* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt - Courses
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
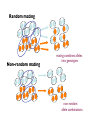
Conditions for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Random mating No natural selection No net mutation No gene flow Large population size Random mating Non-random mating mating combines alleles into genotypes non-random allele combinations Non-random Mating • Will not change the overall allele frequencies; will change _______________ frequencies • Inbreeding coefficient (F) = Inbreeding and genetic diversity • Loss of genetic diversity may mean a species is not able to adapt to a changing environment • Example? Non-random mating: Inbreeding • Inbreeding depression: Deleterious Recessive Alleles • How does natural selection drive frequencies of deleterious recessive alleles down? Deleterious Recessive Alleles • Heterozygotes don’t express the deleterious phenotype • Albinism: – 1/20,000 people are albino (aa) – f(a)= 0.007; f(aa) = 0.00005; f(Aa) = 0.014 – 280X as many heterozygote carriers than albino homozygotes Sexual Selection occurs when individuals vary in their ability to compete with others for mates or to attract members of the opposite sex. . Intrasexual selection Intersexual selection Should natural selection act similarly on the sexes? • Parental Investment: Anisogamy: # of individuals having offspring Reproductive success Males Females # of offspring Sexual Dimorphism IntERsexual Selection • Female choice • Potential benefits of picking the right male: – Direct benefits: – Good genes : Direct Benefits: Good Parents house finch (Hill 1991; Navara et al. 2006 ) Symmetry Symmetrical Asymmetrical Developmental homeostasis Net Mutation • Mutation is a weak force of evolution. • In a single generation, mutation produces very little change in allele & genotype frequencies. Net Mutation • Mutational equilibrium (no net mutation): rarely achieved Lenski Experiment Selection Maintains Polymorphism • Heterozygote Advantage (Overdominance): • Example: • Frequency-dependent selection – Selection changes depending on the frequency of each allele Frequency-Dependent Predatory Selection • An allele has a selective advantage when it is the rarer allele. Examples: Gene flow • Strong evolutionary force • Migration tends to make populations _____ _______ gg Gg GG gg GG GG gg Gg GG GG