* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download To use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Bound variable pronoun wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Contraction (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
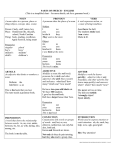
Your 5% To use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate spelling and punctuation. It helps if you read like a writer Can you: identify and comment on the structure and organisation of your present text, including grammatical and presentational features? explain and comment on the writer’s use of language, including grammatical and literary features at word and sentence level? identify and comment on the writer’s purposes and viewpoints, and the overall effect of the text on the reader? Number 1: To use a range of vocabulary nouns A noun can be proper, common or abstract. Get it right! A proper noun starts with a capital letter. Determiners before nouns place a limit e.g. some, this, a, an, two pronouns A pronoun is used in place of the noun. I, you, she, he, it, we, they, this adjectives An adjective describes the noun. It can also be comparative (bigger, higher) or superlative (biggest, highest) verbs A verb is in every sentence. Verbs are being, having and doing words. Get it right! They change according to when they happen (past, present or future). conjunctions A conjunction joins up ideas. and, however, because, whereas, next, such as intensifier emphasises another word or phrase extremely, strongly, unusually or exceptionally adverbs An adverb gives more information. It describes verbs, adjectives or other adverbs. They often end in -ly such as (brightly) Common pronouns he you I her him you me Object Pronoun her his your my Possessive Adjective hers his yours mine Possessive Pronoun herself himself yourself myself Reflexive Pronoun Subject Pronoun she More common pronouns you we it them you us it Object Pronoun their your our its Possessive Adjective theirs yours ours its Possessive Pronoun themselves yourselves ourselves itself Reflexive Pronoun Subject Pronoun they When to use a conjunction adding and as well as in addition furthermore also exceptions however even though except although unless if / even if cause & effect because for so therefore thus comparing equally in the same way similarly time when while since whenever meanwhile until contrasting whereas alternatively yet instead of but on the other hand putting in order next firstly after then finally afterwards giving examples for example such as for instance emphasising above all particularly especially in particular Use a Thesaurus to find more... Number 2: To use a range of sentences They must be different lengths and different structures! simple sentences A simple sentence contains only one verb, but it can be long or short. A sentence using subordinating or co-ordinating conjunctions is useful for adding or explaining your thoughts. A complex sentence using a subordinate clause gives more information. complex sentences To use a range of sentences Vary the order of clauses in your sentence to change the emphasis around your thinking. A question? ? ? ? ? A command starts with an imperative verb. exclamation An exclamation conveys a sense of emotion! Number 3: To use sentences for effect Always design your sentences for the effect you want. short sentences Short sentences can be used to create suspense and tension, or to give factual statements. long sentences Long sentences can be used for more detailed descriptions. To use sentences for effect Using the active or passive voice to write your sentences draws attention to different things. Active voice Blood carries food and oxygen. Passive voice Food and oxygen are carried by blood. Number 4: To use accurate punctuation . Full stop A full stop marks the end of your sentence. The next sentence starts with a capital letter. , Comma A comma in a sentence makes things clearer for your reader. A comma in a list saves you from repeating and. “” Speech marks Use speech marks when you are writing dialogue. Put the speech marks at the beginning and end of the direct speech, and the right punctuation mark inside the speech mark. Speech marks can also be used to quote someone else’s words. Question mark ? A question mark is used at the end of a question. Exclamation mark ! An exclamation mark is used to show emotion. ’ Apostrophe An apostrophe shows who owns something, or where letters have been missed out (a contracted apostrophe) Colon : A colon introduces a list or quotation, or can replace the phrase ‘and that is’. ; Semi-colon A semi colon can be used instead of a full stop when you want to hint that one statement explains another. Dashes - Brackets () Parenthetic commas ,, All three of these types of punctuation are used to surround information that is not essential. Brackets can also be used as an aside to the reader. Commas used in parenthesis usually repeat the same information in a different way. ... Ellipsis The three dots show where words have been left out. They are useful for leaving out irrelevant parts of a quotation when writing a news story. They can also be used to build tension in story writing by showing a pause in dialogue or narrative, or a character trailing off... Paragraphs (use cohesive devices to link your thinking) A paragraph is a section of writing, always around one idea, within your text. 1 Start a new paragraph when you change what you are writing about – place, time, character. 2 Use an introductory sentence, then develop it. 3 Link paragraphs with time references or adverbials so that the readers can follow the thread of your thinking. Number 5: To spell accurately Examples of ways to spell... Understand the meaning of the word Porous rock has spaces between particles (use a mind map to help work out the definition, look for Latin or Greek roots) Split the word into syllables or clap it wa/ter/falls me/an/ders ox/bow Think of the pattern -tion endings mean a process: percolation - cian endings are to do with jobs : musician - sion endings after stems that end in –d: expand/ expansion Examples of ways to spell... Use the root word Faith: faithful, faithfully, unfaithful, unfaithfully Practise the spelling rules from 'I am learning' Practise spelling all the key words you need for your GCSE. Use a dictionary Write it down and check if you are right Make up your memory hook GEOGRAPHY Gary Eats Old Grey Rats And Paints House Yellow Common Greek roots Greek Root Definition Example anthropo man; human anthropologist auto self autobiography bio life biology chron time chronological dyna power dynamic dys bad; hard; unlucky dysfunctional gram thing written telegram graph writing graphic hetero different heterogenous homo same homogenous hydr water hydration hyper over; above; beyond hyperactive hypo below; beneath hypothermia logy study of psychology meter/metr measure perimeter micro small microscope mis/miso hate misanthrope mono one monologue morph form; shape morphing nym name synonym phil love philosophy phobia fear claustrophobia photo/phos light photograph pseudo false pseudonym psycho soul; spirit psychic scope viewing instrument telescope techno art; science; skill technological tele far off telephone therm heat thermal Common Latin roots Latin Root Definition Example ambi both ambiguous aqua water aquarium aud to hear audience bene good benevolent cent one hundred century circum around circumference contra/counter against contradict dict to say dictation duc/duct to lead conduct fac to do; to make factory form shape reform fort strength fortress fract break fracture ject throw projection jud judge prejudice mal bad malevolent mater mother maternal mit to send transmit mort death mortal multi many multimedia pater father paternal port to carry portable rupt to break bankrupt scrib/script to write inscription sect/sec to cut section sent to feel; to send consent spect to look spectator struct to build restructure vid/vis to see video voc voice; to call vocalise Common Prefixes Prefix Definition Example anti- against anticlimax de- opposite devalue dis- not; opposite of discover en-, em- cause to enact empower fore- before; front of foreshadow forearm in-, im- in income impulse in-, im-, il-, ir- not indirect immoral illiterate irreverent inter- between; among interrupt mid- middle midfield mis- wrongly misspell non- not nonviolent over- over; too much overeat pre- before preview re- again rewrite semi- half; partly; not fully semifinal sub- under subway super- above; beyond superhuman trans- across transmit un- not; opposite of unusual under- under; too little underestimate Common Suffixes Suffix Definition Example -able, -ible is; can be affordable -al, -lal having characteristics of universal facial -ed past tense verbs; adjectives the dog walked -en made of golden -er, -or one who; person connected with teacher professor -er more taller -est the most tallest -ful full of helpful -ic having characteristics of poetic -ing verb forms; present participles sleeping -ion, -tion, -ation, -ition act; process submission motion -ity, -ty state of activity -ive, -ative, -itive adjective form of noun active sensitive -less without hopeless -ly how something is lovely -ment state of being; act of contentment -ness state of; condition of openness -ous, -eous, -ious having qualities of courageous gracious -s, -es more than one trains -y characterised by gloomy