* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Moons of the Outer Solar System
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Jumping-Jupiter scenario wikipedia , lookup
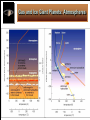
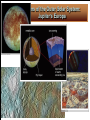
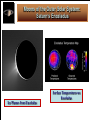
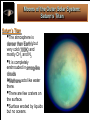
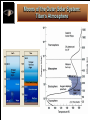
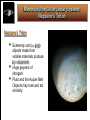
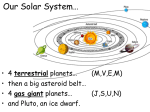
Life Outside the Habitable Zone? Astrobiology Workshop June 27, 2006 Terrestrial Planet Region: Quick Review MERCURY MOON X Terrible Extremes of Temperature No Atmosphere, UV, Cosmic Rays Little or No Volatiles, No Liquids Been There, Done That VENUS Absurdly High Temperatures No or Little Water Young Surface No Fossil Record MARS Evidence for Liquid Water in Past Possible Environments for Life to Survive? Volatiles and Water Present Now X X ? Terrible Extremes of Temperature No Atmosphere, UV, Cosmic Rays Little or No Volatiles, No Liquids Gas and Ice Giant Planets: Interiors Gas Giant Planets Ice Giant Planets Jupiter’s Interior: More Detail XXXXX Gas and Ice Giant Planets: Atmospheres Gas and Ice Giant Planets: Prospects for Life? Prospects for Life? • There are ingredients for organic chemistry, and • Atmospheric layers exist with roughly Earth-like Temperature & Pressure; • But there are no solid surfaces (except ice crystals) and no liquid water (except very deep in Uranus and Neptune), • Violent winds and convective turbulence would mix any life-bearing gas quickly over extremes of T & P. • Although the sunlight is very weak, • Internal heat is available. • They are very difficult to explore! What about Moons of Planets? For instance, the Galilean Satellites of Jupiter Io Europa Ganymede Callisto Moons of the Outer Solar System: Jupiter’s Io Moons of the Outer Solar System: Jupiter’s Europa Moons of the Outer Solar System: Io and Europa Jupiter’s Io Is the most volcanic object in the Solar System due to Tidal heating caused by the gravitational tug of war it experiences from Jupiter and its sister Galilean satellites. Jupiter’s Europa Has similar but weaker tidal heating, Has a young cracked water ice crust perhaps only a few kilometers thick, and May have a warm ocean of liquid water below the crust. Could there be life? Tidal Forces: Tides Raised on Earth by the Moon The misaligned bulges exert a small force on the Moon that increases the size of its orbit, while friction in the bulges slows the Earth’s rotation. Tidal forces are difference forces. Tidal Heating of a Moon: Tides Raised by a Planet on its Moon Tidal heating occurs because Io and Europa’s orbits are Eccentric. The orbits stay eccentric due to a three-way orbital resonance among the three moons Io, Europa, and Ganymede. Effects of Tidal Interactions Rotation Rotation of moons become synchronized with their orbits. They keep the same face toward the planet. The rotation of the planet is slowed down. Orbits Orbits of moons mostly evolve outward. Internal “Tidal Heating” Eccentric orbits lead to periodic flexing of the moon’s shape which heats the interior. Orbital resonances with other moons can maintain eccentric orbits and tidal heating. Roche Radius Roche Radius Objects held together by their own gravity are shattered inside the Roche Radius (about 2 Planet Radii). This is where most giant planet rings are. Comet SL9 was tidally disrupted within the Roche Radius of Jupiter and destroyed Why doesn’t the Space Shuttle get disrupted? Why don’t we get disrupted? Tidal Disruption: Comet Shoemaker Levy 9 Moons of the Outer Solar System: Saturn’s Enceladus Saturn’s Enceladus Small icy moon (500 km) in diameter Young, crater-free surface regions with like those on Europa Orbit resonance with Dione South polar hot spot and ice plumes Thin “atmosphere” of water vapor Subsurface ocean!? Moons of the Outer Solar System: Saturn’s Enceladus Ice Plumes from Enceladus Surface Temperatures on Enceladus Moons of the Outer Solar System: Saturn’s Titan Saturn’s Titan The atmosphere is denser than Earth’s but very cold (100K) and mostly CH4 and N2 It is completely enshrouded in smog-like clouds Methane acts like water there. There are few craters on the surface. Surface eroded by liquids but no oceans. Moons of the Outer Solar System: Titan’s Atmosphere Moons of the Outer Solar System: Saturn’s Titan Moons of the Outer Solar System: Movie of Huygen’s Decent Show the movie outside the ppt if there is time: http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/multimedia Moons of the Outer Solar System: “The Dunes of Titan” Moons of the Outer Solar System: Neptune’s Triton Neptune’s Triton Extremely cold (< 40K) objects made from volatile materials produce icy volcanism. Huge geysers of nitrogen! Pluto and the Kuiper Belt Objects may look and act similarly. Comparative Planetology: Lessons Learned Surfaces of Planets (or Moons) Location, location, location… Size matters (for retaining an atmosphere). The star matters. Overall, However There is an incredible diversity of worlds!!! Warm pockets or oceans of liquids plus organics may exist in a variety of environments outside the classic Habitable Zone. Even on Earth not all life requires starlight for an energy source. Sources of potentially life-giving energy may exist even in the cold outer reaches of our own and other planetary systems. Beyond the Solar System Do We Live in a “Life-Friendly” Universe? Water and Carbon Chemistry are Everywhere! • Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen – 1st, 3rd, 4th, and 6th most abundant elements • Organic Chemistry is found in – Interstellar gas clouds, comets, meteorites, outer planet and moon atmospheres Physical Laws • Copasetic Time Scales – Expansion rate of the Universe & stellar lifetimes compatible with time to evolve complex life • Abundant Materials – Even small changes in physical constants would cause little hydrogen or carbon to exist • Huge Diversity of Environments