* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Picture Review Name
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
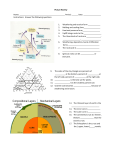
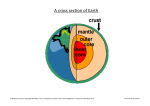
Picture Review Name: ____________________________________________ Period: ______ Date: _________________ Instructions: Answer the following questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Weathering and erosion form ____________ Melting and cooling form________________ Heat and pressure form_________________ Uplift brings rocks to the _________________ The three kinds of rocks are ______________, _________________, ___________________ Weathering, deposition, burial, lithification forms ______________________________. The rock cycle is ______________________ _____________________________________ Igneous rocks can be _____________ or extrusive. 9. The sides of the clay triangle are percents of __________ at the bottom, percent of ___________at the left side, percent of ___________ at the right side. 10. _______________ is the best soil for plants. 11. _______________ has the smallest particle size. 12. Granite rock becomes _________________ because of weathering and erosion. 13. The thinnest layer of earth is the ___________________________ 14. The inner core is ____________ 15. The outer core is ____________ 16. The continental crust is ( thinner, thicker) _____________ than the oceanic crust. 17. The lithosphere is the crust and the ( upper, lower)_____mantle. 18. Describe the position of the earth, moon, sun during Neap tide. ( right angle, straight angle) ______________________________________ 19. Describe the position of the earth, moon, sun during Spring tide. ( right angle, straight angle) ______________________________________ 20. Which has more influence to the tides on Earth? _____ why? ____________________________ 21. How many high tides and low tides do we have everyday? High tide:_______ Low tide:________ The three main types, or classes, of rock are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous and the differences among them have to do with how they are formed. Sedimentary rocks are formed from particles of sand, shells, pebbles, and other fragments of material. Together, all these particles are called sediment. 22. What are the three types of rocks? _________________________________________________________ 23. How are the types of rocks classified or differentiated? _________________________________________________________ 24. How do igneous rocks form? Study the chart on the right. _________________________________________________________ 25. How do sedimentary rocks form? Study the chart on the right. _________________________________________________________ 26. How do metamorphic rocks form? Study the chart on the right. ___________________________________________________________ 27. In a normal fault, the foot wall ( rises, sinks)____________ while the hanging wall ( rises, sinks)____________ 28. In a reverse fault, the foot wall ( rises, sinks)____________ while the hanging wall ( rises, sinks)____________ Draw the direction of Movements of the following using arrows. A. convergent ______ _______ B. divergent ______ _______ C. Transform ______ _______ 29. Pangaea is ________________________________ 30. Lauresia and Gondwanaland are ______________ _________________________________________ 31. What causes continents to move? ____________ ___________________________________________ 32. Continental drift theory is ___________________ ___________________________________________ 33. Plate tectonics is __________________________ ____________________________________________ 34. Describe a divergent boundary. _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 35. What is below the lithosphere? ______________ 36. is ______________current that causes the plates to_____________________. 37. The mid ocean ridge ( divergent boundary) is making the __________________ ocean wider. 38. In convection current, hot ______, cold_______. Subduction zone 39. Where do you find the trench, deepest part of earth, in a convergent boundary?___________________________________ 40. What happens to the subducted plates or plate than sinks? _____________________________________________ 41. What happens to the melted oceanic crust? _____________________________________________ 42. Which is thicker continental crust or oceanic crust? _____________________________________________ 43. Why does the oceanic crust sink (subduction)? _____________________________________________ 44. The Subduction zone recycles (rocks, ocean)__________. 45. What is a convergent boundary? ___________________________________________ 46. Subduction zones along the Pacific Ring of Fire is making the Pacific ocean _________________________________. 47. The Ring of fire is where most ______________ happen. 48. Convection current happens in the ___________________. ridge 49. Sea floor spreading is causing ___________ ocean to become wider. 50. The rising ____________ fills up the gap in the mid ocean ridge. 51. The ( youngest, oldest) _____________ rocks are found near the ridge. 