* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phylum Platyhelminthes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
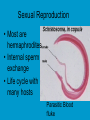
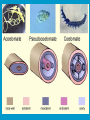
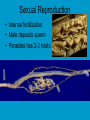
Phylum Platyhelminthes FLATWORMS: planaria, flukes, tapeworms tapeworm Planarian fluke • Habitat –Marine, freshwater, moist land • Importance –Cause disease, parasitic in plants and animals Method of obtaining food/digestive system • Extends pharynx and sucks up food into gastro vascular cavity or absorbs nutrients from host Asexual Reproduction • regeneration (some) • fission Sexual Reproduction • Most are hermaphrodites • Internal sperm exchange • Life cycle with many hosts Parasitic Blood fluke Symmetry • Bilateral Internal Body Cavity • Coelom –Fluid filled space found between the body wall and the digestive tract Internal body cavities/ tissue layers • Ectoderm- outer • Acoelomates- no layer of skin; body cavity • Pseudocoelomates nervous system; sense organs - (false body cavity) body cavity located • Endoderm-lining of digestive tract; between the digestive organs; etc endoderm and • Mesoderm-most of mesoderm the skeleton, • Coelomates-true muscles, coelom…located reproductive organs entirely within the mesoderm Nervous System • • • • Ganglia Eyespots Ability to learn Sensory organs Circulatory/Respiratory • diffusion Fresh water planarian Anything else • Tapeworm can grow 10 m long • Flukes need snails and humans to reproduce. Phylum Nematoda Roundworms Habitat • Soil, marine, animals, freshwater Hook worm ascaris Importance • Parasitic (some) in plants and animals Method of obtaining food/digestive system • Parasitic-absorbs nutrients • Predators-catches food in mouth Digestive system Asexual reproduction • none Sexual Reproduction • Internal fertilization • Male deposits sperm • Parasites has 2-3 hosts Symmetry • Bilateral Nervous System • Free living • Sense organs Circulatory/Respiratory • Diffusion Anything Else • Moves with muscles and cilia