* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch08 - ISpatula
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
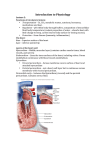
Chapter The Heart CHAPTER CONTENTS Introduction Word Elements Specific to the Heart The Location of the Heart The Structure of the Heart Blood Flow through the Heart Heart Disorders and Procedures Common Abbreviations Exercises Pre-Quiz Checklist Chapter Quiz 90 8 CHAPTER 8 THE HEART 91 he heart, which is part of the cardiovascular system, pumps blood to every cell in the body. That job is critical, because without the oxygen and nutrients that the blood delivers, body cells quickly die. This chapter introduces terms relating to the structure, function, and disorders of the heart, along with those that name some of the procedures and treatments that keep it working when it malfunctions. Chapter 9 deals with the rest of the cardiovascular system, i.e., the blood and blood vessels. T WORD ELEMENTS SPECIFIC TO THE HEART The word elements in Table 8-1 are often found in terms related to the heart. You will recognize them in many of the terms you will learn in this chapter. TABLE 8-1 COMMON WORD ELEMENTS RELATED TO THE HEART Word or Word Element aort/o atri/o bradycardi/o corona Type root root prefix root from the Latin word for “crown” echo English word from Greek mythology; Echo was a nymph who helped Zeus deceive his wife by distracting her with chatter electr/o endo-gram my/o peri-stenosis tachyvalv/o, valvul/o ventricul/o root prefix suffix root prefix suffix prefix root root Refers to aorta atrium slow heart the adjective form “coronary” is sometimes used to describe anatomic structures, such as nerves, ligaments, and blood vessels, especially the arteries of the heart a reverberation of sound; not properly called a root (and therefore written without the slash before its final letter), echo has been adopted for use in forming some medical terms, such as echogram and echocardiography) electrical Inner, inside written record muscle Around, surrounding a narrowing fast valve ventricle THE LOCATION OF THE HEART The heart is encased in and separated from the walls of the pericardial cavity by three linings: the epicardium, which forms the outer part of the heart; the pericardial 92 PART 2 BODY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Pericardium Pericardial sac Pericardial cavity FIGURE 8-1 The location of the heart. sac; and the pericardium. The heart fits tightly inside the pericardial cavity, a subcavity of the thoracic cavity. The pericardial cavity is lined with a serous (thin) membrane called the pericardium, and the heart is within yet a second lining called the pericardial sac. This sac contains about half an ounce of fluid, which lies between it and the heart’s outer lining (Figure 8-1). THE STRUCTURE OF THE HEART The membrane forming the outer lining of the heart is called the epicardium. Immediately beneath the epicardium is the myocardium, comprising the muscles, blood vessels, and nerve tissue that make up the bulk of the heart. The heart’s inner surface is called the endocardium. The heart has four chambers: the right atrium, the right ventricle, the left atrium, and the left ventricle. They are separated by septa (singular, septum). The names and locations of the septa are easy to remember because they include the names of the parts they separate. They are the interventricular septum (separates the two ventricles) and the interatrial septum (separates the two atria). Also, each atrium is divided from each ventricle by an atrioventricular septum, which contains various valves. The right atrioventricular valve, also sometimes called the tricuspid valve, leads from the right atrium into the right ventricle. The pulmonary semilunar valve connects the right ventricle to the lungs, which also connect to the left ventricle through the left atrium by way of the left atrioventricular valve, also sometimes called the bicuspid or mitral valve. The aortic semilunar valve leads out of the left ventricle (Figure 8-2). CHAPTER 8 THE HEART 93 Aortic arch Atrioventricular septum (bundle) Pulmonary valve Interatrial septum Left atrium Left AV (mitral) valve Right atrium Left ventricle Right AV (tricuspid) valve Right ventricle Interventricular septum FIGURE 8-2 The structures of the heart. BLOOD FLOW THROUGH THE HEART The best way to understand how blood flows through the heart is to keep the heart’s job in mind. When