* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO CP 1) The branch of biology dealing with interactions am
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
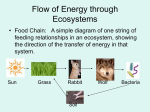
Name _______________________________ Period ____ Date _____________ BIO CP 1) The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called a. economy. b. modeling. c. recycling. d. ecology. 2) Which of the following descriptions about the organization of an ecosystem is correct? a. Communities make up species, which make up populations. b. Populations make up species, which make up communities. c. Species make up communities, which make up populations. d. Species make up populations, which make up communities. 3) The simplest grouping of more than one kind of organism in the biosphere is a. a population. b. a community. c. an ecosystem. d. a species. 4) The lowest level of environmental complexity that includes living and nonliving factors is the a. biome. b. community. c. ecosystem. d. biosphere. 5) Plants are a. primary producers. b. primary consumers. c. herbivores. d. omnivores. 6) How do most primary producers make their own food? a. by using light energy to make carbohydrates b. by using chemical energy to make carbohydrates c. by changing water into carbon dioxide d. by breaking down remains to make carbon dioxide 7) Which of the following organisms does NOT require sunlight to live? a. chemosynthetic bacteria b. algae c. trees d. photosynthetic bacteria Figure 3–1 8) The algae at the beginning of the food chain in Figure 3–1 are a. primary consumers. b. decomposers. c. primary producers. d. heterotrophs. 9) Based on Figure 3-1 which of the following organisms is a tertiary consumer? a. zooplankton b. small fishes c. shark d. squid 10) In which way are plants in a sunny mountain meadow and sulfur bacteria in a deep-sea volcanic vent alike? a. They both use photosynthesis to make their own food. b. They both produce carbohydrates and oxygen. c. They both use chemosynthesis to produce their own food. d. They both produce carbon and hydrogen. 11) All the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a food a. interaction. b. chain. c. network. d. web. 12) The total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level is called the a. organic mass. b. trophic mass. c. energy mass. d. biomass. 13) What is an ecological model of the relationships that form a network of complex feeding interactions among organisms in a community from producers to decomposers? a. food web b. ecosystem c. food chain d. population 14) What animals eat both producers and consumers? a. herbivores b. omnivores c. chemotrophs d. autotrophs 15) What is the term for each step in the transfer of energy and matter within a food web? a. energy path b. food chain c. trophic level d. food pyramid 16) Only 10 percent of the energy stored in an organism can be passed on to the next trophic level. Of the remaining energy, some is used for the organism’s life processes, and the rest is a. used in reproduction. b. stored as body tissue. c. stored as fat. d. eliminated as heat. 17) A word that means the same thing as consumer is a. producer. b. autotroph. c. heterotroph. d. carbohydrate. 18) Animals that get energy by eating the carcasses of other animals that have been killed by predators or have died of natural causes are called a. scavengers. b. omnivores. c. heterotrophs. d. detritivores. 19) Each of the following is an abiotic factor in the environment EXCEPT a. plant life. b. soil type. c. rainfall. d. temperature. 20) What is at the base of all ecological pyramids? a. consumers b. decomposers c. producers d. scavengers Figure 3–4 21) Which of the following is a food chain in the food web shown in Figure 3–4? a. tree, rabbit, hawk, snake b. grass, grasshopper, snake, hawk c. grass, caterpillar, robin, hawk d. tree, deer, mountain lion, fox 22) The number of different species in the biosphere or in a particular area is called a. biodiversity. b. ecosystem diversity. c. genetic diversity. d. species diversity. 23) What is meant by a “natural library” of genetic information in reference to biodiversity? a. The biodiversity of plants and animals is interesting to read about. b. All living organisms contain genetic information that humans can research. c. Species provide humans with many useful products to enhance our lives. d. We have much to admire in the many forms of life that surround us. 24) Introduced species can threaten biodiversity because they can a. cause desertification. b. cause biological magnification. c. out compete native species. d. reduce the amount of fertile land. 25) The goals of biodiversity conservation include all of the following EXCEPT a. protecting individual species b. introducing exotic species into new environments. c. preserving habitats and ecosystems. d. making sure local people benefit from conservation efforts. Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 26) An ecologist who is studying a group of ecosystems that have similar climates and are home to similar organisms is studying a community. _________________________ 27) Producers release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere during the process of photosynthesis. _________________________ 28) Only about 10 percent of the energy in a trophic level is available to organisms at the next trophic level. _________________________ 29) Oxygen is important for ecosystems because it is used by plants during photosynthesis. _________________________ 30) Biodiversity is important to humankind because we are part of it and are dependent upon it for our own survival. _________________________ Completion Complete each statement. 31) Autotrophs capture energy from sunlight or ____________________ to produce food. 32) Organisms that break down organic matter and return it to the environment are called ____________________. 33) In a four-level energy pyramid, if the first level contains 5000 calories of energy, the third level will contain approximately ____________________ calories. 34) If you were walking in a forest and identified a group of organisms like red oak, white maple tree, earthworms, squirrels, and deer than you would be looking at a ___________________. 35) If you noticed all the abiotic and biotic factors living and part of one area in New Jersey you would be looking at an __________________________. Short Answer Figure 3–6 36) List three abiotic and biotic objects found in Figure 3-6. Figure 3–8 37) Interpret Visuals In Figure 3–8, how many first-level consumers are there for each producer? 38) Interpret Visuals In Figure 3–8, how many second-level consumers are there for each producer? 39) Interpret Visuals In Figure 3-8, give one connection between the corn, carrots, flowering shrub, and tree. Figure 6–6 Existing Species and Endangered Organisms Table I. How Many Species Are There? Groups of Species Number Plants 250,000 Roundworms more than 15,000 Mollusks 50,000–200,000 Crustaceans 40,000 Spiders, mites 75,000 Insects more than 1,000,000 Vertebrates 60,000 Table II. Organisms Listed as Endangered in the United States Type of Organisms Number of Endangered Species Mammals 63 Birds 78 Reptiles 14 Amphibians 10 Fishes 70 Snails 20 Clams 61 Crustaceans 18 Insects 33 Spiders 12 Flowering plants 565 Conifers 2 Ferns and other plants 24 40) Interpret Tables According to Table I in Figure 6–6, which group has more species diversity: plants or animals? Support your answer with data from the table. 41) Compare and Contrast Which group in Figure 6–6, Table I is the most diverse? 42) Interpret Tables Which group in Figure 6–6, Table II has the most endangered species? 43) Predict After 10 years, if conservation efforts to protect entire ecosystems succeed, how would Table II in Figure 6–6 likely change? 44) Interpret Tables Based on the information found in Table 1 of Figure 6-6, create a three trophic level energy pyramid.