* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Heart– Structure
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
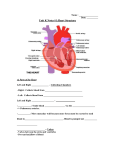
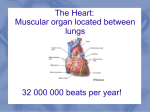
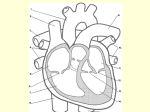
1/22/13 The Human Heart– Structure Interesting Facts • In your lifetime, your heart beats about 3 billion times without a single break • The aorta, the largest artery in your body, is almost the diameter of a garden hose • The heart pumps about 1 million barrels of blood during an average lifetime Anatomy of the Heart The Pericardium Structure • a double wall sac covering the heart Function • protects and anchors the heart • provides a friction-free environment Figure 13.2 1 1/22/13 Anatomy of the Heart Think 4’s! Four Chambers • Right and Left Atrium • Right and Left Ventricle -separating the chambers is the septum Four Vessels • Inferior/Superior Vena Cava and Aorta • Pulmonary Artery and Pulmonary Vein Four Valves • Tricuspid and Bicuspid Valve • Pulmonary and Aortic Semilunar Valve Anatomy of the Heart Review Heart Anatomy Here Figure 13.4 Flow of Blood Through the Heart ü Right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs ü Pulmonary circuit Figure 13.6 2 1/22/13 Flow of Blood Through the Heart ü Left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body ü Systemic circuit Figure 13.6 Flow of Blood Through the Heart ü Atria pump together ü Ventricles pump together ü Valves between chambers direct blood flow in proper sequence Click here to see how the blood flows through the heart! Figure 13.6 Pathway of Blood – Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits R. Atrium Pulmonary Artery R. Ventricle BCV PSLV Vena Cava Lungs Aorta ASLV L. Ventricle TCV L. Atrium Pulmonary Vein 3 1/22/13 Heart Valves u Blood flows through the heart in one direction. u Heart valves open and close to prevent the backflow of blood within the heart. u The valves open and close in response to differences in blood pressure. Figure 13.5 Heart Valves Atrioventricular (AV) valves (bicuspid and tricuspid) u Prevent backflow into atria when ventricles are contracting u Chordae tendinae and papillary muscles anchor and hold valve flaps when closed Heart Valves Semilunar (SL) valves u Prevent backflow into ventricles when ventricles relax u Flaps are small cups, shaped like ‘half moon’ u Lack chordae tendinae of the AV valves, because they close under less pressure Click here to see how the valves work 4