blood comes back to the heart after having delivered oxygen and other nutrients to the body’s cells, it needs to be replenished before going out again. It re-enters the heart at the right atrium. From there it moves into the right ventricle, from which it is pumped into the lungs. After being recharged with oxygen, the blood moves back into the heart through the left atrium and into the left ventricle, from which it is pumped out for yet another trip through the body. HEART DISORDERS AND PROCEDURES The heart can be compared to a mechanical device that relies on electricity for its operation. Electrical impulses emitted within the heart stimulate the heart to pump. When the electrical system malfunctions, the heart will beat too fast, too slow, at an irregular pace, or not at all, depending on the nature of the malfunction. Arrhythmia is most often defined as an irregular heartbeat at any speed. When the heart pumps too fast, defined as any rate greater than 100 beats per minute, the condition is called tachycardia. The Greek word for “fast,” tachys, gives us the prefix tachy- and also the common English word tachometer. A heart that is pumping too slow, which is defined as any rate less than 60 beats per minute, exhibits a condition known as bradycardia. The prefix brady- is also of Greek origin, coming 94 PART 2 BODY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY from the word for “slow”: bradys. Tachycardia is also called tachyarrhythmia, and bradycardia is called bradyarrhythmia. Disorders of the heart are diagnosed and treated by cardiologists, who work in the field of cardiology. Table 8-2 lists common abnormal conditions related to the heart, along with some of the procedures used to diagnose and correct them. TABLE 8-2 COMMON DISORDERS AND PROCEDURES ASSOCIATED WITH THE HEART Term atriomegaly atrioseptoplasty bradycardia cardiac arrest cardiodynia cardiogram (This word and the next are often called “electrocardiogram” and “electrocardiograph,” respectively; the abbreviation for both can be either EKG or ECG.) cardiograph (also “myocardiograph,” as well as “electrocardiograph,” as noted above) cardiomalacia cardiomegaly cardiomyopathy cardiomyoplasty cardiopathy cardiorrhaphy cardiorrhexis cardiotomy carditis endocarditis myocardial infarction (often abbreviated MI) myocarditis pericardiorrhaphy Definition enlargement of an atrium surgical repair of an atrial septum also called bradyarrhythmia; abnormally slow heartbeat abbreviated CA, this condition, as its name suggests, describes the sudden cessation of heart activity heart pain a graphic trace of heart functions a machine to electrically measure heart functions softening of the heart enlargement of the heart disease of the heart muscle (myocardium) a surgical procedure that involves engaging the latissimus dorsi muscle to stimulate the heart; please also note that the term “cardioplasty” is a surgical procedure done on the stomach, NOT the heart. any heart disease suturing of the wall of the heart muscle rupture in the wall of the heart muscle incision into the heart OR incision into the cardia of the stomach inflammation of the heart inflammation of the endocardium heart attack; patients suspected of having had an MI are given a blood test to measure the level of troponin in the blood (troponin is a protein that is released when an MI occurs) inflammation of the heart muscle suturing of the pericardium CHAPTER 8 pericardiotomy THE HEART 95 incision into the pericardium TABLE 8-2 COMMON DISORDERS AND PROCEDURES ASSOCIATED WITH THE HEART (continued) Term Definition incision into the pericardium inflammation of the pericardium also called tachyarrhythmia; abnormally rapid heartbeat surgical repair of a heart valve surgical removal of a blocked heart valve (stenosis of a heart valve) by cutting into it inflammation of a heart valve surgical repair of a heart ventricle examination of a heart ventricle with an endoscope pericardiotomy pericarditis tachycardia valvoplasty; also valvuloplasty valvotomy; also valvulotomy valvulitis ventriculoplasty ventriculoscopy DECIPHERING MEDICAL DOCUMENTS. Read the following excerpt from a cardiac catheterization report and answer the questions: Left ventriculography shows the left ventricle is normal in configuration, dimensions, and segmental wall motion with ejection fraction computed at 58% by area-length method. There is no evidence of mitral regurgitation. Coronary arteriography of left anterior descending artery shows 70% focal stenosis immediately after the first septal perforator branch. 