* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The endocrine system
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
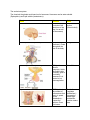
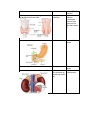
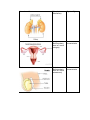
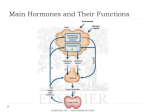
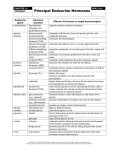
The endocrine system: The chemical the glands would send out is hormones. Hormones can be water soluble (Epinephrine) and Lipid soluble (testosterone). Gland Hormone Action Pineal Melatonin (allows our brain to tell what time of the day it is as well as the season) Circardian rhythm (internal clock) Anterior (To the front) Pituitary GH (Growth Hormone)- Floats throughout the rest of the body. Cell growth Posterior (To the back) Pituitary ADH (antidiuretic hormone)- Holds the fluids inside our body, goes to our kidney because it is in control of our osmoregulation. Water Balance Thyroid T3/T4 (relate to the number of iodine atoms that are in it, speed up the metabolism) Lowers the calcium. Goes into bones. Metabolism (regulates metabolism) Hyperactive means high metabolism, inactive means slow. Calcitonin Lowers Blood Calcium Raises Blood Calcium If the blood calcium level goes too low and then raises it. Parathyroid+ Thyroid work together to keep the blood calcium level right. PTH (parathyroid hormone) Pancreas Insulin Lowers blood sugar Glucagon Raises blood sugar Glucocorticoids (Do the same as what drugs would do) Antiinflammatory Adrenal cortex Adrenal medulla Epinephrine (Adrenaline) Fight or flight Ovary Estrogen (Before puberty there isn’t much estrogen) Female sex characteristics Testes Testosterone (Before puberty there isn’t much testosterone) Male sex characteristics