* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 14.1-14.4
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
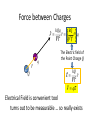
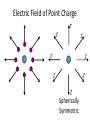
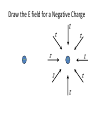
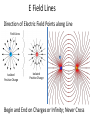
Course Organization • Syllabus • Lesson Plan • Grading • Participation Bonus • Textbook (M&I II Electricity and Magnetism …) • Quest • i-Clickers (register on Quest) What you need to remember from 303K Vectors 𝐴+𝐵 𝐴 𝜃 𝐴 ∙ 𝐵 = 𝐴 𝐵 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝜃 𝐵 𝐴 × 𝐵 = 𝐴 𝐵 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝜃 𝐵 Right Hand Rule 𝐴 How particles move and are affected by forces Momentum: 𝑝~ 𝑚𝑣 𝑝 = 𝛾𝑚𝑣 ; 𝛾 = 1 1− Newton’s 2nd Law: 𝐹 = 𝑑𝑝 𝑑𝑡 𝑣 2 𝑐 ; 𝐹 = 𝑚𝑎 ; 𝑝𝑓 = 𝑝𝑖 + 𝐹∆𝑡 Work and Energy: 𝑊 = 𝐹 ∙ ∆𝑟 = ∆𝐾 = 1 𝑚𝑣𝑓2 2 − 1 𝑚𝑣𝑖2 2 Clicker Question 1 𝐴 =< 2, 1, 0 > and 𝐵 =< 1, 1, 0 > . What are 𝐴 and 𝐵 ? Choice 𝐴 𝑩 A 5 2 B 5 3 3 2 2 C D 2 Clicker Question 2 𝐴 =< 2, 1, 0 > and 𝐵 =< 1, 1, 0 > . What is 𝐴 ∙ 𝐵 ? Recall: 𝐴 ∙ 𝐵 = 𝐴 𝐵 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝜃 = 𝐴𝑥 𝐵𝑥 + 𝐴𝑦 𝐵𝑦 + 𝐴𝑧 𝐵𝑧 Choice A B C Use your results to find 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝜃 . 𝐴∙ 𝐵 2 3 4 Choice A 𝒄𝒐𝒔(𝜽) B 3/ 2 C 3/ 10 3/ 5 What will you learn? Interaction of Matter and Electromagnetic Fields aurora borealis Backpacking in Alaska 𝐵 𝑝 • Sun spits out Charged Particles (Solar Wind) • Earth’s Magnetic Field extends out into space and collects charged solar wind. • Charged particles are concentrated at poles • Collisions of these high velocity charges with air makes the light of the aurora More Mathematically … The interactions between matter and Electric and Magnetic fields can be explained with just a few equations. Maxwell equations: r div( E ) = Ñ × E = e0 div( B) = Ñ × B = 0 ¶B curl(E) = Ñ ´ E = ¶t é ¶E ù curl( B ) = Ñ ´ B = m0 ê J + e 0 ú ¶ t ë û Lorentz force: F = qE + qv ´ B Point Charges • Two types: positive and negative • Like charges: repel • Opposite charges: attract • Charge is quantized in units of e Millikan’s oil drop experiment (1910-1913) • Point charge: Size is small compared to the distance between it and other objects of interest • Electric charge is an intrinsic property of the fundamental particles that everything is made of The Coulomb Force Law Q1Q2 F =F= 2 4pe 0 r 1 "The magnitude of the electrostatic force between two point charges is directly proportional to the magnitudes of each charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges." Q1 Q2 F F Charles-Augustin de Coulomb (1736 - 1806) The Coulomb Force Law 1 Q1Q2 F= r̂ 2 4pe 0 r r + + 2 0 = permittivity constant F21 Force on “2” by “1” 1 Force repulsive r + F21 - 2 1 Force attractive Units and Constants SI units of electric charge: Coulomb, C 1 Q1Q2 F =F= Constants: 2 4 pe r 0 1/40 = 9x109 N.m2/C2 0 = 8.85x10-12 C2/N.m2 permittivity constant e = 1.602x10-19 C 1 C = 6.24x1018 elementary charges Particle electron positron proton antiproton muon pion neutron Charge -e +e +e -e +e or –e +e or –e or 0 0 Structure of Atom Matter consists of atoms 1 cm3 : ~1024 atoms Nucleus: ~104 times smaller than electron cloud, ~104 times heavier than electron. 1Å=10-10m Example: nucleus of the iron atom Size: ~10–15 m, mass: ~10-25 kg Nucleus charge = +Ze, atom with Z electrons is neutral. The Concept of Electric Field Accelerates at 9.8 m/s2 – why? Accelerates at 1011 m/s2 – why? There are many possible configurations of charges to produce the observed effect. Electric Field There is something in space waiting for a charged particle to interact with it! This virtual force is called electric field. An electric field created by charge is present throughout space at all times, whether or not there is another charge around to feel its effect. Force between Charges 𝑘𝑄𝑞 𝑘𝑄 𝐹= 𝑟= 𝑟 𝑞 2 2 𝑟 𝑟 + + 𝑟 q Q The Electric field of the Point Charge Q 𝑘𝑄 𝐸 = 2𝑟 𝑟 𝐹 = 𝑞𝐸 Electrical Field is convenient tool turns out to be measurable … so really exists Electric Field of Point Charge 𝐸 𝐸 + 𝐸 𝐸 𝐸 + 𝐸 𝐸 𝐸 Spherically Symmetric Draw the E field for a Negative Charge 𝐸 𝐸 _ 𝐸 𝐸 _ 𝐸 𝐸 𝐸 𝐸 E Field Lines Direction of Electric Field Points along Line Field Lines + + _ Isolated Positive Charge Isolated Positive Charge + Begin and End on Charges or Infinity; Never Cross Things to do • Homework on Quest: Ch14-h1; review Ch14-h0 • Read Ch14.1-14.8 • i-Clickers (register on Quest) _