* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - AP Biology with Mrs. Davis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
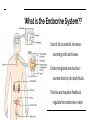
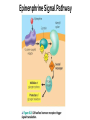
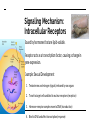
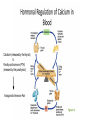
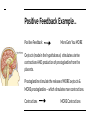
Memory Cells in Your Immune System Part of adaptive (specific) immune response. There are both memory B and T cells. Let’s look at why vaccines are arguably the greatest contribution to medicine in human history... First Exposure (via vaccine) 2nd Exposure (via pathogen) Graphical Representation Hormones & The Endocrine System More Cell Signaling Awesomeness! You Must Know…. 1. How hormones bind to target receptors and trigger specific pathways. 2. The secretion, target, action, and regulation of at least two hormones. 3. An illustration of both positive and negative feedback in What is a hormone anyway? A chemical signal that binds to target receptors causing a response in target cells. Hormones are essential for every activity of life, including the processes of digestion, metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood control. Steroid vs. Protein Hormone Steroid (cholesterol backbone) Not soluble in blood plasma - carried by proteins through blood Hydrophobic - able to pass through plasma membrane/nuclear membrane Binds to a intracellular receptor & often affects transcription of DNA This results in slow mode of action - can be days. Protein Soluble in blood plasma Hydrophilic - cannot pass through plasma membrane Binds to extracellular receptor and message is sent via secondary messengers What is the Endocrine System?? Sum of all an animal’s hormonesecreting cells and tissues. Endocrine glands are ductless secrete directly into body fluids. Positive and negative feedback regulate the endocrine system. Mechanism of Signaling Feedback inhibition and antagonistic hormone pairs are common in the endocrine system! Homeostasis! 2 Mechanisms of Hormone Action 1. Cell-surface receptors 2. Intracellular receptors Signaling Mechanism: Cell-Surface Receptors Bind hormone, signal transduction pathway is triggered. Reception Response Transduction Example: One of the responses during Fight or Flight 1. Epinepherine (signal) released from adrenal medula 2. Binds to receptor on liver cell (reception) 3. Triggers cascade inside the cell (transduction) Epinenphrine Signal Pathway Signaling Mechanism: Intracellular Receptors Bound by hormones that are lipid-soluble. Receptor acts as a transcription factor, causing a change in gene expression. Example: Sexual Development 1. Testosterone and estrogen (signals) released by sex organs 2. Travel to target cells and bind to nuclear receptors (reception) 3. Hormone-receptor complex move to DNA (transduction) 4. Bind to DNA and affect transcription (response) Hypothalamus & Pitutary Central to Endocrine System! Hypothalamus: Receives information from nerves throughout body & the brain. Inititates endocrine signals in response. Posterior Pituitary is an extension of hypothalamus. Stores and releases 2 hormones produced in hypothalamus: 1) oxytocin 2) antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Anterior Pituitary - Synthesizes and releases several tropic hormones (hormones that stimulate other endocrine tissues). Endocrine Glands Regulate Homeostasis, Developement, Behavior. Let’s look at the idea of NEGATIVE FEEDBACK You LESS More Gets Blood Calcium! When blood calcium levels go up - signals are sent to store the calcium in our bones. When blood calcium levels go down - signals are sent to release calcium from our bones. Let’s see how this balancing act works! Calcitonin (released by the thyroid) & Parathyroid hormone (PTH) (released by the parathyroid) Antagonistic Hormone Pair Blood Sugar - Case Study Insulin is released by the beta cells of pancreas in response to high blood glucose levels. Insulin stimulates cells to remove glucose from the blood. What if blood glucose is low? Alpha cells of pancreas release glucagon, stimulating the breakdown of glycogen in the liver and skeletal muscles into glucose. This is a great example of an antagonistic hormone pair. Type 1 Diabetes - Autoimmune; cells that make insulin are destroyed. Type 2 Diabetes - Insulin resistance - cannot use it efficiently, begin making less Positive Feedback Example... Positive Feedback More Gets You MORE Oxytocin (made in the hypothalamus) stimulates uterine contractions AND production of prostaglandins from the placenta. Prostaglandins stimulate the release of MORE oxytocin & MORE prostaglandins -- which stimulates more contractions. Contractions MORE Contractions When is Mrs. Davis’s Birthday? Check the website calendar! It has lots of great information, including my birthday!