* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Station #1: Chemistry
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
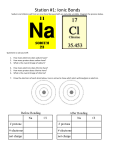
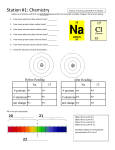
Station #1: Chemistry Sodium and chlorine will form an ionic bond because both are naturally unstable. Diagram the process below. 1. How many electrons does sodium have? 11 2. How many protons does sodium have? 11 3. What is the overall charge of sodium? 0 (neutral) 4. How many electrons does chlorine have? 5. How many protons does chlorine have? 17 17 6. What is the overall charge of chlorine? 0 (neutral) 7. Draw the electrons of each atom below. Use an arrow to show which atom will lose/gain an electron. ee e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e 11+ 17+ 11+ 17+ 11 17 10 18 0 0 +1 1 8. Fill in the pH scale below. Bases 9. Battery acid has a pH of 0.8, so it is considered a strong acid / base . (circle one) 10. Baking soda has a pH of 8.4, so it is considered a strong / weak base. (circle one) Station #2: Cell Part Identification 1. Which organelle transports ribosomes from one end of the cell to another? RER 2. Which organelle creates ribosomes? Nucleolus 3. Which organelle packages and ships proteins outside of a cell? Golgi body 4. Which organelle creates ATP energy? Mitochondria 5. Which two organelles (besides the nucleus) contain their own DNA and were probably once free living organisms? Mitochondria & chloroplasts 6. Which organelle creates lipids? SER Label each part of the cell above. Choices: Plasma membrane 13 Lysosome 10 Smooth ER 11 Golgi body 15 Vesicle 16 Nucleolus 9 Cytoplasm 12 Chloroplast (only in plant cells) Mitochondria 7 Nucleus 8 Cilia N/A Cell wall (only in plant cells) Rough ER 14 Flagella N/A Station #3: The Metric System and Microscope 1. Using LENGTH as your guide, fill out the Metric scale below. km hm dam m dm cm mm 2. Which unit you would use to measure the following objects? a. Distance from LA to Chicago? km kg mm m dm b. Weight of a medicine pill? kg hg mm cm mg c. Weight of a semi truck? g kl kg mg hm d. Height of a person? hl m dg l mm e. Amount of water in a swimming pool? dl kg kl dam cl f. dam mm Length of an eyelash? cg kl 3. In each series, circle the largest number. Hint: Change each number to the same unit. Series A: 3m 325cm .275km 3176mm Series B: 1.5km 150cm 15m 150000mm Series C: 34g 2500mg 34kg 0.024g 4. Identify the letter of the eye piece A a. What is the magnification of the ocular lens found here? 10x magnified 5. Identify the letter of the objective lenses B What is the magnification of the: a. scanning lens? 4x b. low power lens? 10x c. high power lens? 40x 6. Name the focus that should be used under low power and when first finding an object? Course focus 7. Suppose you are viewing a cell under the lowest power (the scanning objective lens), what would be your total magnification (don’t forget about the ocular lens)? 40x 10(eyepiece) x 4(scanning lens) = 40 dm Station #4: The Cell Cycle 1. Place the pictures in order from start to finish. D A E B C 2. Which picture is metaphase? E 3. Which picture has the nucleus dissolving? A 4. Which picture has the cell enlarging? D 7. Which picture has the spindle fibers dissolving? C 8. Which picture has the chromatids being pulled apart? B 9. Cytokinesis takes place at the end of which picture? C 5. Which picture has DNA being duplicated? D 10. Which picture shows Anaphase? B 6. Which picture has the spindle fibers being created? 11. In which picture is the cell performing its normal A operations? D This organism is NOT a human. n=24, so 2n=48 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. How many chromosomes are found in gamete calls? 24 How many chromosomes are found in diploid cells? 48 How many chromosomes are found in muscle cells? 48 How many chromosomes are found in sperm cells? 24 How many chromosomes are found in brain cells? 48 How many chromosomes are found in the zygote? 48 How many chromosomes are found in the egg cell of this individual organism? 