* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physiological roles
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
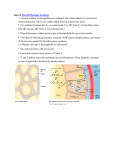
Physiological roles • Influence on many aspects of body function – Direct action – Indirect action • Early growth and development • Deficiency – Abnormalities • • • • • Growth Development Reproduction Behavior Metabolism • Thyroid hormones – Global implications • Tissues • Stage of life • Growth and development – Absence of thyroid hormones • Growth retardation – Lack of bone elongation – Lack of bone maturation – Reduced GH secretion (No effects of replacement in the absence of thyroid hormones) – Tissue development in amphibians – Mammary gland development • Ducts • Alveoli • Require prolactin • Growth and development – Brain development • • • • Protein synthesis Myelin production Axonal ramification/branching Irreversible effects – Mental deficiency • Generation of body heat – Majority of body heat • Activity of Na transporter – Hydrolysis of ATP – Thyroid hormones • Increased oxygen consumption • Generation of ATP by mitochondria • Increased Na/K-ATPase expression – Tissue-specific Relationship between diet and thyroid hormone function • Increase in energy intake – Total calories – Increased carbohydrate content – Increase in thermogenesis • Increased T3 – Increased conversion of T4 to T3 • Reduction in carbohydrate intake – Increased conversion of T3 to rT3 • Increased metabolism of nutrients • Sparing of nutrients from weight gain • Thyroid hormone concentrations during fasting – Decreased T3 – Decreased hepatic T3 receptors • Independent from changes in T3 concentrations • Effects of age – Reduced food intake • Increased longevity – Frequency of diseases – Severity of diseases • Potentially caused by alteration of thyroid hormone secretion Permissive actions of thyroid hormones • Thyroid hormones – Required for action of other hormones • GH secretion and GH action – Increased GH secretion by thyroid hormones • Synergizes with glucocorticoids – Increased ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) activity • Regulation of nucleic acids and protein synthesis – GH plus thyroid hormones (tissue-specific) Mechanism of action • Analogous to steroid hormones – Two nuclear receptors (alpha and beta) • Two isoforms within each receptor (1 and 2) • Beta1, beta2, and alpha1 – High affinity to T3 • Alpha2 – No binding to thyroid hormones – Negative regulator of other receptors – Specific expression within the CNS and pituitary gland • Dimerization – Homodimers – Heterodimers • Retinoic acid receptor • Retinoic acid X receptor • Thyroid hormone receptor auxiliary proteins (TRAPs) • Process of signal transduction – Transport of T4 and T3 from circulation to cytoplasm • Energy-dependent process – Conversion of T4 to T3 – Binding of T3 to TR – Formation of dimer – Interaction with DNA Non-genomic action • Plasma membrane – Increased red cell Ca-ATPase activity – Increased amino acid uptake – Increased glucose uptake • Mitochondria – Increased ADP uptake by mitochondria – Increased oxygen consumption – Changes in mitochondria morphology • Mitochondrial TR – Absent in thyroid hormone refractory tissues Pathophysiology • Hypersecretion/hyposecretion of thyroid hormones – Hypothyroidism – Hyperthyroidism • Hypersecretion/hyposecretion of TRH/TSH – Secondary/tertiary hyperthyroidism – Secondary/tertiary hypothyroidism • Cause – Genetic • Failure on thyroid growth and function • Defects on thyroid hormone biosynthesis mechanism – Iodine trapping or organification – Thyroglobulin synthesis/secretion • Overstimulation of thyroid gland – Autoimmune disease against TSH receptor • Excess secretion of TSH • Grave’s disease – Goiter • Loss of T3/T4 secretion – No negative feedback • Swelling of thyroid glands • Cause – Thyroiditis – Lack of iodine • Cretins – Absence of thyroid hormone • Retarded development of thyroid gland or thyroiditis • More prevalent in females • Retarded growth and maturation of skeletons and muscles • Mental retardation • Generalized tissue resistance to thyroid hormone – Variable clinical manifestation • • • • Tissue-dependent Elevated thyroid hormones Goiter Euthyroid – Cause • Decreased binding affinity • Decreased receptor number • Abnormal postreceptor signal transduction