* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download género Volvox
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
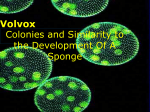
género Volvox ¿Tienes alguna duda, sugerencia o corrección acerca de este taxón? Envíanosla y con gusto la atenderemos. Ver todas las fotos etiquetadas con Volvox en Banco de Imagénes » Descripción de EOL Ver en EOL (inglés) → Description of volvox Colonies large (up to 1.5 mm), more or less spherical to ellipsoidal, usually containing many hundreds to thousands (up to 60,000) cells in a single layer on periphery of a common gelatinous matrix; colonial boundary tripartite, each cell also surrounded by an individual extracellular matrix; 2 cell types, somatic and reproductive; somatic cells identical, spherical, ellipsoidal, pyriform or stellate, with 2 outwardly directed flagella; neighbouring cells attached by cytoplasmic connections; chloroplast single, cupshaped or irregularly disciform, with a single (rarely several) pyrenoid(s); eyespot single, usually largest in anterior cells and progressively smaller or absent in posterior cells; nucleus more or less central; contractile vacuoles 2-6; reproduction, both asexual and sexual, restricted to relatively few reproductive cells (gonidia) which lose flagella and are somewhat larger than somatic cells; asexual reproduction by formation of 2-80 daughter colonies; initial sequence of cell divisions leading to small hollow spheres of cells or plakeas, in which flagellar bases and nuclei are oriented inwards; new gonidial cells being formed by unequal division of certain cells early in cleavage process; developing daughter colonies undergo inversion; sexual reproduction strictly oogamous; most species heterothallic, some homothallic, either monoecious or dioecious, some species heteromorphic with dwarf male colonies; female reproductive cells (2 to 700 per colony) enlarging to form oogonia with single non-flagellated eggs (oospheres); male reproductive cells dividing and developing into plate-like or globose sperm packets or plakeas of 16-512 biflagellate spindle-shaped antherozoids; zygotes thick-walled, smooth or variously ornamented, often with reddish contents; on germination, a single (rarely 4) biflagellate (sometimes aflagellate) gone cell escaping from zygote wall and dividing into a gone colony; nutrition phototrophic or photo-organotrophic; common, in bogs, pools, ponds, ditches, but most species with restricted geographical distribution. Statistics of barcoding coverage 1 Barcode of Life Data Systems (BOLD) Stats Specimen Records:38 Specimens with Sequences:37 Specimens with Barcodes:35 Species:16 Species With Barcodes:16 Public Records:37 Public Species:16 Public BINs:0 References 1. © Barcode of Life Data Systems, some rights reserved