* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Physics at El Alsson
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Woodward effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
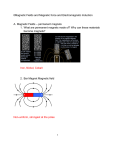
Science Department Scheme of Work Unit of Study: Unit 9 – Magnets and electromagnetism Time allocated: Learning Objectives to be covered: 12 lessons Candidates should be able to: State the properties of magnets Give an account of induced magnetism Distinguish between ferrous and non-ferrous materials Distinguish between the magnetic properties of iron and steel Distinguish between the design and use of permanent magnets and electromagnets State the factors affecting the magnitude of an induced emf Show understanding that the direction of an induced emf opposes the change causing it Describe a rotating-coil generator and the use of slip rings Sketch a graph of voltage output against time for a simple ac generator Describe the construction of a basic iron-cored transformer as used for voltage transformations Recall and use the equation (Vp /Vs) = (Np /Ns) Describe the use of the transformer in high- voltage transmission of electricity Give the advantages of high-voltage transmission Describe the principle of operation of a transformer Recall and use the equation Vp Ip = Vs Is (for 100% effi ciency) Explain why energy losses in cables are lower when the voltage is high Describe the pattern of the magnetic field due to currents in straight wires and in solenoids Describe applications of the magnetic effect of current, including the action of a relay State the qualitative variation of the strength of the magnetic field over salient parts of the pattern Describe the effect on the magnetic field of changing the magnitude and direction of the current State and use the relative directions of force, field and current State that a current-carrying coil in a magnetic field experiences a turning effect and that the effect is increased by increasing the number of turns on the coil Relate this turning effect to the action of an electric motor Describe the effect of increasing the current on a dc motor Important references/resources: Experimental skills and investigations objectives: Oxford Complete Physics for Cambridge IGCSE (p. 201 - 228) Describe methods of magnetisation and of demagnetisation Describe an experiment to identify the pattern of field lines round a bar magnet Describe an experiment that shows that a changing magnetic field can induce an emf in a circuit Describe an experiment to show that a force acts on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field, including the effect of reversing: the current and the direction of the field Describe an experiment to show the corresponding force on beams of charged particles Oxford Complete Physics for Cambridge IGCSE Revision Guide (p.105 – 109, p. 131 139 ) Demonstration 9 from TRK Practicals 9.1 – 9.3 from TRK W/S 9 from TRK Fleming’s rules W/S Transformers W/S Generic Homework Tasks (to be completed by ALL students): 1. Questions 1 – 9 (p.226 - 227) 2. Assessment 9 from TRK Formative Assessment (takes place prior to the summative assessment): Summative Assessment: 1. Practical write up – Investigating the strength of electromagnets. Focus on planning. 2. Assessmnent 9 from TRK 45 minute mixed style question paper (based on past examination questions) completed at the end of the unit of study with questions from P1, P2 and P3.