Class Amphibia: Frog dissection Lab
... Compare the length of your frog to the length of the small intestines. Why do you think they are different? Which parts of the frog’s nervous system can be observed in its abdominal cavity and hind leg? The abdominal cavity of a frog at the end of hibernation season would contain very small fat bodi ...
... Compare the length of your frog to the length of the small intestines. Why do you think they are different? Which parts of the frog’s nervous system can be observed in its abdominal cavity and hind leg? The abdominal cavity of a frog at the end of hibernation season would contain very small fat bodi ...
curative healing of the plantar first metatarsal ulceration
... *Hallux limitus may be concomitantly present. The primary cause of medial shifted lesions is an unstable first metatarsophalangeal joint (i.e., medial column overload and hallux valgus). ...
... *Hallux limitus may be concomitantly present. The primary cause of medial shifted lesions is an unstable first metatarsophalangeal joint (i.e., medial column overload and hallux valgus). ...
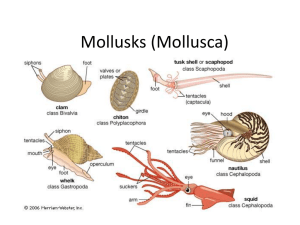
Mollusks - walker2012
... coordinate their movement and behavior Octopi and squids have brains Most mollusks have paired eyes that range from simple eyes (detecting light) to complex eyes (having irises, pupils, and retinas) ...
... coordinate their movement and behavior Octopi and squids have brains Most mollusks have paired eyes that range from simple eyes (detecting light) to complex eyes (having irises, pupils, and retinas) ...
Amputation Explained
... Unless an amputation is performed as an emergency, the patient will probably undergo a number of tests and procedures before the amputation takes place. These tests are designed to assess the type of amputation suitable for the patient, along with anything that may affect their rehabilitation. These ...
... Unless an amputation is performed as an emergency, the patient will probably undergo a number of tests and procedures before the amputation takes place. These tests are designed to assess the type of amputation suitable for the patient, along with anything that may affect their rehabilitation. These ...
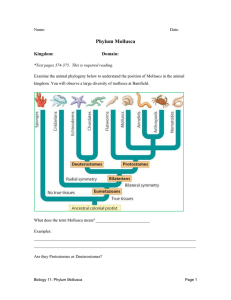
Phylum Mollusca - Bakersfield College
... through shell of prey • Sensory structures – Eyes, tentacles ...
... through shell of prey • Sensory structures – Eyes, tentacles ...
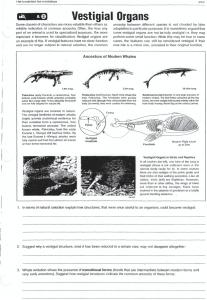
Vestigial Organs
... their evolution from a carnivorous, four footed, terrestrial ancestor. The oldest known whale, Pakicetus, from the early Eocene (- 54mya) still had four limbs. By the fate Eocene (~40mya), whales were fully marine and had fost almost all traces of their former terrestrial life. ...
... their evolution from a carnivorous, four footed, terrestrial ancestor. The oldest known whale, Pakicetus, from the early Eocene (- 54mya) still had four limbs. By the fate Eocene (~40mya), whales were fully marine and had fost almost all traces of their former terrestrial life. ...
Figure 11.13 Trochophore (a) and veliger (b)
... • Head in line with visceral mass • Muscular mantle (figure 11.17) ...
... • Head in line with visceral mass • Muscular mantle (figure 11.17) ...
Running head: AN EVALUATION OF THE ELEPHANT
... that the pad of an elephant is as diverse as the human fingerprint in that it is unique to that particular animal; the pattern of the print can also be used to determine the age and overall size of the elephant as well. Interestingly, the musculoskeletal system of the elephant allows it equal power ...
... that the pad of an elephant is as diverse as the human fingerprint in that it is unique to that particular animal; the pattern of the print can also be used to determine the age and overall size of the elephant as well. Interestingly, the musculoskeletal system of the elephant allows it equal power ...
Mollusca - Ms. Marcos` Biology Wiki
... Colossal Squid off the coast of New Zealand and weighed in at 495 kg. Colossal Squid are larger than the giant squid found off the Mexican coast and are thought to grow in size to 13 meters! ...
... Colossal Squid off the coast of New Zealand and weighed in at 495 kg. Colossal Squid are larger than the giant squid found off the Mexican coast and are thought to grow in size to 13 meters! ...
Phylum Mollusca
... • In some of the more primitive gastropods (keyhole limpets), the shell contains a hole at the top through which the exhalent water stream exits • In the more advanced gastropods, water is brought into the mantle cavity on the left side, passes over a single gill, and exits the right side ...
... • In some of the more primitive gastropods (keyhole limpets), the shell contains a hole at the top through which the exhalent water stream exits • In the more advanced gastropods, water is brought into the mantle cavity on the left side, passes over a single gill, and exits the right side ...
Phylum Mollusca
... *Complete the sentence below using the following words: Oxygen, Cilia, Plankton, Water Bivalves are generally stationary when feeding. They draw _______________in through a siphon, pass it over their gills to extract ___________________and filter out ___________________ in a mucous layer. The plankt ...
... *Complete the sentence below using the following words: Oxygen, Cilia, Plankton, Water Bivalves are generally stationary when feeding. They draw _______________in through a siphon, pass it over their gills to extract ___________________and filter out ___________________ in a mucous layer. The plankt ...
01 Mollusca - Mr. Harshenin
... Introduction to Molluscs Molluscs represent the second largest animal phylum, following the arthropods ...
