* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Structure
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
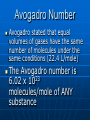
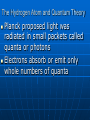
Atomic Structure-1 Democritus is credited with proposing the first atomic theory Proust stated that the elements in substances always combine in definite proportions by mass Dalton’s Atomic Theory Dalton’s atomic theory: 1. All matter is composed of atoms; 2. All atoms of the same element are identical; 3. Atoms of different elements are not alike; 4. Atoms unite in simple ratios to form compounds. Atomic Structure-2 Atoms of the same element may differ in mass. Average mass is used instead of whole-numbered mass The law of multiple proportions states that the ratio of masses of one element that combine with a constant amount of another element can be expressed in small whole numbers Avogadro Number Avogadro stated that equal volumes of gases have the same number of molecules under the same conditions (22.4 L/mole) The Avogadro number is 6.02 x 1023 molecules/mole of ANY substance Isotopes and Atomic Number Isotopes contain the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons The atomic number (Z) of an element equals to the number of protons in the nucleus The mass number (A) of an atom is the total number of its nucleons Number of neutrons = A - Z Nuclear Structure Protons and neutrons are held together by a nuclear force The particles composing atoms are called subatomic particles A mirror-image antiparticle exists for every particle Leptons—elementary particles: electrons, neutrino, muon, tau Hadrons—made of quarks: baryons—3 different quarks; neutrons and protons; mesons— quark+antiquark Quarks are held together by exchanging gluons. Nucleons are held together by exchanging pions Radiation Three forms of radiation: alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays The Rutherford-Bohr model of the atom is called the planetary atomic model because it describes electrons in “orbit” around the nucleus The EM Spectrum and Spectroscopy Heat, AM FM radio, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, microwaves, X rays, gamma rays are all forms of electromagnetic energy The energy emitted by gaseous atoms can be spread into an emission spectrum The lines missing in an absorption spectrum will be the same as the bright lines in the emission spectrum Both ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy must be used to describe the electronic structure of a substance The Hydrogen Atom and Quantum Theory Planck proposed light was radiated in small packets called quanta or photons Electrons absorb or emit only whole numbers of quanta Quantum Theory When an electron absorbs a quantum of energy it moves to a higher energy level. When it releases a quantum of energy it drops back to a lower energy level The smallest orbit an electron can occupy is its ground state Modern atomic theory describes electron cloud around the nucleus, and not planets round the nucleus Nearly all the mass of an atom is in the nucleus Chemists work with moles of atoms rather than individual atoms Atomic Mass 1 atomic mass unit, u, is defined as 1/12 the mass of a C-12 nuclide The average atomic mass of an element is used in calculations A mass spectrometer measures the masses and amounts of the nuclides of elements To account for the varying masses of isotopes, a weighted average is used to find the average atomic mass of each element