* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cognitive therapy
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism therapies wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Substance dependence wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
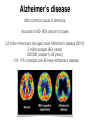
Introduction to Psychology II: Developmental and Social Psychology Psychological therapies Dr. Rachel Wu Fall 2016 December 1, 2016 Research credits? Lecture outline • Office hours 2-3pm • Review of types of disorders Risk/protective factors Different therapeutic approaches • Psychodynamic/Psychoanalytic therapies • Behavior therapy • Cognitive therapy • Biomedical therapy Resilience Questions about the exam • • • • (adapted from Myers, 2010) Review of types of disorders American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) Definition: Disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotion regulation, or behavior that reflects a dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes underlying mental functioning. Anxiety disorders: Phobias, social anxiety, panic disorder, OCD, PTSD Mood disorders: bipolar, depression Schizophrenia Personality, Dissociative, and Eating Disorders Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) 11% of American 4- to 17-year-olds receive this diagnosis after displaying its key symptoms (extreme inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity) Symptoms can be treated with medication and other therapies. Comorbidity Is high energy a psychiatric disorder? Costs of longterm drug use in treating ADHD? Psychological Disorder Percentage Generalized anxiety disorder 3.1 Social anxiety disorder 6.8 Phobia of specific object or situation 8.7 Depressive disorders or bipolar disorder 9.5 Obsessive - compulsive disorder (OCD) 1 Schizophrenia 1.1 Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) 3.5 Attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) 4.1 Dementia Group of symptoms seen in various diseases (including Alzheimer’s disease) characterized by impairment of at least two brain functions, such as memory loss and judgment (Mayo Clinic, 2015) Alzheimer’s disease Most common cause of dementia Accounts for 60- 80% percent of cases 5.2 million Americans (all ages) have Alzheimer's disease (2014): 5 million people (65+ years) 200,000 people (< 65 years) ~ 1/9, 11% of people over 65 have Alzheimer's disease (Clicker) question How many of you know someone with a psychological/psychiatric disorder, who has a ____ case: a) b) c) d) mild moderate extreme Don’t know anyone with a disorder Risk factors Risk Factors • Academic failure • Birth complications • Caring for those who are chronically ill or who have a neurocognitive disorder • Child abuse and neglect • Chronic insomnia • Chronic pain • Family disorganization or conflict • Low birth weight • Low socioeconomic status • Medical illness • Neurochemical imbalance Parental mental illness • Parental substance abuse • Personal loss and bereavement • Poor work skills and habits • Reading disabilities • Sensory disabilities • Social incompetence • Stressful life events • Substance abuse • Trauma experiences • Protective factors Protective Factors • Aerobic exercise • Community offering empowerment, opportunity, and security • Economic independence • Effective parenting • Feelings of mastery and control • Feelings of security • Literacy • Positive attachment and early bonding • Positive parent-child relationships • Problem-solving skills • Resilient coping with stress and adversity • Self-esteem • Social and work skills • Social support from family and friends Therapeutic approaches Different therapeutic approaches Psychotherapy Involves psychological techniques, e.g., trained therapist talking through problems with client to overcome difficulties and/or achieve personal growth Cognitive therapy Involves training cognitive abilities, especially with cognitive disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease Biomedical therapy Involves treatment with medical procedures, e.g., medications prescribed by doctors Psychodynamic therapy Goals: To help people understand current symptoms by exploring and gaining perspectives on thoughts, feelings, and behaviors based on drives and motivation Techniques: Client-centered face-to-face meetings; exploration of past relationship troubles to understand origins of current difficulties Psychoanalysis Goals: To bring patients’ repressed feelings into conscious awareness; to help patients release energy devoted to id-ego-superego conflicts so they may achieve healthier, less anxious lives. Techniques: Historical reconstruction, such as through hypnosis, free association, transference, and interpretation of dreams Differences between psychoanalytic and psychodynamic approaches Psychodynamic therapy Influenced by traditional psychoanalysis but differs from it in important ways Differences • Lack of belief in id, ego, and superego • Briefer, less expensive, and more focused on helping the client find relief from current symptoms Similarity • Helps clients understand how past relationships create themes that may be acted out in present relationships Interpersonal therapy • Brief 12- to 16-session form of psychodynamic therapy that has been effective in treating depression Behavior therapy Classical conditioning techniques Counterconditioning: Uses classical conditioning to evoke new responses to stimuli that are triggering unwanted behaviors Exposure therapies: Treat anxieties by exposing people (via imagination or actual situations) to the things they fear and avoid (e.g., flooding) Systematic desensitization: Associates a pleasant, relaxed state with gradually increasing, anxiety-triggering stimuli Behavior therapy Virtual reality therapy Treats anxiety by creative electronic simulations in which people can safely face their greatest fears, such as airplane flying, spiders, or public speaking Behavior therapy Aversion therapy Training negative responses to unwanted behavior Behavior therapy Operant conditioning therapy: behaviors strongly influenced by their consequences Behavior modification: Desired behavior reinforced; undesired behavior not reinforced, sometimes punished Token economy: People earn a token for exhibiting a desired behavior and can later exchange the tokens for privileges or treats Behavior therapy • What happens when the rewards end? • Who decides what behavior is appropriate? • What is the most humane treatment? Group/family therapy • • • • • Save time and money Exploration of social behaviors and development of social skills Share problems with others in similar situations Feedback from peers and therapist Family as a system Cognitive therapy Teaches people new, more adaptive ways of thinking; based on the assumption that thoughts intervene between events and our emotional reactions (e.g., reduce rumination) Cognitive-behavioral therapy Integrative therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior) Aims to alter the way they act AND think Helps people learn to make more realistic appraisals Cognitive interventions Physical exercise • • • • • Insomnia Aging Side effects Mood disorders Recovery time and many more! Biomedical therapy Psychopharmacology Drug effects on mind and behavior Clinical trials involve placebo and double-blind techniques Relatively “fast” effects, but typically includes side effects and builds dependency Common drug treatments • Antipsychotic • Anti-anxiety • Antidepressant • Mood-stabilizing • Attention deficit Resilience Preventing psych disorders by changing environment and building “reserve” and personal strength Can be seen in New Yorkers after 9/11, spinal cord injury patients, Holocaust survivors, and many others “Returning to baseline” Mindfulness • Awareness of the current situation and your current conscious experience • Opposite of ruminating, worrying, and being distracted • The more mindful a person is, the happier they tend to be • Easy to increase, somewhat effective • Often linked with meditation Optimism • Expecting positive (vs. negative) outcomes • The more optimistic a person is, the happier they tend to be • Very effective • Somewhat difficult to increase Self-esteem • Evaluation of your worth • The higher one’s self- esteem, the happier they tend to be • Somewhat effective • Difficult to increase Pros and cons of different approaches Take home messages? Questions about the exam?