* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download basic of the genetic
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
DNA paternity testing wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
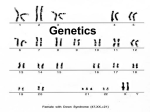
Basic words: • GENOTYPE = complex of all hereditary information of organism (all genes) • PHENOTYPE = complex of visible outward signs and characters, outer demonstration of the genotype • ALLELE = one form of the gene • HOMOZYGOUS = organism, which from perspective of selected gene includes couple of alleles with coincident function (for ex. aa, BB, ...) • HETEROZYGOUS = organism, which perspective of selected gene include couple of alleles with different function (for ex. Aa, Bb) In heterozygotes, for the phenotype demonstration is crucial the functional relationship between different alleles: – DOMINANT – allele is fully functional and rules over the another – RECESSIVE – nonfunctional allele, which is not demonstrated in phenotype • AUTOSOMAL HEREDITY = bounded to nongender chromosomes - autosoms (for ex. Color of eyes, hair, ...) • GONOSOMAL HEREDITY = bounded to gender chromosomes – gonosomes (for ex. daltonism, haemophilia) Some examples • Mother has blue eyes. Allele for blue eyes is recessive. Father has homozygous brown eyes. Which colour of eyes will have their child? • Answer: P-generation: mother: aa gamets: a F1 – generation: x x father: AA A Aa • Concluson: All childs will have heterozygous brown eyes. ??? Ex.2: Allele A response to create the green colour of peas, allele a to create yellow color of peas. Allele B demonstration circle shape of peas, while allele b crisp shape. Cross one with green circle shape peas, which is homozygous and one with crisp shape yellow peas. Answer: P-gen.: gamets: F1-gen: AABB x aabb AB,AB ab, ab AaBb (green circle shape, heterozygous) We continue with crossing to next generation: AaBb x AaBb gamets: AB,Ab,aB,ab AB,Ab,aB,ab We use for calculating combination square: gamets AB Ab aB ab AB AABB AABb AaBB AaBb line of heterozygotes Conclusion: Ab AAbB AAbb AabB AAbb aB aABB aABb aaBB aaBb ab aAbB aAbb aabB aabb line of homozygotes Phenotype gender ratio 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 Gonosomal heredity – different from autosomal, (recessive allele can demonstrate) - is necessarily, if carrier of the sign is father or mother Example: Haemophilia is gonosomal bounded disease. Father bleeder (haemophiler) married with healty woman. Set the child if a) woman is not uttering b) woman is uttering Answer: a) P-gen: Gamets: F1-gen: x mother XX father: XhY Xh , Y X, X Xh X, Xh X, YX, YX Conclusion of a): Girls will by healty, but will uttering (Xh X) Boys will by healty XY b) P-gen: Gamets: F1-gen: father XhY x mother XXh Xh , Y X, Xh XhX, XhXh , XY, XhY Conclusion: 50% of girls will be healty but will uttering (XhX), 50% of girls will ill (bleeder) (XhXh). 50% of boys will be healthy (XY), 50% will be ill (bleeder) (XhY). Example: Gene for brown eye color is dominant to the gene for blue eye color. Man with blue eyes marries broweyed woman, whose mother had blue eyes. What ratio of their children will have blue eyes? • Man naemophilic marries his cousin. Mothers of both partners were sisters, whose father had haemophillia. Married couple had one son, who had haemophillia, two daughters, with haemophillia and one healthy daughter. – What were the genotypes of all family memebers? – What is the prognosis for the sons of ill daughters? – What is the prognosis for the sons of healthy daughter? Good luck to you at final test ☺