* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Forces and Fields
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
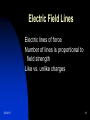
Electric Forces and Fields Electric Charge Positive and Negative Charge is conserved Millikan Oil Drop Experiment Charge on the electron/proton Conductors vs. Insulators Insulators and conductors can be charges by contact Conductors can be charged by induction Insulators can be charged by polarization 5/2/2017 1 Coulomb’s Law The force of electrical attraction or repulsion between charges. F = kcq1q2/r2 Kc = Coulomb’s Law Constant = 8.99 x 109 nm2/c2 Note: Attractive force would be negative and repulsive positive. 5/2/2017 2 17-2 Coulomb’s Law q 1q 2 Fe = kc 2 r kc = Coulomb’s Constant kc = 8.99x109 Nm2/C2 5/2/2017 1780’s Charles Coulomb was experimenting to find how charges create forces The force depends on Charge Distance He found the following relationship 3 17-2 Coulomb’s Law n+ +n e- Find the force between the nucleus and an electron in a helium atom if the are separated by 1.00 nm. q1 = 2(1.60x10-19) C q2 = 1.60x10-19 C 5/2/2017 4 17-2 Coulomb’s Law P+ A proton is being levitated by a charged floor with a charge of 3.6 picoCoulomb. How high does the proton hover above the ground? (pico = 10-12) Q = 3.6pC 5/2/2017 5 17-2 Coulomb’s Law 1 q1 = - 6 mC 2 2m q2 = +2 mC 3 1m q3 = - 3 mC Find the net force on q3 1 3 2 5/2/2017 What would change if this were the original orientation? 6 17-2 Coulomb’s Law 1 q1 = - 6 mC 2 2m q2 = +2 mC 3 x q3 = - 3 mC What is the value of x if q2 is in equilibrium? 5/2/2017 7 17-2 Coulomb’s Law 1 q1 = - 6 mC 2 y q2 = +2 mC 3 x q3 = - 3 mC Q2 is equilibrium with q1 and q3. What is the value of x and y if the distance between q1 and q3 is 10.0 m? 5/2/2017 8 Electric Field Strength E = F/q (N/c) For a point charge: E = kq/r2 5/2/2017 Example: What is the force on an electron due to an electric field of 50 N/C? If the mass of an electron is 9.11 x 10-31 kg, what would be the resulting acceleration of this electron? 9 Electric Field Lines Electric lines of force Number of lines is proportional to field strength Like vs. unlike charges 5/2/2017 10 Review Questions 1) An electron is pushed due to an electric field of 50N/C. If the mass of an electron is 9.11 x 10-31 kg, what would be the resulting acceleration of this electron? 2) What would the net electric field be for an object directly between a 6.0nC and a -7.5nC charge that is 3.2m apart? 5/2/2017 11 Review Question 2 5/2/2017 An electron is released from rest from the negative plate between parallel plates separated by a distance of 15 cm. It strikes the other plate in 1 E –7 sec. Determine the electric field between the plates. 12 Review Question 3 (honors) Given the isosceles triangle above with identical charges, Q, on either corners of the bottom vertices. 1) What is the net electric field acting at position C? 2) Where should a new charge, +2Q, in order to make the net electric field at point C zero? 5/2/2017 13