* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
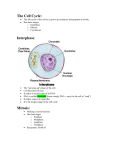
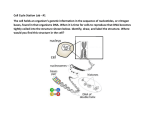
Name: Date: Period: Cell Division Study Guide 1. List 3 reasons why the cells of multicellular organisms divide. 2. Explain why unicellular organisms such as bacteria divide. 3. Explain why an adult human is larger than a baby, even though their cells are exactly the same size. 4. List 2 reasons why cells can’t get very big. 5. Explain why DNA replication must occur before the cell divides. 6. Relate “chromosome” to “DNA.” 7. Explain why chromosomes must form before the cell divides. 8. When looking at cells through a microscope, explain how you could identify a cell that is about to divide. 9. When looking at cells through a microscope, explain how you could identify a cell that is in the process of replicating its DNA. 10. Describe what happens to chromosomes after division is complete. 11. List four important events of the cell cycle. 12. Explain why it is referred to as a cell “cycle.” 13. Explain how skin cells and liver cells differ in terms of the rate at which they complete the cell cycle. 14. Explain why brain injuries and spinal cord injuries are permanent. 15. Relate “cyclin” to “cell cycle.” 16. Explain cells know when to progress to the next step in the cell cycle. 17. Describe what would happen to a cell without cyclin. 18. Define “cancer” using the term “cell cycle” in your answer. 19. Explain how tumors form. 20. Explain how a change in DNA could cause cancer. 21. List three things that could cause cancer by changing DNA. 22. Identify the two main parts of the cell cycle. 23. Explain why cells spend most of their lives in interphase. 24. Explain why DNA is not visible during interphase. 25. List the three parts of interphase, and briefly describe what happens during each part. 26. Explain how you can identify cells that are in G1 of interphase. 27. Explain why S phase is the longest part of interphase. 28. Explain how DNA starts to change at the end of G2. 29. List the two main parts of M phase. 30. Briefly describe what happens during mitosis. 31. Briefly describe what happens during cytokinesis. 32. Explain why “mitosis” and “cell division” do not mean the same thing. 33. Explain why mitosis must be a careful, four-step process. 34. List the four parts of mitosis in order according to PMAT. 35. Briefly describe what happens during prophase. 36. Briefly describe what happens during metaphase. 37. Explain how cells are moved into position during metaphase. 38. Briefly describe what happens during anaphase. 39. Explain how chromosomes are pulled apart during anaphase. 40. Briefly describe what happens during telophase. 41. Explain how DNA changes once M phase is complete. 42. Briefly describe what occurs during cytokinesis. 43. Differentiate between cytokinesis in plant cells and animal cells. 44. For each event, identify the specific part of the cell cycle when it occurs: a. b. c. d. DNA is replicated: DNA loosens up again: Cytoplasm divides: Chromosomes start to form: e. Chromosomes form completely: f. Cell increases size: g. Nucleus divides: h. Chromosomes line up: