* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
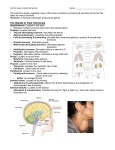
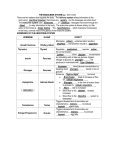
The Endocrine System Are your hormones runnin’ wild? Glands Exocrine - Secrete into ducts or onto a free surface - sweat, sebaceous, mucous, digestive Endocrine - secrete into cellular space then into blood - hormones Hormones Hormones are chemical messages Regulate the chemical composition and volume of the internal environment What are some examples of regulation of chemical composition of blood. How about volume Glucose, Water Regulated by insulin and a hormone called ADH (antidiuretic hormone) Hormones Help regulate organic metabolism and energy balance Thyroid gland Help body cope with emergency environmental demands - infection, trauma, emotional stress, dehydration, starvation, hemorrhage, and temperature extremes. Adrenaline (epinephrine) Fight or flight syndrome Sympathetic Hormone producing cells are sent information from sensing and signaling systems - permit regulation of amount and duration of hormone release Examples: Blood glucose, Na+, K+, Ca++, O2 Target cells - cells that are affected by specific hormones Receptors - most cells have receptors that bind to one or more hormones There are about 50 different hormones - cells only respond to specific hormones Once a hormone binds to a cell’s receptors, there is a set of reactions within the target cell to produce the desired effects Feedback Systems “Circular situation in which information about the status of something is continually reported (fed back) to a central control region.” Like a thermostat. Negative feedback system - reverses the direction of the initial condition Negative - response is opposite to the stimulus Hypothalamus Thalamus Pituitary Gland Thyroid Parathyroids Pancreas Thymus Adrenals Ovaries Testes Posterior Pituitary ADH (Anti-Diuretic Hormone) Controls Kidneys Oxytocin Stimulates mammary glands to produce milk Stimulates uterine contractions Anterior Pituitary HGH (Human Growth Hormone) Stimulates cell division, protein synthesis, bone growth Prolactin Milk production MSH (melanocyte-stimulating hormone) Skin color in lower verts, unknown in humans Anterior Pituitary TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) Stimulates thyroid ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Stimulates adrenal cortex Gonadotropic Hormones Gamete and sex hormones Thyroid Thyroxin Increases metabolic rate regulates growth and development Calcitonin Lowers blood Calcium levels Parathyroid PTH Raises blood Calcium levels Adrenal Medulla Epinepherine and Norepinephrine Adrenaline Cardiac and other muscles Adrenal Cortex Glucocorticoids Raise blood glucose level, stimulates breakdown of protein Mineralcorticoids Stimulates kidneys to reabsorb sodium and excrete potassium Sex Hormones puberty Pancreas Insulin Lowers blood glucose Promotes formation of glycogen, proteins, fats Glucagon Raises blood glucose Promotes breakdown of glycogen, proteins, fats Gonads Testes Androgens (Testosterone) Stimulates spermatogenesis Develop and maintain male characteristics Ovaries Estrogen and Progesterone Growth of uterine lining Develop and maintain female characteristics Thymus Tymosins Stimulates maturation of T Lymphocytes Disorders of Endocrine Glands Diabetes Mellitus: Insulin Lack and Insensitive Cells Symptoms: Sugar in urine Frequent urination Abnormal thirst Rapid Weight Loss Itching Visual Disturbances Skin disorders - boils, infections Diabetes Sugar is not being metabolized Liver fails to store glucose as glycogen Cells fail to utilize glucose efficiently Body turns to breakdown of protein and fats