* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrient_Cycles_WSs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
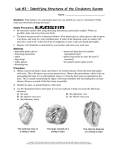
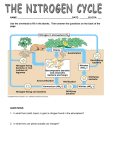
DATE: NAME: CHAPTER 2 The Carbon Cycle CLASS: BLM 1-19 Goal • Use this page to review the carbon cycle. Copyright © 2008, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher. DATE: NAME: CHAPTER 2 CLASS: The Carbon Cycle Concept Map BLM 1-20 Goal • Use this page to make a concept map about the carbon cycle. What to Do Use the following terms to construct a concept map that provides meaningful information about the carbon cycle. algae cellular respiration long-term stores photosynthesis trees atmosphere coal deposits ocean sedimentation volcanic eruption oil and gas short-term stores calcium carbonate decaying matter Copyright © 2008, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher. DATE: NAME: CHAPTER 2 The Nitrogen Cycle CLASS: BLM 1-21 Goal • Use this diagram to review the nitrogen cycle. Copyright © 2008, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher. DATE: NAME: CHAPTER 2 CLASS: Questions about the Nitrogen Cycle BLM 1-22 Goal • Use this page to record information about the nitrogen cycle. What to Do Read the following questions. Complete the answers as you read pages 78–83 in your student book. Points to Know Why is nitrogen necessary for living organisms? How is nitrogen stored? How is nitrogen cycled through the ecosystem? What is nitrogen fixation? What is nitrification and uptake? How does nitrogen return to the atmosphere? How is excess nitrogen removed from ecosystems? How do human activities affect the ecosystem? Copyright © 2008, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher. DATE: NAME: CHAPTER 2 CLASS: Know Your Nitrogen BLM 1-23 Goal • Use this page to learn terms about nitrogen. What to Do Cut out the terms on the left, pair each with the correct definition on the right, and paste them together on another sheet. Or make flash cards by pasting the definition to the back of the term. Terms Definitions Nitrogen fixation The process of making nitrates Denitrification Provide nitrogen for the host plant and in return obtain sugars Nitrifying bacteria Certain bacteria that convert nitrate back into nitrogen gas Nitrate NO2– Nitrogen uptake Nitrogen gas is converted into nitrate using electrical energy from lightning. Nitrification The process where nitrates are converted into nitrogen gas Ammonium N2 Denitrifying bacteria The process where nitrates enter plant roots Nitrite NH4+ Nitrogen-fixing bacteria Certain bacteria that convert ammonium into nitrite or nitrite into nitrate Nitrogen NO3– Copyright © 2008, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher. DATE: NAME: CHAPTER 2 The Phosphorus Cycle CLASS: BLM 1-24 Goal • Use this diagram to help you study the phosphorus cycle. Copyright © 2008, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher. DATE: NAME: CHAPTER 2 Nutrients True or False CLASS: BLM 1-25 Goal • Use this page to check your understanding of nutrients. Beside each statement below, write the letter T if you think the statement is true or F if you think it is false. If you think the statement is false, write the correct sentence in the space provided. 1. _____ Green plants add carbon dioxide to our atmosphere through a process of photosynthesis. 2. _____ Decomposers are a very important part of every nutrient cycle. 3. _____ Green plants occupy the second trophic level in food chains. 4. _____ There is a loss of energy at each trophic level. 5. _____ Carrying capacity is the largest number of organisms that can survive in an area. 6. _____ In a food chain, a deer feeding off leaves would be a secondary consumer. 7. _____ Carnivores are organisms that eat plant material. 8. _____ The process of nitrogen fixation uses oxygen to produce carbon dioxide. 9. _____ While a pyramid of numbers or biomass can be inverted, a pyramid of energy cannot. Copyright © 2008, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher.