* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7 grade life science review packet
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
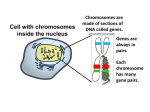
1 Name__________________________________________________Period_________Date______________ 7th GRADE LIFE SCIENCE REVIEW PACKET PART 1. SCIENTIFIC METHOD I. STEPS 1. PROBLEM - always in the form of a ____________________________________ 2. HYPOTHESIS - ____________________________________________ 3. EXPERIMENT - 3 parts: Control, dependent variable, independent variable 4. OBSERVATIONS - analyze data, charts, graphs… 5. CONCLUSION - is your hypothesis right or wrong? II. DEFINE THE FOLLOWING TERMS: 1. CONTROL = _________________________________________________________________________ 2. INDEPENDENT VARIABLE = ___________________________________________________________ 3. DEPENDENT VARIABLE = _____________________________________________________________ 4. Example: A student set up the experiment shown to learn about plant growth. The student added a different amount of water to 4 identical containers, each containing 4 seeds in 100 cubic centimeters of soil. All of the containers were placed in the same sunny location. The height of the plants were measured and recorded for 5 weeks. a. State a hypothesis for this experiment. ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ b. Independent variable = ________________________ c. Dependent variable = ________________________________________ d. Identify the factors that must remain constant in this experiment. _______________________________________________________________________________________ III. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The first step in the scientific method is a. state the hypothesis b. state the problem c. experiment d. observation 2 2. What is the factor in an experiment that remains constant? a. control b. variable c. theory d. hypothesis 3. A student placed 10 radish seeds of the same variety on moist paper in each of three petri dishes and placed the dishes in the following environments: Dish 1: Refrigerator, 5°C Dish 2: Room Temperature, 20°C Dish 3: Incubator, 37°C Which factor is the independent variable in this investigation? a. temperature b. kind of seeds c. moisture d. number of seeds 4. Identify 2 safety rules that must be followed when performing a lab.___________ _____________________________________ PART 2. MEASUREMENT I. LENGTH – meter 1. What is the length of the tadpole at the right? a. In centimeters= ________________ b. In millimeters = ________________ II. MASS - __________________________________________________________________________ 1. What instrument is being used to measure the mass of the object at the right? ______________________________________ 2. What is the mass of the object? _____________ III. VOLUME - ______________________________________________________________________ 1. Calculate the volume of the block below. Show all work in the work space below. 4. What is the volume of rock below? 2. What is the name of the instrument at the right? ________________________________ 3. What is the volume of the water? __________________________ 3 V. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. What is the temperature shown in the thermometer shown below? 2. What is the length of the snail? 4. Draw the staircase we use to convert from 1 metric unit to another. 3. What are the volumes of the 2 liquids shown below? a. b. 5. Convert the following measurements: a. 2.45 cm = ___________________ km b. 0.546L = ___________________ mL 8. In the metric system, the height of a building would be given in a. centimeters b. milliliters c. meters d. millimeters 6. Which instrument would be used to obtain the volume of a glass of water? a. triple beam balance c. beaker b. graduated cylinder d. metric ruler 9. Which piece of equipment could be used to determine the mass of a frog? a. triple beam balance c. beaker b. graduated cylinder d. metric ruler 7. Which group of measurement units is correctly arranged in order of increasing size? a. millimeter, centimeter, meter, kilometer b. millimeter, kilometer, centimeter, meter c. meter, kilometer, centimeter, millimeter d. kilometer, centimeter, millimeter, meter 10. Mass is best defined as the a. size of an object c. density of an object b. amount of matter in an object d. weight of an object 4 PART 3. MICROSCOPE I. PARTS & FUNCTIONS: 1. eyepiece/ocular lens – lens that you look through to magnify specimen 2. coarse adjustment knob – focusing under low & medium powers (NOT HIGH POWER) 3. fine adjustment knob – focusing for high power, sharpening image 4. objective lens – lenses that magnify specimen low = 4x medium = 10x high = 40x 5. arm – supports body tube (for carrying) 6. body tube – connects objective & eyepiece 7. stage – table that holds the slide 8. mirror/light source – provides light to view specimen 9. base – structure that supports microscope (for carrying) 10. diaphragm – openings that controls the amount of light used (under stage) II. LABEL THE PARTS OF THE MICROSCOPE BELOW. A. ____________________________________ A B. ____________________________________ C. ____________________________________ H D. ____________________________________ B I E. _____________________________________ J C F. _____________________________________ D G. _____________________________________ E F H. _____________________________________ G I. ______________________________________ J. ______________________________________ III. USING THE MICROSCOPE 1. What would happen if you used the coarse adjustment under high power? _____________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. When you observe a specimen using a microscope, how does the specimen appear? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. When you move the slide in any direction, how does the specimen on the slide appear to move? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Which objective lens allows you to observe LARGER field of view? ____________________________ 5. Calculate the total magnification: 5 a. Eyepiece lens = 15x, Objective lens = 5x Total Mag = _____________________ b. Eyepiece lens = 10x, Objective lens = 10x Total Mag = _____________________ c. Eyepiece lens = 20x, Objective lens = 40x Total Mag = _____________________ 6. What is the student in the picture at the right preparing? ___________________________________________ 7. Why should the student make sure the cover slip is lowered at an angle? __________________________________________ IV. MEASURING WITH THE MICROSCOPE 1. What is the diameter of the field of view shown below? 2. What is the length of one of the cells shown below? 3. Determine the lengths of the objects in the microscopes field of view below. a. b. 4. How many micrometers make up one millimeter? ________________________ PART 4. CELLS I. CELL THEORY 1. Who developed the cell theory? a. Hooke = looked at cork under a microscope, name what he saw “cells” b. Schleiden = all plants are made of cells c. Schwann = all animals are made of cells d. Virchow = all cells come from other cells 6 2. List the parts of the CELL THEORY below. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ II. CELL ORGANELLES 1. Cell membrane – semi-permeable structure that allows only certain materials to enter & leave cell 2. Nucleus - controls all cell activities a. Nuclear membrane – surrounds nucleus b. Nucleolus – produces ribosomes c. Chromosomes – genetic material 3. Cytoplasm – jelly-like materials that holds all organelles 4. Mitchondria – produces energy (by respiration) – POWERHOUSE OF THE CELL 5. Endoplasmic Reticulum –tunnels in the cytoplasm that transport materials (highway of the cell) 6. Vacuoles – storage 7. Ribosomes – produce proteins 8. Golgi bodies – collects, packages, and ships materials out of the cell (UPS/POST OFFICE) III. ORGANELLES FOUND ONLY IN PLANT CELLS 1. Cell Wall – outer wall made of cellulose, protects, gives plant cell shape 2. Chloroplasts – carry out photosynthesis, contain chlorophyll (absorbs light) IV. ORGANELLES FOUND ONLY IN ANIMAL CELLS 1. Lysosomes – contain enzymes that break down/digest materials 2. Centrioles – aid in cell division V. LABEL THE CELLS AND THEIR ORGANELLES BELOW: 1. ____________________ CELL A. ______________________ H. _____________________ B._______________________ I. ______________________ C._______________________ J. ______________________ D._______________________ K. _____________________ E._______________________ L. ______________________ F._______________________ M. _____________________ G. _____________________ 7 2. ____________________ CELL A. _______________________ H. _____________________ B. _______________________ I. ______________________ C. _______________________ J. ______________________ D. _______________________ K. _____________________ E. _______________________ L. ______________________ F. _______________________ M. _____________________ G. _______________________ VI. TRANSPORT 1. PASSIVE TRANSPORT a. 2 TYPES: 1. DIFFUSION – movement of materials from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration -WITH THE CONCENTRATION GRADIENT -NO ENERGY REQUIRED 2. OSMOSIS – diffusion of water (high low) -WITH THE CONCENTRATION GRADIENT -NO ENERGY REQUIRED b. What happens to a cell if it’s placed in salt water? b. What happens if it is placed in pure water? __________________________________________ ________________________________________ __________________________________________ ________________________________________ 2. ACTIVE TRANSPORT – the movement of materials from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration a. AGAINST THE CONCENTRATION GRADIENT b. ENERGY IS REQUIRED c. opposite of diffusion a. Label each diagram as diffusion, osmosis, or active transport. H2 O H2 O 1. __________________ 2. _________________ H2 O H2 O H2 O H2 O 3. _________________ 8 VII. RESPIRATION – process in which glucose is broken down to produce ENERGY (ATP) -OCCURS IN THE MITOCHONDRIA TYPES: 1. AEROBIC RESPIRATION – uses oxygen, produces 36 ATP a. Label the equation below. C6 H12 O6 _______________ + 6O2 ___________ 6CO2 + 6H2 O + _______________ _________ 36ATP ___________ 2. ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION – fermentation, does not require oxygen, produces only 2 ATP VIII. LIVING THINGS a. UNICELLULAR ORGANISM - ________________________________________________________ b. MULTICELLUAR ORGANISM - ________________________________________________________ c. Identify the 5 LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION IN A MULTICELLULAR ORGANISM = _____________________________________________________________________________________ d. HOMEOSTASIS - ___________________________________________________________________ IX. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The cell theory states that all living things are made up of a. organisms b. cells c. tissues d. proteins 2. When cells similar in structure & function join together, they form a. tissues b. organs c. systems d. organisms 3. A sac in the cytoplasm of a cell that stores water, food, and other materials is a. nucleus b. vacuole b. DNA d. ribosome 4. The control center of the cell is the a. nucleus b. chloroplast c. cytoplasm d. lysosome 5. A process in which glucose is broken down to release energy. a. diffusion b. respiration c. photosynthesis d. osmosis 6. Water passes through the cell membrane by a special process called a. division b. mitosis c. forced movement d. osmosis 7. Aerobic respiration requires a. oxygen b. light c. carbon dioxide d. chlorophyll 8. One substance that is generated from aerobic respiration is a. ATP b. glucose c. protein d. oxygen PART 5. CLASSIFICATION I. CLASSIFICATION – grouping organisms according to similar characteristics 1. HETEROTROPH - __________________________________________________________________ 2. AUTOTROPH - ______________________________________________________________________ II. ORGANISMS ARE ORGANIZED INTO 7 LEVELS OF CLASSIFICATION: KINGDOM PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES (largest, most diverse) (smallest, most similar) Kings Play Chess On Fine Green Stools 9 III. BINOMIAL NOMENTCALTURE 1. How we name organisms 2. Genus species Example: Homo sapiens Homo = Genus, sapiens = species IV. 5 KINGDOMS 1. Fill in the missing parts of the chart. KINGDOM CHARACTERISTICS EXAMPLES 1. 2. PROTISTS -unicellular -no nucleus (prokaryotic) -heterotrophic or autotrophic -unicellular -has nucleus (eukaryotic) -heterotrophic or autotrophic Animal like = Plant like = 3. FUNGI -heterotrophic - 4. -multicellular -autotrophic Mushroom, yeast, mold, mildew Jellyfish, humans, dogs, fish, grasshoppers, bears 5. ANIMAL VI. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Bacteria are found in the kingdom a. fungi b. monera c. protista d. animalia 2. Mushrooms and molds belong to the kingdom a. fungi b. monera c. protista d. animalia 3. The scientific name for a lion is Panthera Leo. The word Panthera tells us the lion’s a. kingdom b. phylum c. genus d. species HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS PART 6. SKELTAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS 1. movement 2. shape 3. protection & support 4. makes blood cells 5. stores materials (calcium & phosphorus) II. PARTS 1. BONES – 206 in body 2. CARTILAGE a. flexible connective tissue b. protection & support c. ends of bones d. cushioning (bw vertebrae) e. make up body parts (nose, ears) 3. TENDONS – connective tissue which connects MUSCLES TO BONES 10 4. LIGAMENTS – connective tissue which connects BONE TO BONE 5. JOINT – where 2 bones meet a. immoveable – skull b. pivot – neck (side to side, up & down) c. ball and socket – hip, shoulder (circular) d. hinge – elbow, knee (back & forth) e. gliding – wrist (all directions) PART 7. MUSCULAR SYSTEM I. FUNCTION 1. LOCOMOTION (movement) by contracting and relaxing of the muscles II. TYPES OF MUSCLES Fill in the missing parts of the chart below. MUSCLE 1. VOLUNTARY/INVOL STRIATED/NONSTRIATED LOCATION voluntary -attached to bones 2. SMOOTH MUSCLE 3. -digestive system, blood vessels… Involuntary striated 4. How do skeletal muscles WORK IN PAIRS? ______________________________________________ 5. LABEL THE DIAGRAM BELOW. A. ______________________ C B. ______________________ C. ______________________ D. ______________________ D PART 8. