* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vocabulary
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
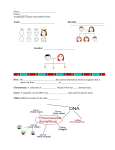
Chapter 3 Genetics: The science of heredity MENDEL ! Gregor Mendel was a priest and teacher in the 1850 s ! Mendel is famous for his observations and studies of pea plants and their traits (physical characteristics) ! Mendel is known as the father of genetics, which is the study of heredity (the passing of traits from parents to offspring) Mendel s Experiments ! Pea plants were easy to study because most of their traits exist only in two(2) forms (ex - either tall or short, no medium heights) ! Pea plants produce a large number of off spring in one generation = easy to collect lots of data Mendel s Experiments ! Mendel started by cross-breeding purebred plants with opposite forms of traits (ex - crossing a tall plant with a short plant) ! Purebred plant - one that always produces offspring with the same form of the trait as the parent Mendel s Experiments ! All of the offspring(F1 generation) from the cross of two purebred parents(P generation) showed only one of the traits! ! One of the traits seemed to disappear ! Then, he crossed two of the F1 generation………….. Mendel s Experiments ! HOLY COW!!!!!!!!!!! ! Even though all of the F1 generation showed only one form of the trait, their offspring (the F2 generation) showed a mix of the two forms of the trait! ! 3/4 showed one and 1/4 showed the other Mendel s Experiments ! Mendel studied a number of different traits and all of his experiments showed similar results. Mendel s Results ! Individual factors control the inheritance of traits ! The factors exist in PAIRS ! The female contributes one factor while the male contributes the other ! One factor in the pair can MASK (or hide) the other factor Modern Mendel The factors that control traits = GENES Different forms of genes = ALLELES One allele is inherited from each parent Some alleles are DOMINANT - the trait always shows up when this allele is present ! Some alleles are RESESSIVE - the trait is masked or covered up when the dominant allele is present and will only show up if the dominant allele is not present ! ! ! ! Which allele is dominant and which allele is recessive? The F1 generation plants are called HYBRIDS. Hybrids have two (2) different alleles for a given trait Genetic Shorthand ! Use letters to represent alleles of traits ! Dominant alleles are represented by a capital letter (ex - F for purple flower color) ! Recessive alleles are represented by lower case letters (ex - f for white flower color) ! FF = two dominant alleles ! ff = two recessive alleles ! Ff = one dominant and one recessive allele Section 3.2 - Probability Vocabulary ! probability ! Punnett square ! phenotype ! genotype ! homozygous ! heterozygous ! Codominance GENETICS TEST THIS FRIDAY!! REVIEW NOTES. Paper Pet Assignment 1. Choose partner 2. By end of slide show be prepared to draw a Punnet square for the combination of your 2 paper pets. 3. Determine the ratio AND the percentage for the different genotypes and phenotypes that are possible in the offspring of your 2 paper pets. Probability ! Probability - is the likelihood that a particular event will occur ! Mendel was the 1st scientist to recognize that the principles of probability can be used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses Practice ! Suppose you were to toss a coin 20 times. Predict how many times the coin would land heads up and how many tails up. ! Test your hypothesis and record data. ! How did your results compare to your prediction? Compare your results to the overall class results. http://mathslover.hubpages.com/hub/How-to-calculate-probabilty Punnett Squares ! Punnett squares are used to show all possible genetic outcomes of a genetic cross and to determine the probability of a particular outcome What we can see and what we can t ! Phenotype - an organisms physical appearance or physical traits ! Genotype - an organisms genetic makeup or allele combinations ! Homozygous - purebred, two identical alleles for a given trait (TT) ! Heterozygous - hybrid, two different alleles for a given trait (Tt) Codominance ! Codominance is when neither allele is recessive or dominant ! Both forms of the trait are seen in the hybrid Solving Crosses (problems) Steps for Solving a Genetics Problem: 1. Start by drawing a box. Divide it into 4 squares. 2. Write the male parent’s alleles along the top of the square and the female parent’s alleles along the left line. 3. Copy the alleles into the boxes R ____ r ____ as shown. R RR R r 4. The completed Punnett ____ r rR r r ____ square shows all possible allele combinations. Let s Solve Together ! Short hair (L) is dominant to long hair (l) in mice. Give the probabilities for the different phenotypes if a short-haired mouse (male) is crossed with a longhaired mouse (female)? ! Genotype ratio: ½ Ll: ½ ll ! Phenotype ratio: ½ short hair: ½ long hair Let s Solve Together ! In humans, brown eyes (B) are dominant over blue (b)*. A brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and they have three children, two of whom are brown-eyed and one of whom is blue-eyed. Draw the Punnett square that illustrates this marriage. What is the man’s genotype? What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the children? Coin Crosses ! Use coins to model Mendel’s cross between 2 Tt pea plants 1. Place a small piece of masking tape on each side of 2 coins. 2. Write a T (for tall) on one side and a t (for short) on the other. 3. Toss both the coins together 20 times. Record the letter combinations that you obtain from each cross. 4. Report fraction AND percentage of crosses that would results in a tall plant. Paper Pet Assignment 1. Pick one paper pet to be male and one to be female. 2. Record the alleles for the male and female. 3. Draw a Punnet square for the combination of your 2 paper pets. 4. Determine the ratio AND the percentage for the different genotypes and phenotypes that are possible in the offspring of your 2 paper pets.