* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit K * Heart Structure and Function
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
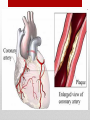
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
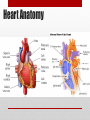
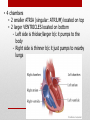
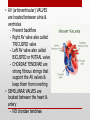
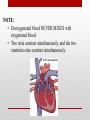
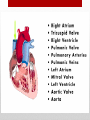
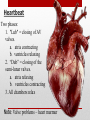
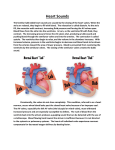
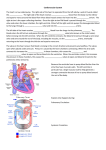
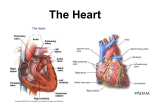
Heart Structure and Function pp. 242-245 Heart Anatomy The Heart: • Function: circulates the blood throughout the body • very muscular organ about the size of a fist. • Surrounded by fluid & a pericardial sac • 2 pumps (right side pumps blood to lungs & left side pumps blood to the rest of the body) • Left & right sides divided by SEPTUM • 4 chambers • 2 smaller ATRIA (singular: ATRIUM) located on top • 2 larger VENTRICLES located on bottom - Left side is thicker/larger b/c it pumps to the body - Right side is thinner b/c it just pumps to nearby lungs • AV (artioventricular) VALVES are located between atria & ventricles - Prevent backflow - Right AV valve also called TRICUSPID valve - Left AV valve also called BICUSPID or MITRAL valve - CHORDAE TENDINAE are strong fibrous strings that support the AV valves & keep them from inverting • SEMILUNAR VALVES are located between the heart & artery - NO chordae tendinae Coronary arteries and veins 1. Vitally important blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle itself 2. Heart does not use the blood in its inner chambers. 3. Arteries branch off the aorta just above the aortic semilunar valve, and lie on the outside of the heart. 4. Coronary veins empty into the right atrium. Path of Blood Through the Heart: A. DEOXYGENATED blood enters the right atrium through the SUPERIOR & INFERIOR VENA CAVA B. RIGHT ATRIUM contracts, pushing blood through the TRICUSPID VALVE & into the RIGHT VENTRICLE. B. Right ventricle contracts, pushing blood through the PULMONARY SEMILUNAR VALVE & into the PULMONARY TRUNK. C. The pulmonary trunk divides into PULMONARY ARTERIES, which take the deoxygenated blood to the capillaries of the LUNGS. E. At the lungs, carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood & oxygen diffuses into it. F. OXYGENATED blood moves into the PULMONARY VEINS, which take to the LEFT ATRIUM G. Left atrium CONTRACTS, pushing blood through the BICUSPID VALVE into the LEFT VENTRICLE. H. Left ventricle CONTRACTS, pushing blood through the AORTIC SEMILUNAR VALVE into the AORTA I. Aorta divides into smaller arteries, which carry oxygenated blood to all body tissues. NOTE: • Deoxygenated blood NEVER MIXES with oxygenated blood. • Two atria contract simultaneously, and the two ventricles also contract simultaneously. Heartbeat Two phases: 1. "Lub" = closing of AV valves. a. atria contracting b. ventricles relaxing 2. “Dub” = closing of the semi-lunar valves. a. atria relaxing b. ventricles contracting 3. All chambers relax Note: Valve problems – heart murmur Control of Heart • Heart muscle tissue can contract on its own = intrinsic • Cardiac cells will coordinate their contractions if cells touch Coordination of Heartbeat • Heart has NODAL TISSUE which has characteristics of nerve & muscle tissue • 2 nodes: 1) SA node – sinoatrial node - upper back wall of rt. Atrium - Initiates heartbeat by sending out a signal every 0.85 seconds making atria contract - both atria contract almost simultaneously - Called “pacemaker” because it keeps beat regular 2) AV node – atrioventricular node - base of right atrium - receives signal from SA node - sends out signals along “Bundle of His” down septum to Purkinje fibres - Purkinje fibres spread through ventricles - Purkenje fibres stimulate cardiac muscles at base of ventricles - ventricles contract Control by the Brain: • MEDULLA OBLANGATA controls heart rate • brain signals SA node through VAGUS nerve & sets heart rate • Regulation is autonomic (not under conscious control) • Nervous impulses are sent via autonomic nervous system • Sympathetic branches tell heart to “SPEED UP!” • Parasympathetic branches tell heart to “SLOW DOWN!” • Various factors (stress, oxygen levels, blood pressure) determine how the autonomic system will affect heart rate.