* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table A. Bohr Model of the
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
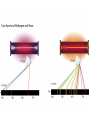
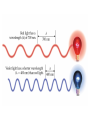
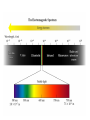
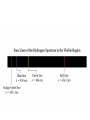
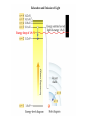
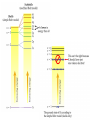
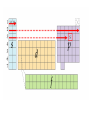
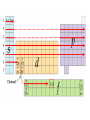
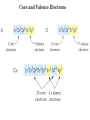
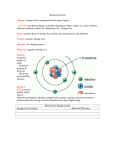
Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table A. Bohr Model of the Atom 1. Solar System Model 2. Created to Fit a “Quantized” Picture of Energy Transfer 3. Basis: Noncontinuous Emission Spectra of the Elements 4. Basic Postulates a. Electrons reside in certain allowed energy states b. Energy absorption and emission by atoms is caused by electrons “jumping” between energy states. B. Quantum Model (Quantum Mechanics) 1. No Specific Orbits or Paths 2. Mathematical Description of Where the Electrons Are 3. Electrons Reside in Principal Energy Levels Level 1 (K) 2 (L) 3 (M) 4 (N) 5 (O) 6 (P) 7 (Q) Theoretical Number Actual Number of Electrons of Electrons 2 8 18 32 50 72 98 2 8 18 32 32 18 8 4. Electron Configuration - The most probable and most stable arrangement of electrons in an atom. Core and Valence Electrons Shapes of Atomic Orbitals