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. FUNCTION – NUTRITION a. INGESTION – taking in food b. DIGESTION – breakdown of food c. EGESTION – removal of undigested wastes 11 II. NUTRIENTS – substances needed by the human body 1. CARBOHYDRATES -sugars & starches -provide ENERGY 4. VITAMINS -normal functioning 2. PROTEINS -amino acids -build & repair 5. MINERALS -normal functioning 3. FATS -energy -protection -insulation 6. WATER -makes up body -transport -chemical reactions III. 2 TYPES OF DIGESTION 1. MECHANICAL DIGESTION – physical breakdown of food 2. CHEMICAL DIGESTION – breaking down of food using ENZYMES IV. PARTS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. MOUTH b. HELPER ORGANS (produce substances which a. where mechanical digestion begins (teeth) b. chemical digestion begins – enzymes in saliva, ptyalin (starches sugar) 2. EPIGLOTTIS – flap that closes over trachea when swallowing to prevent choking 3. ESOPHAGUS – carries food to stomach by PERISTALSIS a. PERISTALSIS – wavelike motion of esophagus that pushes food through digestive system 4. STOMACH a. mechanical digestion by churning food b. chemical digestion of proteins by pepsin (proteins amino acids) c. mix of food = chyme 5. SMALL INTESTINE – where most digestion occurs, where digestion finishes a. INTESTINAL JUICES contain many enzymes are placed into small intestine) - LIVER – makes bile that mechanically breaks down fat by EMULSIFICATION (big droplets smaller droplets) Big fat droplet -GALL BLADDER – stores bile -PANCREAS – pancreatic juice contains many enzymes c. ABSORBS NUTRIENTS -VILLI – fold in wall of small intestine that absorb nutrients & place them into bloodstream. 6. LARGE INTESTINE – water absorbed from feces, bacteria which make vitamins 7. RECTUM – stores waste (feces) 8. ANUS – where wastes leave the body V. LABEL THE DIAGRAM BELOW. B A K C J I D H G E A. _______________________________________ B. ________________________________________ C. ________________________________________ D. ________________________________________ E. ________________________________________ F. K (not F)_________________________________ G. ________________________________________ H. ________________________________________ I. ________________________________________ J. ________________________________________ 12 VI. DISORDERS 1. DIARRHEA – not enough water absorbed in large intestine 2. CONSTIPATION – too much water absorbed in large intestine PART 9. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I. FUNCTION – TRANSPORT (movement of materials throughout the body, in & out of cells) II. PARTS 1. HEART – cardiac muscle, pumps blood a. ATRIA – upper chambers b. VENTRICLES – lower chambers (atria ventricles) c. VALVES – flaps of tissue that prevent backflow of blood d. SEPTUM – wall that separates left & right sides (prevents mixing of oxygenated & deoxygenated blood) 2. BLOOD VESSELS a. ARTERIES – thickest blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart -AORTA – largest artery -PULSE -GREATEST BLOOD PRESSURE b. VEINS – carry blood to the heart -VALVES – prevent back flow c. CAPPILARIES – thinnest blood vessels where oxygen & carbon dioxide are exchanged between blood & cells, connect arteries & veins 3. Label the right and left sides of the heart, label which sides pumps oxygenated & deoxygenated blood, and label all parts of the heart. A. ________________________________ B. ________________________________ A C. ________________________________ K B D. ________________________________ E. ________________________________ C F. ________________________________ G. ________________________________ D J H. ________________________________ E I. _________________________________ I F H J. _________________________________ K. _________________________________ G 13 4. BLOOD - connective tissue a. PLASMA – liquid part which carries materials b. RED BLOOD CELLS – contain hemoglobin, carry oxygen c. WHITE BLOOD CELLS – fight disease d. PLATELETS – blood clotting (make fibrin) 5. Label the parts of the blood. A. ____________________ C. _________________ B. _____________________ D. ___________________ PART 10. IMMUNE SYSTEM I. FUNCTION – defends the body against disease II. PARTS a. 1st line of defense = skin, saliva, stomach acids… b. 2nd line of defense = inflammatory response & interferons c. 3rd line of defense = ANTIBODIES – proteins, help destroy pathogens (attach to pathogen to slow it down) TYPES: 1. ACTIVE IMMUNITY – immune system produces own antibodies, permanent a. by acquiring the disease (chicken pox) b. by receiving a vaccination (weak or dead antigens injected into the body) 2. PASSIVE IMMUNITY – receive antibodies from another organism, temporary III. ALLERGIES – reaction that occurs when the body is sensitive to certain substances IV. AIDS 1. Auto Immune Deficiency Syndrome 2. Caused by HIV virus 3. Kills T- cells (WBC’s that tell B-cells to make antibodies) destroys immune system PART 11. