* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio 152 – Summer 2006 Week 2 OBJECTIVES: Lecture 5 1. What is
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
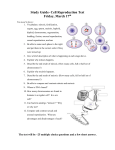
Bio 152 – Summer 2006 Week 2 OBJECTIVES: Lecture 5 1. What is meant by the term evolution in action? 2. How did M. tuberculosis become resistant to antibiotics? 3. How was drought a selective agent in medium ground finches of the Galapagos? 4. Can pollinators cause natural selection on flower characteristics? Lecture 6 1. Explain what is meant by the term “selection acts on individuals but evolutionary change occurs in populations”. 2. Is evolution progressive? 3. Differentiate between the “progressive ladder of life” and the “tree of life”. 4. Briefly summarize the constraints on evolution. Lecture 7 1. Describe reproduction in prokaryotes. 2. Briefly summarize the mitosis cycle. 3. What is the purpose of mitosis? 4. Briefly summarize the meiosis cycle. 5. What are the unique features of meiosis? 6. When do mitosis and meiosis occur during the life of an organism? 7. Explain the term nondisjunction. Lecture 8 1. Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction. 2. What are the advantages of asexual reproduction? 3. What costs are associated with asexual reproduction? 4. How does meiosis lead to genetic variation? 5. What are the advantages of sexual reproduction?