1. What word root and suffix are contained in the term ventriculography? What does the term mean? 2. What does the adjective coronary mean? 3. What does the word stenosis mean? A STUDY TABLE 8-1 THE HEART Term and Pronunciation Analysis Meaning STRUCTURE & FUNCTION aortic semilunar valve (ay-ORT-ik sem-ih-LOON-uhr) atria (singular: atrium) (AY-tree-ah; AY-tree-uhm) endocardium (en-doh-KARdee-uhm) epicardium (ep-ih-KAR-dee-uhm) left atrioventricular valve (ay-treeoh ven-TRIK-yu-lahr) also known as the bicuspid or mitral valve (by-KUSS-pihd; MY-trahl) aortic (adjectival form of aorta, the large artery leading away from the heart); semi- (“half ”); lunar (English adjective from the Latin word luna, meaning “moon”) from the Latin word atrium (“hall”) endo- (“inside”); cardium (“heart”) epi- (“outside”); cardium (“heart”) atri/o (“atrium”); ventricul (“ventricle”); -ar (adjectival suffix); valve connects the left ventricle to the aorta two of the four heart chambers, composed of the right atrium and left atrium the inner surface of the heart the outer lining of the heart connects the left atrium to the left ventricle 96 PART 2 BODY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY A STUDY TABLE 8-1 THE HEART (co nt inued) Term and Pronunciation myocardium (my-oh-KARdee-uhm) pericardial (pehr-ih-KAR-dee-ahl) pericardial cavity (pehr-ih-KARdee-ahl) pericardial sac (pehr-ihKAR-dee-ahl) Analysis my/o (“muscle”); cardium (“heart”) peri- (“around”); cardial (adjective for “heart”) peri- (“around”); cardial (adjective for “heart”); cavity peri- (“around”); cardial (adjective for “heart”); sac (from the Latin word saccus, meaning “bag”) peri- (“around”); cardium (“heart”) pulmonary (adjective denoting the lungs); semi- (“half ”); lunar (adjective for “moon”) atri/o (“atrium”); ventricul/o (“ventricle”); -ar (adjectival suffix) pericardium (pehr-ihKAR-dee-uhm) pulmonary semilunar valve (PULL-moh-nahr-ee SEMee-LUN-ahr) right atrioventricular valve (ay-treeoh-ven-TRIK-yu-lahr) also known as the tricuspid valve (try-KUSS-pihd) septa (singular septum) (SEPP-tah; SEPP-tuhm) from the Latin saeptum (“partition”) troponin (TROH-poh-nihn) etymology unknown ventricle (VEN-trik-uhl) ventricle (“cavity,” from the Latin word ventruculus, meaning “belly”) Meaning the heart muscle, which includes nerves and blood vessels adjective form of pericardium the subcavity of the thoracic cavity in which the heart is enclosed another lining of the pericardium closest to the heart serous membrane lining the pericardial cavity valve connecting the right ventricle and lungs valve connecting the right atrium to the right ventricle thin wall that separates cavities or masses; in the heart, septa separate the right atrium from the left atrium and the right ventricle from the left ventricle a protein that is released into the bloodstream when a heart attack occurs two of the four heart chambers, composed of the right ventricle and left ventricle COMMON DISORDERS arrythmia (ah-RITH-mee-ah) atriomegaly (AY-tree-ohMEG-ah-lee) bradycardia (bray-dee-KARdee-ah) cardiac arrest (KAR-dee-ak) cardiodynia (kar-dee-ohDIN-ee-ah) cardiomalacia (kar-dee-ohmah-LASH-ee-ah) the prefix a- (“against”); rhythmos (common English word derived from the Greek word rhythmos meaning the same thing); -ia (“condition”) from the Latin atrium (“hall”); -megaly (suffix meaning “enlargement”) brady- (prefix meaning “slow”); -cardia (“heart”) card/i/o (“heart”); -ac (adjectival suffix); arrest (English word meaning “stopped”) cardi/o (“heart”); -dynia (“pain”) cardi/o (“heart”); -malacia (“softening”) abnormal rhythm; irregular heartbeat enlargement of an atrium abnormally slow heartbeat cessation of heart activity heart pain softening of the heart CHAPTER 8 A STUDY TABLE 8-1 THE HEART THE HEART (co nt inued) Term and Pronunciation cardiomegaly (kar-dee-ohMEG-ah-lee) cardiomyopathy (kar-dee-oh-myAWP-uh-thee) cardiopathy (kar-deeAWP-uh-thee) cardiorrhexis (kar-deeoh-REX-ihs) carditis (kar-DY-tiss) endocarditis (en-doh-kar-DY-tiss) myocardial infarction (often abbreviated MI) (my-oh-KAR-deeahl in-FARK-shun) (Note: MI is an abbreviation, not an acronym.) myocarditis (my-oh-kar-DY-tiss) pericarditis (pehr-ih-kar-DY-tiss) tachycardia (tak-ih-KAR-dee-ah) valvulitis (valv-yu-LY-tiss) Analysis cardi/o (“heart”); -megaly (“enlargement”) cardi/o (“heart”); my/o (“muscle”); -pathy (“disease”) cardi/o (“heart”); -pathy (“disease”) cardi/o (“heart”); -rrhexis (“rupture”) cardi/o (“heart”); -itis (“inflammation”) endo- (“inside”); cardi/o (“heart”); -itis (“inflammation”) my/o (“muscle”); cardi/o (“heart”); -al (adjective form for heart) Meaning enlargement of the heart disease of the heart muscle (myocardium) any heart disease rupture in the wall of the heart inflammation of the heart inflammation of the endocardium heart attack my/o (“muscle”); cardi/o (“heart”); -itis (“inflammation”) peri- (“around”); cardi/o (“heart”); -itis (“inflammation”) tachy- (“rapid”); cardi/o (“heart”); -ia (“condition”) valvul/o (“valve”); -itis (“inflammation”) inflammation of the heart muscle electro- (“electric”); cardi/o (“heart”); -gram, -graph (“writing”) a graphic trace of heart functions my/o (“muscle”); cardi/o (“heart”);-graph (“writing”) a machine to electrically measure heart functions ventricul/o (“ventricle”); -scopy (“viewing”) looking at a heart ventricle with an endoscope cardi/o (“heart”); -logist (“one who studies”) cardi/o (“heart”); -logy (“study of ”) heart specialist inflammation of the pericardium abnormally rapid heartbeat inflammation of a heart valve DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT cardiogram (KAR-dee-oh-gram) (Note: Associated terms are are “electrocardiogram” [ee LEK-troh-KAR-dee-oh-gram] and “electrocardiograph” [ee-LEK-troh-KAR-dee-oh-graf]; the abbreviation for any of them can be either EKG or ECG) myocardiograph (MY-oh-kardee-oh-graf), cardiograph (KAR-dee-oh-graf) ventriculoscopy (ven-trik-yuLAWS-koh-pee) PRACTICE & PRACTITIONERS cardiologist (kar-dee-AWL-oh-jist) cardiology (kar-dee-AWL-oh-jee) medical specialty dealing with the heart 97 98 PART 2 BODY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY A STUDY TABLE 8-1 THE HEART (co nt inued) Term and Pronunciation Analysis Meaning surgical repair of an atrial septum cardiomyoplasty (kar-dee-ohMY-oh-plass-tee) from the Latin words atrium (“hall”) and saeptum (“partition”); -plasty (suffix meaning “surgical repair”) cardi/o (“heart”); my/o (“muscle”); -plasty (“surgical repair”) cardiorrhaphy (kar-dee-ohRAF-fee) cardiotomy (kar-dee-AW-tuhmee) cardi/o (“heart”); -rrhaphy (“suturing”) cardi/o (“heart”); -tomy (“cutting”) pericardiorrhaphy (pehr-ih-KARdee-oh-raff-ee) peri- (“around”); cardi/o (“heart”); -rrhaphy (suffix meaning “suturing”) peri- (“around”); cardi/o (“heart”); -tomy (“cutting”) valv/o or valvul/o (“valve”); -plasty (“surgical repair”) SURGICAL PROCEDURES atrioseptoplasty (AY-tree-oSEP-toh-plass-tee) pericardiotomy (PEHR-ih-cardee-AW-toh-mee) valvoplasty (VALV-oh-plass-tee); also valvuloplasty (VALV-yu-lohplass-tee) valvotomy (valv-AW-toh-mee); also valvulotomy (valv-yuLAWT-oh-mee) ventriculoplasty (ven-TRIK-yuloh-plass-tee) ENHANCEMENT TERMS atrial (AY-tree-uhl) cardiac (KAR-dee-ack) cardiogenic (kar-dee-oh-JEN-ik) ventricular (ven-TRIK-yu-lahr) valv/o or valvul/o (“valve”); -tomy (“cutting”) ventricul/o (“ventricle”); -plasty (“surgical repair”) from the Latin word atrium (“hall”) adjectival form of cardium (“heart”) cardi/o (“heart”); -genic (“origin”) ventricul/o (“ventricle”); -ar (adjectival suffix) surgical procedure that involves engaging the latissimus dorsi muscle to stimulate the heart (Note: The term “cardioplasty” [without the “my” between cardio and plasty] is a surgical procedure done on the stomach, NOT the heart.) suturing of the wall of the heart incision into the HEART or incision into the cardia of the STOMACH suturing of the pericardium incision into the pericardium surgical repair of a heart valve surgical removal of a blocked heart valve (stenosis of a heart valve) by cutting into it surgical repair of a heart ventricle adjectival form of atrium relating to the heart adjective describing something originating in the heart adjectival form of ventricle (Note: The brain also contains ventricles.) CHAPTER 8 THE HEART 99 ABBREVIATION TABLE 8-1 COMMON ABBREVIATIONS The Heart Abbreviation ACV CA CAD CCU CHD CIPS CRFS CSU CT CVICU CVIS EKG or ECG MI c Meaning acute cardiovascular [disease] cardiac arrest coronary artery disease cardiovascular care unit cardiovascular heart disease cardiovascular imaging procedure cardiovascular risk factors cardiovascular surgery unit cardiovascular technologist cardiovascular intensive care unit cardiovascular imaging systems electrocardiogram; electrocardiograph; electrocardiography; cardiogram myocardial infarction Exercises Exercise 8-1 Completing Sentences Fill in the missing terms to complete the sentences. 