism’s chance of survival in it’s environment 3 types of adaptations: 1. Structural – parts of an organism that help it to survive in its environment; external features ex. large ears for cooling (desert foxes) large teeth (beavers) 2. Physiological – body chemistry or metabolism that help it survive in its environment; internal features ex. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics Bad-tasting chemicals (ladybugs) 3. Behavioral – how an organism acts that helps it survive in its environment ex. Hibernation (bears) Mating behaviors (birds of paradise) Bird of Paradise Evidence of Evolution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Fossils Embryology Homologous Structures Analagous Structures Vestigial Structures Physiological Evidence Biochemical Evidence 1. Fossils (Paleontology) Provides direct evidence for evolution Gives rise to theory of divergent evolution, whereby organisms evolve into a variety of specialized life forms to ensure a group’s survival. Eventually each of these life forms may become a distinct species. Ancient Fly in Amber Earring Phylogenetic Trees Used to explain the common structures found among species. Determining the Age of Fossils 1. Relative Dating -fossils nearer to the surface are younger 2. Radiometric Dating -radioactive isotopes: are present in rock in which fossils may be encased are unstable, and decay into new isotopes the length of time of their decay can be measured by comparing the amount of radioactive isotope to the amount of the new isotope, based on the half-life Radiometric Dating Example: Potassium-40 decays to Argon-40. Potassium-40 decays to half its original amount in 1.3 billion years. If there are equal amounts of Potassium-40 and Argon-40 in a rock sample, how old is the rock sample? Answer: 1.3 billion years. Dinosaur Eggs in Chinese Rock Shop Petrified Wood - California 2. Embryology Embryo’s of different species look similar (1880’s)… due to a common ancestor? Every organism repeats its evolutionary development (phylogeny) in the stages of embryo development (ontogeny) Fish Chick Pig Human 3. Homologous Structures structures in different creatures (often with different functions) have the same organization Gives evidence for divergence, in which a single structure can change to meet an organisms needs in a new environment. Example: Bat wing, mole arm, wolf leg 4. Analagous Structures have the same function, but different orgins environment can affect the structure of an organism Example: butterfly and bird wing. 5. Vestigial Structures structures that no longer serve a useful purpose usually greatly reduced in size some structures that were once considered vestigial are now known to be necessary for the organism Example: dew claws on dogs, pigs and horses / hips on snakes and whales. Shallow Hal Ambulocetus Basilosaurus with well developed hind limbs, though reduced in size. Sperm whales retain hind limb atavisms. 6. Physiological Evidence evidence shows that wastes excreted from birds and reptiles have the same biochemical make-up hormones (I.e. Insulin) from cows and pigs can be injected into humans 7. Biochemical Evidence DNA comparisons show a great deal of similiarity humans and chimps share 96% of their DNA. the number of genetic differences between humans and chimps is approximately 60 times less than that seen between human and mouse and about 10 times less than between the mouse and rat the number of genetic differences between a human and a chimp is about 10 times more than between any two humans