* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 2 ppt version - University of Southampton
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
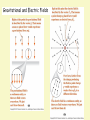
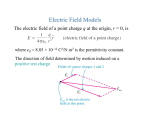
Last lecture: Electric Charge • Charge conservation • Charge quantisation Conductors and insulators Coulomb’s Law + EXERCISE: Draw a on the figure below to show the position or positions where a proton would experience no net force. 4+ + Answer Would the force on an electron at this position be A. to the left, B. to the right, or C. zero? Answer: C. the force on an electron would be zero, the same as for the proton. So what is special about this position? 20.3 The Electric Field Charges and Forces: a closer look Questions: How does q ‘know’ of the presence of any of the Qs? If we move one of the Qs, the force on q changes. Does it change immediately? An electric field is set up in the space surrounding a charge. It has both magnitude and direction, ie it is a vector field. Information about the move of a charge travels outward (in all directions) as an electromagnetic wave at the speed of light c. The Electric Field Gravitational and Electric Fields A small test charge q0 near a system of charges q1, q2,….., experiences a force F that is proportional to q0. The ratio F/q0 is the electric field at that point (the field point). The net electric field at a point P due to a distribution of point charges is found by summing the fields due to each charge separately SI unit for electric field is the Newton per coulomb (N/C) CHECKPOINT: What is the direction of the electric field due to the electron at (a) point S A. Right (b) point R? B. Left What is the direction of the net electric field at (c) point S A. Right (d) point R? A. Right or B. Left B. Left If four charges are placed at the corners of a square as shown, the field E is zero at A. all points along the sides of the square midway between two charges B. the midpoint of the square C. midway between the top two charges and midway between the bottom two charges D. none of the above Answer: B Example 20.4 p 335 Finding the field of two protons Two protons are 3.6 nm apart. Find the electric field at a point between them, 1.2 nm from one of the protons. Then find the force on an electron at this point. Go over this example Registering for Mastering Physics Course ID: PHYS1022EANDM Registration code: USMPEY-TTBBO-SPEND-MINNA-WERSHWIRES On the Access Information page, you will be asked if you have a Pearson Education account. If you have not yet registered – select No and enter your log in name (ie your university email address), and follow instructions for setting your password. If you have already registered for the e-Book - select Yes and enter your log in name, and the same password. The link to the presentation with all instructions for registering is on the front page of my course. http://www.phys.soton.ac.uk/teach/year1/notes/phys1022/ Deadlines Assignment 1 Coulomb’s Law must be completed by midnight on Friday 15 October. The Electric dipole - a pair of equal and opposite charges -- molecules can be modelled approximately as dipoles Example 20.5 p 335 A molecule may be modelled approximately as a positive charge q at x = a and a negative charge –q at x= -a. Find an expression for the electric field on the y axis. Find an approximate expression valid at large distances (y>>a) Problem 51: Electric field on the x axis - compare results with the electric field on y axis. Do on board The Electric dipole moment The field of a dipole depends on both the distance and the orientation of the dipole, since it is not spherically symmetric. Hence the dipole moment is defined as a vector p of magnitude p = qd in the direction from negative to positive.