* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sinus Node as the Pacemaker of the Heart
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
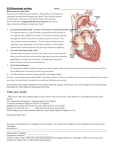
Chapter 10 : Rhythmical Excitation of the Heart Dr. Aisha Riaz Department of Physiology parts of the heart normally beat in orderly sequence contraction of the atria (atrial systole) is followed by contraction of the ventricles (ventricular systole) during diastole all four chambers are relaxed heartbeat originates in a specialized cardiac conduction system & spreads via this system to all parts of the myocardium The Sinus Node as the Pacemaker of the Heart SA node discharge at an intrinsic rhythmical rate of 70- 80/min (AV nodal fibers 40-60/min, & Purkinje fibers 1540/min Located in superior posterolateral wall of the right atrium each time the SA node discharges, its impulse is conducted into both the A-V node & the Purkinje fibers SA node discharges again before either the A-V node or the Purkinje fibers can reach their own thresholds for selfexcitation the sinus node controls the beat of the heart Mechanism of sinus nodal rhythmicity : THREE types of channels : fast sodium channels, slow sodium-calcium channels and potassium channels RMP : -55 to 60 mV At this RMP, fast sodium channels have already become “ inactivated” Action potential is caused only by slow sodiumcalcium channels So nodal potential is slower to develop than Ventricular muscle Inherent leakiness of the sinus nodal fibres to sodium and calcium ions causes their self-excitation. WHY DOES THIS LEAKINESS TO SODIUM AND CALCIUM IONS NOT CAUSE THE SINUS NODAL FIBRES TO REMAIN DEPOLARIZED ALL THE TIME? Two events prevent this : First, Sodium-calcium channels become inactivated within about 100-150 msec after opening Second, increased number of potassium channels open Both of them causes negativity inside the cells Transfers the action potential from sinus node to the atrial muscle fibres Three bands : Anterior, Middle and Posterior All internodal bands terminate in the AV-node Delay of impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles to empty blood into ventricles Total delay in the A-V nodal and A-V bundle system is about 0.13 seconds CAUSE OF SLOW CONDUCTION : Diminished numbers of gap junctions Inability of action potential to travel backwards from ventricles to the atria Fibrous tissues b/w atria and ventricles act as an insulator and prevent passage of cardiac impulse In abnormal cases, cardiac impulse can re-enter the atria from the ventricles causing serious cardiac arrythmias Purkinje fibers are very large fibres 1.5-4.0 m/sec Rapid tranmission is due to high level of permeability of gap junctions at intercalated discs Have few myofibrils, therefore contract little or not at all Tissue SA node Atrial muscle Atrial pathways AV node Bundle of His Purkinje system Ventricular muscle Conduction rate (m/s) 0.05 0.3 1 0.05 1 4 0.3-0.5 Once the impulse reaches the purkinje fibres it is transmitted through the ventricular mass by the ventricular muscle fibres Velocity now is 0.3-0.5 m/sec It takes another 0.03 sec for transmission of impulse from endocardial surface to the epicardial surface of ventricles Abnormal Pacemakers—“Ectopic” Pacemaker occasionally some other part of the heart develops a rhythmical discharge rate that is more rapid than that of the sinus node a pacemaker elsewhere than the sinus node is called an “ectopic” pacemaker an ectopic pacemaker causes an abnormal sequence of contraction of the different parts of the heart another cause of shift of the pacemaker is blockage of transmission of the cardiac impulse from the sinus node to the other parts of the heart Important functions: pacemaker setting the rhythm of electrical excitation that causes contraction of the heart conduction system ensures that cardiac chambers become stimulated to contract in a coordinated manner, which makes the heart an effective pump Thank You