* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Muscle Tissue Types Muscle Tissue Types
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
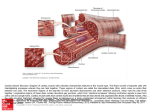
Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue Types • Function is to produce movement • Three types • Skeletal muscle – Under voluntary control – Contracts to pull on bones or skin – Produces gross body movements or facial expressions – Characteristics of skeletal muscle cells – Skeletal muscle – Cardiac muscle – Smooth muscle • Striated • Multinucleate (more than one nucleus) • Long, cylindrical Muscle Tissue Types Skeletal tissue (striated) 40X 1000X Figure 3.20a Muscle Tissue Types Muscle Tissue Types • Cardiac muscle – Under involuntary control – Found only in the heart – Function is to pump blood – Characteristics of cardiac muscle cells • Cells are attached to other cardiac muscle cells at intercalated disks • Striated • One nucleus per cell Figure 3.20b 1 Cardiac Muscle Tissue Types • Short, cylindrical cells with single nucleus • Smooth muscle – Under involuntary muscle – Found in walls of hollow organs such as stomach, uterus, and blood vessels – Characteristics of smooth muscle cells 400X 40X 100X • No visible striations • One nucleus per cell • Spindle-shaped cells Muscle Tissue Types Smooth muscle • Looks like flowing river, lots of nuclei 40X 100X Figure 3.20c 400X Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue • Composed of neurons and nerve support cells • Function is to send impulses to other areas of the body – Irritability – Conductivity Figure 3.21 2 Nervous tissue (spinal cord, cs) Nervous tissue (cerebellum) 400X 40X 100X 40X Glandular Epithelium 400X 100X Parathyroid • Gland – One or more cells responsible for secreting a particular product • Two major gland types – Endocrine gland • Ductless since secretions diffuse into blood vessels • All secretions are hormones – Exocrine gland 100X 400X • Secretions empty through ducts to the epithelial surface • Include sweat and oil glands Pituitary 100X 400X 3