* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Glossary
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
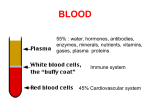
Glossary 1. Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)– This test is used to see if a person has a clotting or bleeding problem like hemophilia. It measures the time it takes for a clot to form after certain substances have been added to the blood sample. The normal time is between 16 to 40 seconds. 2. Adapter – A device used to connect two things together. 3. Allergic reaction – A reaction of the immune system to a foreign substance; sometimes patients can have an allergic reaction to clotting factor replacement medicines. 4. Anaphylaxis – A serious, sometimes life-threatening allergic reaction to a foreign substance. 5. Anemia – A lower number of red blood cells in the body than normal. 6. Antibody – Substances made by the immune system in response to antigens or foreign substances. Antibodies are unique and protect the body against a specific antigen. In people with hemophilia B, the body may develop antibodies, called inhibitors, that stop the clotting factor replacement medicine from stopping a bleed. 7. Bethesda assay – A test used to find out if the body had developed inhibitors to clotting factor replacement treatment. 8. Bleeding time – Used as part of screening for hemophilia. A test that measures the time it takes for blood to stop flowing from a small wound. 9. Blood clotting factors – Substances in the blood that are needed to make the blood clot. 10. Carrier – A person who has one gene that gives information for a specific disease, and one normal gene. Because of the normal gene, this person may not show any signs or symptoms of the disease, but they may be able to pass along the disease to their children. 11. Cellulitis – An infection of the skin and the tissue just under the skin. 12. Chromosome – Long pieces of hereditary information found in the center of each cell. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total). Half come from the mother and half come from the father. 13. Coagulation – The process by which blood cells clump together to form a clot. 14. Continuous infusion – A controlled way to deliver a liquid drug into the body through a vein over a prolonged period of time. The safety and efficacy of BeneFIX® [Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant)] by continuous infusion have not been established. 15. Deficient – Less than what is considered normal; for example, a person with hemophilia is deficient in clotting factor activity. 16. Diluent –A liquid used to dissolve a solid substance to make it a liquid ready for infusion. 17. Diluent syringe – The syringe containing the diluent or liquid used to dissolve the medicine. 18. Gene – The basic unit of DNA that makes up chromosomes. Genes contain a person’s hereditary information. 19. Hemophilia – A blood disorder in which a person’s blood does not clot properly and they bleed longer than normal. 20. Hemophilia Treatment Center – a treatment facility that provides a range of comprehensive services for patients with bleeding disorders and their families. 21. Hypersensitivity – The body’s reaction to a foreign substance. 22. Hypoxia – A lack of oxygen. 23. Immune tolerance induction – A process in which factor concentrate is given regularly over a period of time so the body gets trained to recognize the treatment without reacting to it. 24. Infusions – Injecting a liquid (other than blood) into the body through a vein. 25. Infusion port – A silicone case that is placed under the skin that has a catheter (tube) threaded into a vein. The port allows long-term access to a vein. 26. Inhibitor – Something that stops or blocks another substance. In hemophilia B, inhibitors are antibodies that stop clotting factor replacement medicine from helping to form a blood clot. 27. Luer end – A type of tip on a syringe that allows for quick and firm attachment of the needle. 28. Mutations – A change to hereditary information that may be passed on to children; not all mutations are harmful, but some may cause diseases. 29. Nanofiltration – a process of filtering a liquid or a drug to remove large molecules like viruses or proteins. 30. Nephrotic syndrome – The result of any number of diseases that damage the kidneys. Nephrotic syndrome causes a large amount of protein in the urine, low protein levels in the blood, high cholesterol, and swelling. 31. Phlebitis – Pain and tenderness of a vein. 32. Prothrombin time (PT) – This test is used to see if a person has a clotting or bleeding problem, like hemophilia. This test measures how long it takes for a person’s blood to clot after certain substances are added. 33. Recombinant – When genetic material is combined from different sources. 34. Recombinant DNA – Refers to DNA that has been altered by joining genetic material from different sources. A recombinant DNA molecule can enter a cell, multiply, and be made into a protein. BeneFIX® [Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant)] is a purified protein produced by recombinant DNA technology. 35. Reconstitution – The process of adding a liquid, called a diluent, to a powdered medicine to make a solution. 36. Renal infarct – The death of tissue in the kidney caused by a blocked artery in the kidney. 37. Surgical prophylaxis – Administering clotting factor replacement around the time of an operation, or surgery. Also called peri-operative management. 38. Synovium – A layer of tissue that lines the inside of joint cavities. It secretes a fluid that lubricates the joint. 39. Tourniquet – A device that is used to apply pressure over a vein to make it easier to inject medicine. 40. Vial – A small bottle of medicine.