* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PHYSICAL GEOLOGY
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
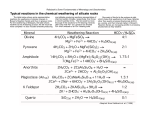
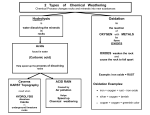
Revised 2/93 NVCC COLLEGE-WIDE COURSE CONTENT SUMMARY GOL 105 - PHYSICAL GEOLOGY (4 CR.) COURSE DESCRIPTION Introduces the composition and structure of the earth and modifying agents and processes. Investigates the formation of minerals and rocks, weathering, erosion, earthquakes, and crustal deformation. Lecture 3 hours. Laboratory 3 hours. Total 6 hours per week. GENERAL COURSE PURPOSE This is an introductory course in geology that is intended to meet the needs of the student pursuing a career in earth or natural sciences or a student working to fulfill a science requirement for other majors. The course deals in a fundamental way with the processes of the distribution on the surface and in the interior of the earth. ENTRY LEVEL COMPETENCIES The student is assumed to have had not other college science courses but posses some proficiency in high school science and math. COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. know on sight several minerals and rocks that commonly occur on the earth’s surface distinguish the major classes of rocks and explain their origin understand the various processes of physical and chemical weathering and be able to recognize them in the field explain the different agents of erosion and recognize the landforms they leave on the earth’s surface write an essay on one of the major theories of the cause of glaciation distinguish the major categories of faults and folds that define the earth’s surface and interior diagram the earth’s interior zones and discuss the mineral and rock composition of each zone list the most common elements found in sea water and describe the tridal and wave motion of sea water explain how oil and coal are formed, where they are, and how they are extracted understand the theories of continental drift, sea floor spreading, and plate tectonics and the relationships between them 1 MAJOR TOPICS TO BE INCLUDED A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. Earth materials (minerals, rocks) Weathering Mass wasting Streams Groundwater Deserts Glaciers Oceans and shorelines Earthquakes Structure of continents Continental drift, sea floor spreading, plate tectonics 2