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. FUNCTION – Gas Exchange II. PARTS 1. NASAL CAVITY a. mucus – moistens air, traps materials b. cilia – filters air c. blood vessels – warm air 2. PHARYNX - throat 3. LARYNX – vocal cords (voice box) 4. EPIGLOTTIS 5. TRACHEA – windpipe made of rings of cartilage (prevent collapsing) 6. BRONCHI – 2 tubes that branch off trachea 7. ALVEOLI – clusters of air sacs surrounded by capillaries where oxygen & carbon dioxide are exchanged by diffusion (GAS EXCHANGE) 8. DIAPHRAGM – sheet of muscle under lungs TRACHEA BRONCHI BRONCHIAL TUBES BRONCHIOLES ALVEOLI 14 III. LABEL THE DIAGRAM BELOW. A. _________________________________ B. __________________________________ A C. __________________________________ E B D. __________________________________ F E. __________________________________ F. __________________________________ C G H G. ___________________________________ H. ___________________________________ I I. ___________________________________ D J J. ____________________________________ IV. BREATHING 1. INHALATION (breathing in) a. diaphragm contracts (down) b. air pressure decreases 2. EXHALATION (breathing out) a. diaphragm relaxes (up) b. air pressure increases 3. Breathing rate increases when amount of carbon dioxide in the blood increases. 4. Label the BELL JAR below. A B A. __________________ B. __________________ C C. __________________ D D. __________________ PART 12. EXCRETORY SYSTEM I. FUNCTION – EXCRETION – removal of cellular (metabolic wastes) II. PARTS 1. LIVER a. Produces UREA b. DETOXIFICATION 2. LUNGS – excrete CO 2 & H2 0 3. SKIN a. excretes perspiration/ sweat (water, urea, salt) b. maintains body temperature (cools down body) c. contains epidermis & dermis (oil glands, sweat glands, nerves, hair follicles, blood vessels) 4. URINARY SYSTEM a. KIDNEYS – contain nephrons that filter the blood & maintain water balance produces URINE (water, urea, salt) b. URETERS – tubes that carry urine from kidneys to the bladder c. URINARY BLADDER – stores urine d. URETHRA – tube that carries urine out of the body 15 5. Label the parts of the urinary system. A BC D PART 13. NERVOUS SYSTEM I. FUNCTION 1. REGULATION a. processes & sends out messages b. control & coordination c. helps to maintain homeostasis II. PARTS 1. What is a NEURON? ___________________________ 2. IMPULSE – message sent by neurons a. STIMULUS – change in the environment that starts an impulse 3. RECEPTOR – sense organs, pick up stimuli (ears, eyes, nose, skin, tongue) 4. EFFECTOR – parts of the body that responds to a stimulus (MUSCLES & GLANDS) 5. PARTS OF A NEURON a. dendrites – branches at start of neuron that pick up impulses b. cell body (cyton) – contains nucleus c. axon – long single fiber that carries impulse to end of neuron (surrounded by myelin) d. terminal branches – branches at end of neuron 6. What is a SYNAPSE? __________________________________________________________ 7. NEUROTRANSMITTER – substances released into a synapse that “carries” impulse to next cell 8. Label parts of the neuron below. A. ____________________________ B. ____________________________ C. ____________________________ D. ____________________________ E. _____________________________ III. TYPES OF NEURONS 1. SENSORY NEURON – receptors brain & spinal cord 2. INTERNEURONS – make up brain & spinal cord 3. MOTOR NEURONS – brain & spinal cord effectors 16 IV. RELEX ARC (RSIME) Receptor Sensory Neuron Interneuron Motor Neuron Effector V. REFLEX 1. Reflex – involuntary response controlled by the spinal cord VI. DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM – brain & spinal cord 2. PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM – branching nerves that carry messages to all body parts a. somatic – voluntary b. autonomic – involuntary VII. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. BRAIN (3 parts) – protected by cranium a. Cerebrum – largest -controls VOLUNTARY activities. the senses, thinking, memory, language… b. Cerebellum – back -controls BALANCE c. Medulla – brain stem -controls all INVOLUNTARY activities (heart beat, breathing, digestion…) d. Label the parts of the central nervous system below. A. ________________________________ B. _________________________________ C. _________________________________ D. _________________________________ 2. SPINAL CORD – protected by vertebrae PART 14. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM I. FUNCTION 1. REGULATION - produces hormones that control body functions 2. HORMONE – a. chemical produced by endocrine glands b. chemical messengers that travel through the BLOODSTREAM a. How are the nervous & endocrine systems similar? _________________________________________ b. How are they different? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 17 II. PARTS 1. HYPOTHALAMUS – part of the brain that controls the pituitary gland 2. PITUITARY GLAND - in the brain -MASTER GLAND – secretes hormones that control other glands (FSH, TSH, LH) -secretes Growth hormone 3. THYROID produces hormone that controls metabolism 4. PARATHYROIDS 5. THYMUS – behind breast bone, larger in babies 6. ADRENAL GLANDS produce -ADRENALINE – released in times of stress (increases heart rate, breathing rate…) 7. PANCREAA produce -INSULIN – decreases blood sugar level -GLUCAGON – increases blood sugar level 8. OVARIES 9. TESTES III. NEGATIVE FEEDBACK 1. How endocrine glands work 2. A hormone causes a gland to produce or stop producing another hormone PART 15. REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM I. FUNCTION 1. REPRODUCTION -the process through which living things produce new individual of the same kind II. MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SPERM CELLS – male sex cells 1. TESTES -produce sperm cells and testosterone 5. PENIS –deposits sperm into female 2. SCROTUM -external organ that surrounds testes 6. URETHRA – tube in the penis which transports 3. GLANDS -adds liquid to sperm (semen) urine & semen 4. SPERM DUCTS/VAS DEFERENS -tubes that carry sperm to the penis 7. Label the diagram of the male reproductive system. A. __________________________ A. B. B. __________________________ C. C. __________________________ D. __________________________ D. E. __________________________ E. F. __________________________ G. __________________________ F. G. III. FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EGGS – female sex cells 1. OVARIES - makes eggs and estrogen 2. FALLOPIAN TUBES - (oviduct) tubes in which an egg travels through from ovaries to the uterus 18 -FERTILIZATION OCCURS HERE 3. UTERUS - muscular organ where zygote attaches and develops into a baby 4. CERVIX - lower end of the uterus 5. VAGINA – birth canal, where sperm is deposited 6. Label the diagram of the female reproductive system. A. A. ________________________________ B. B. ________________________________ C. ________________________________ C. D. D. ________________________________ E. ________________________________ F. E. IV. MENSTRUAL CYCLE (28 days) 1. STEPS a. Egg develops in ovary b. OVULATION – egg released from ovary c. Lining of uterus thickens with blood d. NO FERTILIZATION MENSTRUATION (uterus lining sheds, egg leaves body) V. EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT 1. FERTILIZATION : EGG + SPERM ZYGOTE (fertilized egg) 2. ZYGOTE EMBRYO (8 weeks) FETUS (after 8 weeks) (BY CELL DIVISION) 3. STRUCTURES FORMED a. AMNIOTIC SAC – surrounds fetus & contains amniotic fluid that protects baby b. PLACENTA – network of blood vessels where nutrients & wastes are exchanged between the mother’s blood & baby’s blood by diffusion c. UMBILICAL CORD – blood vessels that connect the fetus to the placenta -Carry nutrients & and wastes to and from the placenta d. Label the diagram below. A.__________________________ B.__________________________ C.__________________________ D. __________________________ E.__________________________ F.__________________________ G.__________________________ 19 HUMAN BODY REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The body system responsible for the exchange of gases between the external environment and the body’s cells is the a. digestive b. circulatory c. respiratory d. excretory 2. Which of the following organs is not part of the circulatory system? a. heart b. blood c. veins d. trachea 3. Infectious diseases are caused by a. deficiencies in diet c. allergies b. pathogens d. malfunctioning organs 8. Which system breaks down food into smaller pieces that can be used by the body’s cells? a. endocrine b. excretory c. digestive d. nervous 9. The nervous system is made up of special cells called a. bones b. tendons c. neurons