* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HeartStructure
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
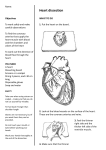
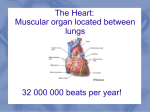
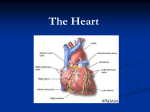
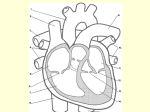
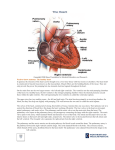
The Human Heart– Structure Today’s Learning Goal • Learn and memorize external anatomy of the heart, including all chambers and vessels. • Learn and begin to memorize the flow of blood through the heart. Check for Understanding - Friday • Label chambers and vessels on heart image. Interesting Facts • In your lifetime, your heart beats about 3 billion times without a single break •The aorta, the largest artery in your body, is almost the diameter of a garden hose •The heart pumps about 1 million barrels of blood during an average lifetime Heart External Anatomy Review Heart Anatomy Here Heart Chambers Review Heart Anatomy Here Heart Vessels Review Heart Anatomy Here Anatomy of the Heart Think Four! Four Chambers • Right and Left Atrium • Right and Left Ventricle Four Vessels • Inferior/Superior Vena Cava and Aorta • Pulmonary Artery and Pulmonary Vein Four Valves • Tricuspid and Bicuspid Valve • Pulmonary and Aortic Semilunar Valve Flow of Blood Through the Heart Right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs Pulmonary circuit Flow of Blood Through the Heart Left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body Systemic circuit Flow of Blood Through the Heart Atria pump together Ventricles pump together Valves between chambers direct blood flow in proper sequence Click here to see how the blood flows through the heart! Pathway of Blood – Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits R. Atrium Pulmonary Artery R. Ventricle TCV PSLV Vena Cava Lungs Aorta ASLV L. Ventricle BCV L. Atrium Pulmonary Vein Anatomy of the Heart Heart Valves Blood flows through the heart in one direction. Heart valves open and close to prevent the backflow of blood within the heart. The valves open and close in response to differences in blood pressure. Figure 13.5 Heart Valves Atrioventricular (AV) valves (bicuspid and tricuspid) Prevent backflow into atria when ventricles are contracting Chordae tendinae and papillary muscles anchor and hold valve flaps when closed Heart Valves Semilunar (SL) valves Prevent backflow into ventricles when ventricles relax Flaps are small cups, shaped like ‘half moon’ Lack chordae tendinae of the AV valves, because they close under less pressure Click here to see how the valves work Pericardium Structure • a double wall sac covering the heart Function • protects and anchors the heart • provides a friction-free environment