* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System Introduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
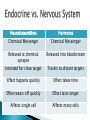
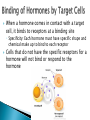
Journal: What is the function of hormones? ***Hand in your journals when you are done. Made up of glands that secrete hormones into the circulatory system ◦ Hormones are chemical messengers that are either proteins or lipids Controls rate of metabolism and tissue maturation Regulates ion concentrations in the blood Water balance in the blood Controls the production of immune cells Controls blood glucose levels Controls the development and functions of the reproductive system Hormone is produced in small amounts by a gland Secreted into the interstitial fluid Enters the circulatory system where it is transported around the body Acts on specific target cells by binding to specific receptors either on the cell membrane or inside cells The concentration of hormones determines the strength of the signal and the magnitude of the response ◦ Small concentration = weak signal = small response ◦ Large concentration = stronger signal = larger response Neurotransmitters Hormones Chemical Messenger Chemical Messenger Released at chemical synapse Intended for close target Released into bloodstream Effect happens quickly Effect takes time Effect wears off quickly Effect lasts longer Affects single cell Affects many cells Travels to distant targets Regulated through negative feedback loops in one of three ways ◦ Humeral Control Ex: Insulin secretion is controlled by blood glucose levels ◦ Neural Control Ex: Epinephrine is released from the adrenal gland because of nervous system stimulation ◦ Hormonal Control Ex: Thyroid-stimulating hormone is released from the pituitary gland and stimulates the release of thyroid hormone When a hormone comes in contact with a target cell, it binds to receptors at a binding site ◦ Specificity: Each hormone must have specific shape and chemical make up to bind to each receptor Cells that do not have the specific receptors for a hormone will not bind or respond to the hormone The number of functional receptors affects the amplitude of the cell’s response to a hormone ◦ More receptors produce a larger response Controlled through: ◦ Down-regulation : reducing the number of functional receptors ◦ Up-regulation: increasing the number of functional receptors Drugs with similar structures to specific hormones may compete with those hormones for their receptors ◦ Agonists: drug that binds to a hormone receptor and activates it ◦ Antagonist: drug that binds to a hormone receptor and inhibits it