1. The heart is enclosed in three linings: the ____________, the ____________, and the ____________. 2. There are four chambers in the heart, called the ____________, the ____________, the ____________, and the ____________. 3. When blood returns to the heart from the body, it enters the heart at the ____________; from there, it moves to the ____________, which pumps it to the lungs to be re-oxygenated. 4. The blood moves back to the heart through the ____________ and into the ____________, which pumps it out to the body. 5. Cessation of heart activity is called cardiac ____________________. 6. __________________ from within the heart stimulate it to pump. 7. When the heart malfunctions and beats too slowly, the phenomenon is called ____________. Conversely, if the heart beats too fast, the condition is called ____________. 8. Tachycardia and bradycardia are occasionally also referred to as ____________ and ____________. However, the word ___________ generally refers to a heart beat that is irregular at any speed. 9. A sufficiently higher-than-normal troponin level is an indicator of ____________. 10. The abbreviation for myocardial infarction is ____________. 100 PART 12 BODY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Exercises Exercise 8-2 Converting Nouns to Adjectives Convert each of the following nouns to its adjective form by using one of the following suffixes: -al, -ar, -ic, -ous, -ated. Noun Adjective 1. septum ____________ 2. ventricle ____________ 3. oxygen ____________ 4. atrium ____________ 5. pericardium ____________ 6. aorta ____________ 7. valve ____________ 8. serum ____________ 9. endocardium ____________ 10. epicardium ____________ 11. membrane ____________ 12. arrhythmia ____________ 13. tachycardia ____________ 14. bradycardia ____________ 15. stenosis ____________ 16. electrocardiography ____________ 17. ventriculoscopy ____________ 18. incision ____________ 19. pericardium ____________ 20. cardium ____________ Exercises Exercise 8-3 True, False, and Correction Read each statement, then indicate whether you think it is true or false. If false, write the correct answer in the “Correction, if False” box at the right. Statement True False Definition 1. The term for inflammation of the pericardium is valvulitis. ___ ___ ____________ 2. Atriomegaly is enlargement of an atrium. ___ ___ ____________ 3. MI is the abbreviation that stands for an abnormally rapid heartbeat. ___ ___ ____________ CHAPTER 8 Statement THE HEART 101 True False 4. Tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat. ___ ___ ____________ 5. Cardiotomy is the surgical repair of an atrial septum. ___ ___ ____________ 6. Softening of the heart is termed cardiomalacia. ___ ___ ____________ 7. A myocardiograph is used to examine a heart ventricle. ___ ___ ____________ 8. Cardiorrhaphy is a surgical repair of a heart valve. ___ ___ ____________ 9. The surgical procedure that involves engaging the latissimus dorsi muscle to stimulate the heart is a pericardiotomy. ___ ___ ____________ ___ ___ ____________ 10. Arrhythmia is the general term for an irregular heartbeat. Definition Exercises Exercise 8-4 Matching Terms with Definitions Place the letter of the definition in the right column in the space next to the matching term in the left column. Term 1. ______ myocardial infarction Definition A. a separation between the two ventricles of the heart 2. ______ aortic semilunar valve B. inflammation of the pericardium (the serous membrane lining the pericardial cavity) 3. ______ intraventricular septum C. the heart muscle, which includes 4. ______ endocardium D. the valve leading from the right 5. ______ left ventricle E. the serous membrane forming 6. ______ cardiologist F. the heart’s inner surface the nerves and blood vessels atrium to the right ventricle the outer lining of the heart 7. ______ myocardium G. a heart specialist 8. ______ epicardium H. heart attack 9. ______ pericarditis J. the heart chamber responsible for pumping oxygenated blood out to the body 102 PART 12 BODY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Term Definition 10. ______ right atrioventricular K. the valve leading out of the (tricuspid) valve left ventricle 11. ______ troponin 12. ______ septum L. enlargement of the heart M. coronary artery disease, which refers to