* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System: Cranial Meninges
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
Perivascular space wikipedia , lookup
Spinal cord wikipedia , lookup
Minimally conscious state wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak wikipedia , lookup
Trigeminal nerve wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
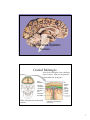
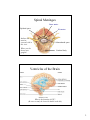
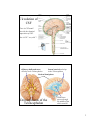
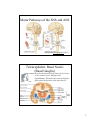
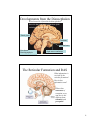
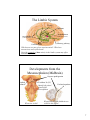
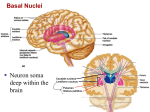
The Nervous System: The Brain Cranial Meninges If the brain and spinal cord contain no pain receptors, what are the possible explanations for head pain? What is the function of the dural sinuses? 1 Spinal Meninges Dura mater Epidural space Pia mater Indicate the anterior (ventral) side in this view. Subarachnoid space Where are the dorsal root ganglia? Vertebral body Ventricles of the Brain What is the function of CSF? (Be sure to study the ventricle model in the lab.) 2 Circulation of CSF Where is CSF made? Describe the chemical composition of CSF. How is CSF “recycled”? Olfactory bulbs and tracts develop in the Telencephalon Lateral ventricles develop in the Telencephalon Cerebral hemispheres Developments of the Telencephalon What tissue passes through the middle of the third ventricle? 3 Telencephalon: The Cerebrum List some of the functions of the cerebrum. Are the functions of both hemispheres identical? Functional Areas of the Cerebral Cortex List and briefly describe the 4 types of functional areas. 4 Motor Pathways of the SNS and ANS Which is the post-ganglionic fiber? Telencephalon: Basal Nuclei (Basal Ganglia) Describe the location of the basal nuclei relative to the cerebral cortex, thalamus and hypothalamus. What does this structural feature imply about the function of the basal nuclei? 5 Developments from the Diencephalon Which ventricle is found in the diencephalon? Describe the structure and function of the reticular formation (RAS). Pineal gland Thalamus Hypothalamus Not shown: Neurohypophysis Optic nerves and tracts The Reticular Formation and RAS What information is received by the reticular formation? How is that information used? Where does awareness of sensation occur, and how is this different from sensation, and perception? 6 The Limbic System Fornix Thalamus Hypothalamus (mammillary bodies) Basal ganglia (caudate nucleus) Olfactory pathway Cerebral cortex Which areas are part of our conscious mind? Which are unconscious areas of the brain? Describe examples of how activity in the limbic system may affect autonomic functions. Developments from the Mesencephalon (Midbrain) Corpora quadrigemina Cerebral peduncle What view is this? Trochlear N. (IV) Identify the pineal gland of the diencephalon. Cerebral aqueduct What features of the hindbrain are visible in this figure? 7 Developments of the Rhombencephalon (Hindbrain) Cerebellar The reticular formation extends peduncles from the spinal cord to the diencephalon (thalamus). Name the brain structures in which this neuron “network” is found. 4th ventricle Cerebellum What kinds of information are sent to the cerebellum, and how is this related to its function? Pons Medulla oblongata Name the important nuclei (control centers) in the pons and medulla. 8