* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BLOOD CELLS / FORMED ELEMENTS (REVIEW) 1. (red blood cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
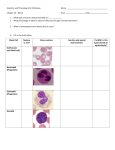
BLOOD CELLS / FORMED ELEMENTS (REVIEW) 1. _______________________________ (red blood cells) • Transport (bound to pigment ) 2. _______________________________ (white blood cells) granulocytes __________________________________ • • • most numerous phagocytes release cytotoxins __________________________________ • • • • staining reveals bright red granules phagocytes defend against parasitic worms/flukes release anti-inflammatory chemicals __________________________________ • • • staining reveals dark blue granules release histamines (trigger inflammation) associated with allergic reaction agranulocytes _________________________________ • • • second most abundant leukocyte small cells with a large nucleus produce antibodies (B cells) and coordinate immune defense (T cells) _________________________________ • very large phagocytes 3. ________________________________ (platelets) • numerous small cellular fragments • function in hemostasis NOTE : blood cells are formed from _______________________ in ________________________________ by the process of _______________________________. HEMATOPOIESIS = (occurs in ) leukopoiesis __________________________ = __________________________________ • regulated by and • numbers of WBCs vary and are produced in response to (colony stimulating factors) thrombocytopoiesis __________________________ = __________________________________ • thrombocytes form by • formation regulated by hormone addition to interleukin-6 and CSF (produced in kidneys), in erythropoiesis __________________________ = __________________________________ • mature RBC’s have no • synthesis requires hemoglobin ( • to make pigment ) → tetramer of fetal hemoglobin has • each Hb chain contains (Fe molecule within a porphyrin ring) within (protein component) • each iron can bind a single the globins can bind • • red blood cell synthesis takes • make approximately • production enhanced by → → of body’s iron supply → steps in erythropoiesis: control of erythropoiesis • glycoprotein hormone _________________________ (EPO) • EPO secreted by hemorrhage ↓ O2 levels ↑ secretion of ↑ O2 demand degradation of RBCs • lifespan ≈ • RBC’s become less flexible and more fragile → (rupture) • + trap old RBC’s → phagocytize • hemoglobin components recycled hemoglobin (green pigment) bound to transport protein in blood (yellow pigment) stored as iron / protein complexes metabolized THINK! What causes jaundice? obstructive jaundice physiological jaundice HEMOSTASIS Def’n • occurs in response to • triggered by • functions to 3 steps 1. • • of damaged vessel → constriction endothelial cells release 2. • to endothelium and • results in formation of • activated platelets release → → → (stimulates vascular spasm) (platelet derived growth factor; promotes vessel repair) (stimulates platelet aggregation) → and (promote clotting) 3. • coagulation = • results in formation of a clot = • → sequential activation of (“procoagulants”) 2 pathways: i) • begins with chemicals • triggered by • requires platelets) • can occur when platelets are exposed to glass (eg. in a ) • ( released by aggregating (about 2-3 min) ii) • begins with chemicals • initiated by release of damaged cells) • ( released by (< 2min….about 15 sec faster) NOTE: both pathways activate which initiates the (shared by both the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways) → normally, both pathways are triggered simultaneously by injury COMPLETE THE PATHWAYS ON THE FOLLOWING PAGE CONSIDER! What factors / chemicals / ions are required by both pathways? clot retraction and repair CLOT PLATELETS PDGF (pulls torn edges of damaged vessel closer together making repair easier) promotes healing of vessel wall plasmin dissolves fibrin “ “ tPA plasminogen NOTE: clot retract s (shrinks as serum is squeezed out of coagulated blood) THEN the fibrin is dissolved. clotting abnormalities hemophilia thrombus embolus anticoagulants (prevent clotting) aspirin coumadin (warfarin) / dicumarol heparin EDTA