narrowing and/or blockages of the heart muscle 13. ______ cardiomegaly N. a heart rate less than 60 beats per minute 14. ______ tachycardia O. a protein released into the blood- 15. ______ stenosis P. disease of the heart muscle stream when an MI occurs 16. ______ CAD Q. a thin wall that separates cavities or masses 17. ______ atrioseptoplasty R. a heart rate over 100 beats per minute 18. ______ cardiomyopathy S. sudden cessation of heart activity, not necessarily a result of MI 19. ______ bradycardia T. surgical repair of an atrial septum 20. ______ cardiac arrest U. a narrowing and/or blockage Exercises Exercise 8-5 Choosing from Options Choose the term in the right column that correctly answers the question. 1. The names of two of the four heart chambers come from the Latin word for “hall.” What is it? _______________ 2. Epicardium is the word for the outside of the heart. Which part of the word means “outside”? _______________ 3. What part of the term myocardium refers to the muscle in the heart? _______________ 4. Since cardio refers to the heart, what does the rest of the term cardiodynia mean? _______________ 5. Valvulitis indicates that a valve is what? _______________. 6. The word “cardium” is the last part of what term that refers to the inside of the heart? _______________ Choices atrium; aortic; atrial epicard; epi; cardi myocardi; myocard; myo hardening; pain; softness hardened; inflamed; infected endocardium; epicardium; pericardium CHAPTER 8 THE HEART 103 Choices 7. What is the surgical removal of a blockage from a heart valve called? _______________. valvulitis; ventriculoplasty; valvotomy 8. What separates the right atrium from the left atrium and the right ventricle from the left ventricle? atria; septa; arrhythmia 9. What is the name of a valve that connects the atrium to a ventricle? aortic semilunar; atrioventricular; ventricular 10. What is the name given to a graphic trace of heart functions? cardiogram; myocardiograph; ventriculoscopy Exercises Exercise 8-6 Identifying the Structures of the Heart Label the following parts of the heart on Figure 8-3. 8 7 6 1 5 2 3 4 FIGURE 8-3 Selected structures of the heart (Exercise 8-6). aortic arch left atrium mitral valve right AV tricuspid valve intraventricular septum left ventricle right atrium right ventricle 104 PART 2 BODY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Pre-Quiz Checklist _____ Study the word roots specific to the heart (Table 8-1). _____ Using the study table, practice pronouncing the terms learned. _____ Review the definitions and etymologies listed in the study table. _____ Check the exercises with the answers in the Appendix, and consult the study table again to correct your errors. Chapter Quiz Write the answers to the following items in the spaces provided to the right. 1. What is the abbreviation for myocardial infarction? 1. ________________________ 2. Which valve of the heart connects the right ventricle to the lungs? 2. ________________________ 3. What stimulates the heart to pump? 3. ________________________ ________________________ 4. Which is the lining of the pericardium that is closest to the heart? 4. ________________________ 5. What does arrhythmia generally refer to? 5. ________________________ 6. Which atrium receives the blood from the body? 6. ________________________ 7. What is the adjectival form of ventricle? 7. ________________________ 8. What is the function of a valve? 8 9. If someone has been diagnosed with CAD, does this mean that he or she has had an MI? Explain. 9. ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ 10. Which heart ventricle would have to perform the strongest pumping action, and why? 10. ________________________ ________________________ 11. Name a surgical procedure involving removal of a heart valve. 11. ________________________ 12. What is a myocardial infarction, and what area of the heart would be affected by it? 12. ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ 13. If an individual has had an MI (heart attack), does this also mean that he or she has had a cardiac arrest? Explain. 13. ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ 14. Name the medical specialty dealing with the heart. 14. ________________________ 15. What is an electrocardiogram? 15. ________________________ ________________________ 16. What would bradycardia and tachycardia indicate? 16. ________________________ ________________________ ________________________