0 It’s a male Station #5: Chemical Reactions, ATP, & Organic Molecules 1. Match the following words with the proper definition: a. The amount of energy that is needed for a chemical reaction to start. b. When a reaction takes place at an equal rate in both directions. d. A chemical reaction the releases more energy than it absorbs. e. Increases a reaction by lowering the activation energy. f. A chemical reaction that absorbs more energy that it releases. ____b___ Equilibrium ____e___ Enzyme ____f___ Endothermic ____a___ Activation Energy ____d___ Exothermic 2. True / False (circle one): Enzymes are not specific and can only be used once by the cell. 3. Fill in the ATP diagram below: Use the four monomer choices to answer questions 4 14. a. Monosaccharide b. Fatty acid 4. Which forms the genetic code of a species? C 5. Which bonds with a glycerol molecule to make a wax? B 6. Which is made from a sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base? C c. Nucleotide d. Amino acid 9. Which is a chain of C, H, and O atoms in a 1: 2: 1 ratio? A 10. Which will bond to make a polypeptide? D 11. Which is a monomer of carbohydrates? A 12. Which is the monomer of nucleic acids? C 7. Which is a simple sugar? A 13. Which is the monomer of lipids? B 8. Which will form the basis of an enzyme? D 14. Which is the monomer of proteins? D 15. Circle the example of an organic molecule. Station #6: Cellular Transport Fill in the table below with the correct details for each type of cellular transport COMPARE/CONTRAST the kinds of transport What does it use Active (ATP) to help: or Membrane proteins Passive Vesicles (Diffuses w/o Needs no help using energy) Other Example of substance(s) that use this kind of transport in cells Oxygen, water, etc. DIFFUSION Passive Needs no help FACILITATED DIFFUSION Passive Membrane protein (protein channel) Large molecules WATER! Passive Needs no help Active Membrane protein (pump) Any molecule going against the concentration gradient ENDOCYTOSIS (PHAGOCYTOSIS) Active vessicle Solids (“cell eating”) ENDOCYTOSIS (PINOCYTOSIS) Active vessicle Liquids (“cell drinking”) vessicle Anything the cell is getting rid of OSMOSIS ACTIVE TRANSPORT (USUALLY INVOLVES PROTEIN PUMP) EXOCYTOSIS Active Station #7: Genetics Answer the following questions. Autosomal Dominance Punnett Squares: Huntington’s disease (H) is a dominant disorder where the healthy allele (h) is recessive. Rebecca is heterozygous with Huntington’s disease and Jarrod is homozygous recessive. They want to start a family, but also want to know the risk of passing the disease on to their children. 1) What is Rebecca’s genotype? a. HH b. Hh c. hh d. Healthy e. Huntington’s disease 2) What is the probability of each child being healthy? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% 3) What is the probability of having a homozygous dominant child? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% 4) What is the probability of having four children, each with Huntington’s disease? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% f. 1/16 Incomplete dominance: A homozygous blue bird and a homozygous white bird produce offspring that are heterozygous silver. Cross two silver birds with each other. 5) What is the genotype of the silver birds? a. SS b. Ss c. BB d. WW e. BW 6) What is the probability of producing a silver bird? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% 7) How many different phenotypes are created by this cross? a. Zero b. One c. Two d. Three e. Four Sex Linked Inheritance: 8) Sex Linked Inheritance: The pedigree shows hemophilia in a small family. Determine the genotypes of every involved. Use XH for healthy and Xh for hemophilia. a. XhY e. XHXh or XXh b. XHXHor XX f. XY c. XY g. XhY d. XY h. XY Station #8: Transcription and Translation 1. Write the amino acids created from the piece of DNA (gene) below. GAAGCACTATTTATA (remember, DNA RNA Protein, so turn this into RNA first) CUUCGUGAUAAAUAU Leucine arginine aspartic acid lysine tyrosine 2. Fill in the table below using the rules of transcription and translation. DNA Codon Anticodon G C G C G C A U A G C G A U A U A T C G C C G C T A U Amino acid ARGININE LEUCINE GLYCINE 3. Fill in the table below with the proper enzymes. (A) RNA Polymerase DNA Replication B A (B) DNA Helicase Enzyme function Separates the DNA helix Rejoins the DNA helix (C) DNA Polymerase Transcription C Name not given Station #9: Cellular Energy (Doubled Sided) Answer the following questions and fill in the graphic organizer with the correct details. Define Photosynthesis: In photosynthesis, sunlight is absorbed (water & carbon dioxide are used) and sugars are made that store chemical energy (oxygen is released as waste). Chloroplast Sunlight Thylakoid Chlorophyll 6 O2 (oxygen) Energy Transferred 6 H2O (water) C6H12O6 (sugar) 6 CO2 (carbon Dioxide) Stroma Write the equation for photosynthesis: 6 H2O + 6 CO2 6 O2 + C6H12O6 Draw a box around the reactants and circle the products. Define Cellular Respiration: The overall process of cellular respiration converts sugar into ATP using oxygen. Mitochondria Kreb’s Cycle Anaerobic process that splits glucose. Into 2 pyruvate and makes a small amount of ATP Matrix energy 2 3 carbon molecules (pyruvate) 6 CO2 (carbon dioxide) Energy Transferred 36 ATP! energy 6 O2 (oxygen) 6 H2O (water) Write the equation for cellular respiration: 6 O2 + C6H12O6 6 H2O + 6 CO2 Draw a box around the reactants and circle the products.