d. ligaments 10. In addition to bone tissue, the skeletal system contains a. cartilage b. cardiac muscle c. glands d. smooth muscle 4. Which system removes cellular wastes from the body? a. digestive b. skeletal c. endocrine d. excretory 11. Which of the following body systems is not involved in locomotion? a. endocrine b. muscular c. skeletal d. nervous 5. The male reproductive cell is called the a. sperm b. egg c. gonad d. ovary 12. Cardiac muscle is found in the a. brain b. liver c. hear 6. What is the name of a female reproductive organ? a. testes b. scrotum c. ovary d. stomach 13. After food is digested, it passes into the a. excretory system c. circulatory system b. nervous system d. endocrine system 7. The chemicals secreted by the endocrine glands are called a. enzymes b. hormones c. auxins d. acids 14. The largest part of the human brain is the a. cerebellum c. medulla b. spinal cord d. cerebrum PART 16. REPRODUCTION & DEVELOPMENT I. CHROMOSOMES – rod shaped structures in nucleus 1. consist of genes which contain genetic information (DNA) 2. sex chromosomes – determine sex of an organism a. EGGS = X SPERM = X or Y b. FEMALE = XX MALE = XY II. MITOSIS – cell division 1. 1 cell 2 cells 2. daughter cells have the SAME # OF CHROMOSOMES as parent cell 3. asexual reproduction 4. production of ALL body cells EXCEPT sex cells IV. PLANT CELL MITOSIS 1. no centrioles 2. CYTOKINESIS – cell plate forms instead of cell membrane pinching in V. MEIOSIS – cell division 1. 2 divisions (1 2 4) 2. for sexual reproduction 3. 4 new daughter cells with ½ the number of chromosomes as parent cell 4. TO PRODUCE SEX CELLS ONLY (in ovaries & testes) d. kidney 20 MALES = ___________________ FEMALE= ___________________ VI. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1. 1 parent 2. offspring identical to parent 3. MITOSIS = 1 cell 2 cells VII. TYPES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1. FISSION – one-celled organism divides into 2 identical cells (ameba and paramecium) 2. BUDDING – unequal division of organism (Yeast) 3. SPORULATION – spores (specialized cells) develop into new organism (mold, mushrooms) 4. VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION – used by plants (NO SEEDS) -runners (strawberries), buds/tubers (potatoes), grafting (roses), bulbs (onions) VIII. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1. 2 parents, each give sex cell 2. Offspring NOT identical to parents 3. FERTILIZATION = SPERM + EGG ZYGOTE 4. ZYGOTE DEVELOPS INTO EMBRYO (1st 8 weeks) FETUS 5. Label the diagrams below. A. B. C. D. E. F. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The process in which the egg and sperm unite is a. pollination b. fertilization c. mitosis d. meiosis 2. In flowering plants, the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma is called a. pollination b. fertilization c. mitosis d. meiosis 3. The male part of the flower is the a. stamen b. pistil c. ovary d. ovule 4. In humans, sperm and egg cells have 23 a. genes b. nuclei c. chromosomes d. chloroplasts 5. Which of the following statements is true? a. Sexual reproduction leads to the possibility of variation in the next generation. b. Asexual reproduction leads to the possibility of variation in the next generation. 21 c. Sexual reproduction results in identical offspring. d. Sexual reproduction requires only one parent. 6. A fertilized egg is also called a(n) a. embryo b. baby c. zygote d. fetus 7. The division of the nucleus and cytoplasm and duplication of chromosomes is called a. mitosis b. reproduction c. osmosis d. diffusion 8. Sexual reproduction requires a type of cell division called a. mitosis b. diffusion c. meiosis d. passive transport a. vacuole b. cell membrane c. chromosomes d. cell wall 10. Which of the following is not a method of asexual reproduction? a. vegetative propagation c. fission b. budding d. fertilization 11. Which of the following is true about cells produced by mitosis? a. They are genetically identical to the parent cells. b. They contain half the number of chromosomes that are found in the parent cells. c. They are called sperm cells. d. They are called egg cells. 9. Which cell structure contains genes? PART 17. GENETICS I. GREGOR MENDEL – founder of genetics (crossed pea plants to study heredity = passing on of traits) 1. GENES – make up chromosomes a. 2 genes (ALLELES) for every trait (1 from each parent) 2. DOMINANT GENE/TRAIT – more frequent/common gene – CAPITAL LETTER (T) 3. RECESSIVE GENE/TRAIT – less frequent/common gene – lower case (t) 4. PHENOTYPE – physical appearance (what offspring look like) 5. GENOTYPE – genetic makeup T = tall plant, t = short plant GENES PHENOTYPE TT Tall tt Short Tt Tall GENOTYPE Homozygous OR pure dominant Homozygous OR pure recessive Heterozygous OR hybrid II. PUNNETT SQUARES 1. Cross a pure dominant tall plant with a hybrid plant. T T Phenotype = T t 2. B = Brown eyes, b = blue eyes Genotype = 22 Cross a blue eyed person with a hybrid brown eyed person. Give the phenotypes & genotypes of their offspring. 