... Introduction to Molluscs Molluscs represent the second largest animal phylum, following the arthropods ...
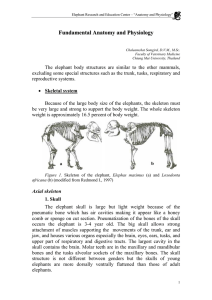
Fundamental Anatomy and Physiology
... after the birth. Elephants have 6 sets of molar teeth during their life span but they cannot hold all 6 sets at one time. The molar teeth are shed periodically. They move foreword in the jaw to displace old and worn teeth that fragment and usually fall out on their own and are swallowed. The structu ...
... after the birth. Elephants have 6 sets of molar teeth during their life span but they cannot hold all 6 sets at one time. The molar teeth are shed periodically. They move foreword in the jaw to displace old and worn teeth that fragment and usually fall out on their own and are swallowed. The structu ...
Mollusks
... A study emerged in March 2008 in which scientists have found that the hard and soft materials of a Humboldt squid’s beak may be used to improve artificial limbs for humans. ...
... A study emerged in March 2008 in which scientists have found that the hard and soft materials of a Humboldt squid’s beak may be used to improve artificial limbs for humans. ...
mollusca classification
... • Majority of them are enclosed in a calcareous shell. The shell may be external or in a few molluscs it may be internal, reduced or absent. ...
... • Majority of them are enclosed in a calcareous shell. The shell may be external or in a few molluscs it may be internal, reduced or absent. ...
Section 27–4 Mollusks
... 14. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about mollusk response. a. Clams have a simple nervous system. b. Octopi and their relatives have the most highly-developed nervous system of all invertebrates. c. Clams have well-developed brains. d. Vertebrates are more intelligent than octopi. 1 ...
... 14. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about mollusk response. a. Clams have a simple nervous system. b. Octopi and their relatives have the most highly-developed nervous system of all invertebrates. c. Clams have well-developed brains. d. Vertebrates are more intelligent than octopi. 1 ...
Winston Knoll Collegiate
... 14. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about mollusk response. a. Clams have a simple nervous system. b. Octopi and their relatives have the most highly-developed nervous system of all invertebrates. c. Clams have well-developed brains. d. Vertebrates are more intelligent than octopi. 1 ...
... 14. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about mollusk response. a. Clams have a simple nervous system. b. Octopi and their relatives have the most highly-developed nervous system of all invertebrates. c. Clams have well-developed brains. d. Vertebrates are more intelligent than octopi. 1 ...
Exam 4 Review Questions
... 74. Gastropods, bivalves and cephalopods all have a _______ that secretes the shell. a) foot b) mantle c) gill d) visceral mass e) chromophore 76. Molluscs differ from nematodes in that mollusks have _____, which is not found in nematodes. a) bilateral symmetry b) three germ layers c) an anus that d ...
... 74. Gastropods, bivalves and cephalopods all have a _______ that secretes the shell. a) foot b) mantle c) gill d) visceral mass e) chromophore 76. Molluscs differ from nematodes in that mollusks have _____, which is not found in nematodes. a) bilateral symmetry b) three germ layers c) an anus that d ...
chiton
... algae from the rocks • Mouth is anterior and anus is posterior; linear digestive tract ...
... algae from the rocks • Mouth is anterior and anus is posterior; linear digestive tract ...
Homologous Structures
... • Comparative anatomy looks at the similarities and differences in the anatomy of organisms, and how these structures are used. – The anatomy is the way the body is designed: bone structure and organ structures. – Comparing the way organisms are put together ...
... • Comparative anatomy looks at the similarities and differences in the anatomy of organisms, and how these structures are used. – The anatomy is the way the body is designed: bone structure and organ structures. – Comparing the way organisms are put together ...
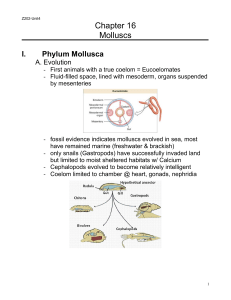
Chapter 16 Molluscs
... Form and Function A. Three Part Molluscan Body Plan 1. Head-foot portion contains feeding, cephalic sensory & locomotor organs 2. Visceral mass portion contains digestive, circulatory, respiratory, & reproductive organs 3. Mantle forms a protective covering ...
... Form and Function A. Three Part Molluscan Body Plan 1. Head-foot portion contains feeding, cephalic sensory & locomotor organs 2. Visceral mass portion contains digestive, circulatory, respiratory, & reproductive organs 3. Mantle forms a protective covering ...
Comparative foot morphology

Comparative foot morphology involves comparing the form of distal limb structures of a variety of terrestrial vertebrates. Understanding the role that the foot plays for each type of organism must take account of the differences in body type, foot shape, arrangement of structures, loading conditions and other variables. However, similarities also exist among the feet of many different terrestrial vertebrates. The paw of the dog, the hoof of the horse, the manus (foot) and pes (foot) of the elephant, and the foot of the human all share some common features of structure, organization and function. Their foot structures function as the load-transmission platform which is essential to balance, standing and types of locomotion (such as walking, trotting, galloping and running).The discipline of biomimetics applies the information gained by comparing the foot morphology of a variety of terrestrial vertebrates to human-engineering problems. For instance, it may provide insights that make it possible to alter the foot's load transmission in people who wear an external orthosis because of paralysis from spinal-cord injury, or who use a prosthesis following the diabetes-related amputation of a leg. Such knowledge can be incorporated in technology that improves a person's balance when standing; enables them to walk more efficiently, and to exercise; or otherwise enhances their quality of life by improving their mobility.