* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Table 13-2
Hormonal breast enhancement wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Signs and symptoms of Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
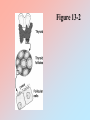
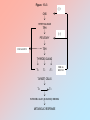
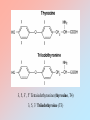
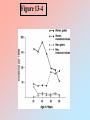
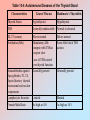
Stress (cont.) During stress, the priorities of the secretions of the hypothalamo-pituitary peripheral-endocrine axes are shifted in favor of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis. During stress: HPA GHRH GH GnRH FSH LH Hypothalmo-Pituitary-Thyroid System Figure 13-1: Diagrammatic representation of the thyroid gland Figure 13-2 Table 13.3 Major Actions of Thyroid Hormones • Calorigenesis • Metabolism • Brain maturation • Behavior • Growth & development Figure 1 3- 3 (-) CNS HYPOTHALAMUS TRH (-) PITUITAR Y TSH CLE ARANCE THYROID GLAND T3 T4 r T3 FREE & BOUND TA RGET CELLS T4 T3 INTRACELLULAR (N UCLEAR) BINDING METABOLIC RESPONSE 3, 5, 3’, 5’ Tetraiodothyronine (thyroxine, T4) 3, 5, 3’ Triiodothyroine (T3) Table 13-2: Some MORPHOLOGIC Changes in the Thyroid Gland with Aging FOLLICLES: - Are distended - Change in color - Epithelium flattened w/ reduced secretion Fewer mitoses Increased connective tissue; Fibrosis Atherosclerotic changes Table 13-2 (con’t.): Some SECRETORY Changes in the Thyroid Gland with Aging circulating T3 levels but generally within the normal (lower) range Simultaneously decreased secretion and metabolic clearance of T4 with resulting essentially normal levels TSH levels in 10% of the elderly, associated peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 Failure of up-regulation of T3 nuclear receptors in antithyroid antibodies, present even in the absence of manifestations of hypothyroidism Table 13-1: Some Critical Aspects of Thyroid Hormone Regulation 1. Major source of circulating T3 from peripheral deiodination of T4 (NOT from thyroid gland secretion) 2. The negative feedback at the pituitary anterior lobe is mainly through T4 (taken from circulation & converted into T3) 3. The peripheral deiodination of T4 depends on the physiological state of the organism. It allows an autonomy of response of the tissues to the hormones. 4. Deiodination can convert T4 (a less biologically active hormone) to T3 (a more active hormone). This conversion depends on the activity of the various deiodinating enzymes. Figure 13-4 Basal Metabolic Rate from birth to 70 years old Basal Metabolic Rate Table 13-5 In the Elderly, Thermoregulatory Insufficiency Results from: heat production, body mass, muscle activity, shivering, sweating response, vasomotor responses, temperature perception. Table 13-6 Autoimmune Diseases of the Thyroid Gland Characteristics Graves’ Disease Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Thyroid Status Hyperthyroid Hypothyroid TSH Generally undetectable Normal to elevated T4, T3 (serum) Above normal Below normal Antibodies(ABs) Stimulatory ABs compete with TSH at receptor sites Loss of TSH control over thyroid function Some ABs block TSH actions Autoantibodies against Generally present thyroglobulin, T3, T4, thyroid destroy thyroid microsomal and nuclear components Generally present Lymphocytic Invasion Limited Marked Female:Male Ratio As high as 10:1 As high as 10:1