3. G = green, g = yellow Cross a yellow plant with a pure dominant plant. Give the phenotypes & genotypes for all offspring. III. CHROMOSOMES 1. CHROMOSOMES – rod shaped structures in the nucleus that control all cell activities & contain hereditary information a. CHROMOSOMES made of GENES made of DNA 2. SEX CHROMOSOMES – chromosomes that determine sex of organism EGGS = X SPERM = X or Y FEMALE = XX MALE = XY 3. MUTATION – change in a gene that may cause a new trait (good or bad) a. in body cells (example: skin cells) cannot be passed on to offspring b. in SEX CELLS can be passed on to offspring c. Examples: sickle cell anemia BOTH MUTATIONS & NONDISJUNCTION MAY LEAD TO GENETIC DISORDERS IV. DNA 1. DNA = Deoxyribonucleic acid (discovered by Watson, Crick, & Franklin) 2. STRUCTURE a. DOUBLE HELIX – 2 twisted strands (like a spiral staircase) b. Made up of 2 chains of NUCLEOTIDES 3. NUCLEOTIDE (building block) a. Label the nucleotide below. deoxyribose B A phosphate C b. NITROGEN BASES - 4 of them -Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C) c. The 2 DNA strands are COMPLIMENTARY (base pairs match up) A–T G–C (hint: AT Garden City) A T T A C G G C 23 d. Fill in the bases for the complimentary DNA strand below. A C G T A G VI. SEX-LINKED TRAITS – gene for a trait carried ONLY by an X chromosome 1. Examples: colorblindness & hemophilia 2. XX = normal female XY = normal male X’X = female carrier X’Y = male with trait X’X’ = female with trait THERE ARE NO MALE CARRIERS!!! 3. A man who is colorblind marries a woman who is a carrier. Will their kids be colorblind, carriers, or not possess the trait. Draw a Punnett square to show your work and give the phenotypes & percentages of their offspring. VII. DNA REPLICATION – making a copy of DNA (duplicating) 1. occurs during interphase in the nucleus 2. STEPS OF DNA REPLICATION a. DNA double helix unzips b. 2 strands separate c. free nitrogen bases attaché to strands form 2 new DNA molecules Each new DNA molecule contains 1 old strand and 1 new strand. VIII. PEDIGREE CHARTS - trace a genetic trait in a family 1. Example: 24 2. The pedigree chart below traces the appearance of earlobes through 3 generations of a family. Based on the chart, attached earlobes is a a. dominant trait b. recessive trait c. mutated trait d. trait common in females IX. APPLIED GENETICS 1. GENETIC ENGINEERING a. the alteration of genes to get rid of undesirable traits or to produce desirable traits b. SELECTIVE BREEDING – breeding organisms with desirable traits Example: a farmer choosing to grow only disease-resistant plants X. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The units of heredity are called a. genes b. cells c. hybrids d. traits 2. The visible characteristics of an organism are called a. cells b. genotypes c. chromosomes d. phenotypes 9. B represents the gene for brown eyes, & b represents the gene for blue eyes. Which represents a homozygous dominant individual? a. Bb b. bb c. BB d. none of these 3. Who studied the inheritance patterns of pea plants? a. Crick b. Watson c. Mendel d. Punnett Base your answers to questions 10 & 11 on the information below. 4. A trait that is not seen often of two traits is a. incomplete b. dominant c. hybrid d. recessive The ability to roll your tongue into a U-shape is a dominant trait. A father has 1 dominant gene for rolling (R) and 1 gene for nonrolling (r), and a mother also has 1 dominant gene for rolling and 1 gene for nonrolling. Both parents would then have a Rr genotype. 5. In humans, which chromosome combination is that of a male? a. XX b. YY c. XY d. none of these 6. A change in genes or chromosomes that causes a new trait to be inherited is called a(n) a. alteration b. variation c. mutation d. hybrid 7. The rod-shaped structures located in the nucleus of every cell of an organism are the a. chromosomes b. cell membrane c. traits d. genes 8. The passing on of traits from an organism to its offspring. a. biology c. chemistry b. heredity d. zoology 10. Which percentage of their children will likely have an RR genotype? a. 25% b. 50% c. 75% d. 100% 11. As long as a child has at least one dominant R trait, he or she will be able to roll his or her tongue. Which percentage of children are likely to be able to roll their tongue? a. 25% b. 50% c. 75% d. 100%