52. The Atlantic ocean is getting wider because of Sea _____________. It is a _________ boundary. 53. The Pacific Ring of Fire is located around the ____________________________________________ 54. Most earthquakes happen in the ______________ Ring of Fire. It is formed by a _____________boundary 55. Which states of the United States are along the Pacific Ring of Fire?______________________________________ 56. Volcanoes in the Pacific Ring of Fire formed from What type of plate boundary? ( convergent, divergent, transform)____________________________________ 57. What are the three types of seismic waves? _____________, ___________________, ___________________ 58. Seismic waves are caused by ( earthquake or tsunami) ____________________________________. 59. Secondary or S-waves are stopped by the earth’s ( mantle or core)____________________. 60. Primary or P-waves (refract or bend or disappears ) ______________________ in the earth’s core. 61. The inner core is (solid or liquid) __________________. 62. What is the shadow zone? ( No seismic wave zone or refracted seismic wave zone) _________________________________________________ 63. Epicenter is directly above the ( focus or density) _____. 64. Scientists learn about the ( layers or mass)___________ of earth by studying seismic wave. Refraction - bends 65. What causes the pencil to become distorted? _______________________________ Ellipse or oval orbit 66. Kepler’s law explains earth’s planetary (motion or density) ______________________. 67. Aphelion is when earth is ( closest or farthest) ____________ from the sun. 68. Perihelion is when earth is ( closest or farthest) ____________ from the sun. 69. Kepler’s 1st law: The shape of planetary orbits are ( circular or ellipse)_____________. 70. Kepler’s 2nd Law states that planets cover the equal amount of ( areas or volumes) __________in equal amount of times. 71. 72. 73. 74. The most abundant gas in the atmosphere is ______________. Oxygen is __________% of our air. The gas that we breathe is _____________________________. Plants use ( oxygen, carbon dioxide) _____________________ to perform photosynthesis and produce food. 75. Carbon dioxide is a ( greenhouse, ozone) ___________ gas. 76. Burning fossil fuel produces ___________________ gas. 77. What are the three types of volcanoes? ___________________________________________________ 78. What is a volcano? ___________________________________________________ 79. What is the biggest type of volcano? ______________________ 80. Where are most volcanoes found? ___________________________________________________ 81. What are the three types of stress? _______________________________________________________ 82. What kind of stress is caused by convergent boundary? ______________________________________________________ 83. What kind of stress is caused by divergent boundary? ______________________________________________________ 84. What kind of stress is caused by transform boundary? ______________________________________________________ 85. Which planet has fastest orbital velocity? __________________ 86. Which planet is nearest to the Sun? ______________________ 87. Which planet has the slowest orbital velocity? ______________ 88. Which planet is farthest from the Sun? Not Pluto! ___________ 89. What is the relationship between orbital velocity and planet’s distance from the Sun ( Kepler’s 2nd law)? ______________________ ________________________________________________________ 90. What is the angle of earth’s axis ( 23.5 degrees tilt or, distance from the sun)? ________________________________________________________________ 91. Season in the USA when northern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun ? ____ 92. If the season in the United States (northern hemisphere) is winter, what is the season in Australia ( southern hemisphere) ______________ 93. What is the season in the United States when the earth is nearest to the Sun or perihelion? ____________ 94. What is Karst topography? ____________________________________ 95. What kind of rock forms Karst topography? ( limestone or granite) ___________________________________ 96. What happens when Karst topography becomes so massive or so big? ( aquifer or sink hole) ____________________ 97. What is precession? __________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 98. What is nutation? ___________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 99. Nutation are caused by the uneven pull of the ( moon’s or star’s) __________________ gravity. 100. Precession and nutation affect the ( seasons or magnetic field) ________ _________________of earth 101. Precession completes one rotation in ______________ years. 102. Precession causes the ( Northern or Western) _______________ star to change in thousands of years. 103. Name the types of fronts a. Number 1 is _____________________causes cumulonimbus clouds, thunderstorm, even tornado. b. Number 2 is _______________causes warm temperature and light rain c. Number 3 is _______________ appears when storm dissipates. d. Number 4 is _______________ causes long days of rain and flood. e. Warm front is when warm air moves ___________ cold air. f. Cold front ( fastest) is when _______air moves towards warm air. 104. What are the names of the layers of the atmosphere ( bottom to top)? 5.Exosphere 105. Give the number and name of the layer in which Earth's weather occurs. 106. Give the number and name of the layer that contains the ozone layer. 4.Thermosphere 107. Within layer 2, what happens to the temperature as you go higher? 108. Give the number and name of the highest layer of the atmosphere. 3.Mesosphere 109. What happens to the air pressure as you go into higher altitude? (increases or decreases) 2.Stratosphere 1.Troposphere . 110. What is the temperature of the dry-bulb thermometer? 111. What is the temperature of the wet-bulb thermometer? 112. Dry temperature reading - Wet temperature reading=_____ Steps in Finding the Relative Humidity Step 1: Dry bulb temperature – Wet bulb temperature= ___________ Step 2: Find this number at the top of the chart and place your finger on it. Step 3: Find the dry-bulb temperature in the first column on the left. Step 4: The relative humidity is where column and row intersect on the chart. 113. At 100% relative humidity (dew point )precipitation happens. What do you need to determine the relative humidity? 114. Based on the temperatures shown, what is the relative humidity of the air? _____________________ Each graduation=2C 24C 20C Tundra-polar Zone A Taiga 0 degree is the equator ( Zone C), 66.5-90 degrees N and S are the polar zones, 23.5- 66.5 degrees N and S are the temperate zones, United States is in the Northern zone. 0- 23.5 degrees is the tropical zone. 115. Which zones are polar zones? temperate - USA ZoneB 116. Which zone is a tropical zone? tropical Zone C tropical 117. Which zones are temperate zones? 118. Which continent lies almost completely within the tropical zone? 119. Which continent lies completely within a polar zone? temperate Antarctic - polar Zone D Zone E 120. Give the names of the zones in which South America lies. Picture Review: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. Sediment Igneous rock Metamorphic rock Surface Igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary ( any order) Sedimentary rock When rocks are recycled or changes from one type of rock to another. Intrusive Sand, clay, silt Loam Clay Sand Crust Solid iron and nickel Liquid iron and nickel/ molten iron nickel Thicker Upper Right angle or 90 degrees Straight angle or 180 degrees Moon, because it is closer to earth 2, 2 Sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks Based on how they formed Melting and crystallization Weathering, erosion, deposition, lithification Heat and pressure, metamorphism Rises, sinks Sinks, rises Supercontinent Two broken continents of Pangaea Convection current in the asthenosphere Continents are drifting apart ( Alfred Wegener ) What explains the continental drift theory. Plates move because of the convection current in the mantle. Plates separate or moves away from each other. Asthenosphere Convection Atlantic Up, down Along the subduction zone It melts in the mantle Recycled into rocks or forms volcanoes. Continental crust It is heavier Rocks Plates move towards each other. Smaller/narrower Earthquakes Asthenosphere Atlantic Magma Youngest Floor spreading/ divergent Pacific ocean Pacific/convergent Washington, Oregon, California Convergent boundary Primary, secondary, surface waves Earthquakes Core Refract or bend Solid NO seismic wave zone Focus Layers Bending of light or refraction 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. 98. 99. 100. 101. 102. motion farthest nearest ellipse areas Nitrogen 21 Oxygen Carbon dioxide Greenhouse Carbon dioxide or greenhouse gas Shield, cinder, composite ( any order) Earth’s vent Composite Pacific Ring of Fire Tensional, compressional, shear ( any order) Compressional Tensional Shear Mercury Mercury Neptune Neptune The nearer to the Sun the faster is the planet’s orbital velocity. 23.5 Summer Summer Winter Cavity or underground cave Limestone Sink hole Rotation of Earth’s axis. Earth precession wobbles or sways. Moon’s Seasons 26,000 Northern 103. A. cold front B. warm front C. Occluded front D. Stationary front E. Towards F. Cold 104. 1, troposphere; 2, stratosphere; 3 mesosphere; 4, thermosphere; 5, exosphere 105. 1, troposphere 106. 2, stratosphere 107. It increases. 108. 6, thermosphere 109. decreases 110. 24°C 111. 20°C 112 The wet-bulb temperature is 4 degree Celsius lower than the dry-bulb temperature. 113. dry thermometer, wet thermometer, relative humidity chart 114. 69 percent 115. A ( tundra) and E (Antarctic) 116. C (tropical) 117. B and D ( temperate) 118. Africa 119. Antarctica 120. Zones C and D, Tropical and temperate 1. 2. 3. 4. Wet-bulb temperature - dry-bulb temperature= ___________ Find this number at the top of the chart and place your finger on it. Find the dry-bulb temperature in the first column on the left. Place your finger on it. The relative humidity percentage appears where column and row intersect on the chart. http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/webprojects2002/spence/page3.htm