* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Questions for Exam #2
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Tunnel valley wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Overdeepening wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
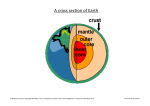
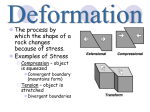
Exam II on quizzes 5-9 Tectonics and Landscape chapter will not be on the test Be capable of recreating figure 21.3, p 600 Quiz 5 1) Dip and strike measurements are used to describe the orientation of A) bedding planes. B) joints. C) faults. D) planar surfaces in metamorphic rocks. E) all of the above 2) Tight folds are commonly associated with A) strike-slip faults. B) bedding plane faults. C) thrust faults. D) normal faults. E) complex faults. 3) Lateral offset in drainage lines is commonly associated with A) normal faults. B) reverse faults. C) thrust faults. D) strike-slip faults. 4) Compared to a fault, the rocks along a joint A) have experienced no appreciable displacement. B) are intensely deformed. C) are older on the upthrown side. D) are younger on the upthrown side. E) are metamorphosed. 5) The formation of the Basin and Range province of the western United States is believed to be the result of A) horizontal compression caused by plate collision. B) tensional forces. C) lateral motion caused by plate rotation. D) cracking of the Earth's crust caused by tidal forces. E) fracture system caused by igneous intrusions at a shallow level. 6) Continental collision is commonly marked by A) the formation of large fold belts. B) the development of normal faults. C) thrust sheets. D) all of the above E) only A and C 7) Horizontal compression of continental crust most commonly results in the formation of A) normal faults. B) thrust faults and folds. C) folds and normal faults. D) strike-slip faults and normal faults. 8) An unconformity is A) a sedimentary unit. B) a period of deposition. C) a buried erosional surface. D) a type of fold. E) a type of fault. 9) Ductile behavior of rocks is favored by which conditions? A) high pressure - high temperature - low rate of deformation B) low pressure - high temperature - low rate of deformation C) high pressure - low temperature - high rate of deformation D) high pressure - high temperature - high rate of deformation E) low pressure - low temperature - high rate of deformation 10) What global tectonic features are found where horsts and grabens are common? A) rift valleys B) transform plate boundaries C) folded mountain belts related to convergent boundaries D) mantle plumes E) none of the above 11) Which statement is characteristic of an eroded dome? A) the oldest rocks are found around the rim of the structure B) the oldest rocks are found in the middle and of the structure 12) Which statement is characteristic of an eroded dome? A) the beds dip inward toward the center of the structure. B) the beds dip away from the center of the structure. Quiz 6 1. What is meant by ‘Uniformitarianism’? a. The past is the key to the present b. Physical laws of the Universe are the same today as they were in the past c. All nature tends to move toward a Uniform condition, i.e. Equilibrium d. The present geologic landscape was created in a series of catastrophic Extinction events e. Both A and B are correct 2. What is an Unconformity? a. Old rocks on top of young ones b. Young rocks on top of old ones c. An surface of erosion or non-deposition between two rock strata that represents a large gap time d. A contact between two strata where the lower rocks are poised at an angle relative to the upper rocks e. None of the above 3. What is the Principle of cross-cutting relationships? a. The oldest rocks are on the bottom b. The youngest rocks are on the bottom c. Intrusions or faults are younger than the rocks they cross d. Intrusions or faults are older than the rocks they cross e. None of the above 4. What is the difference between relative and absolute ages? a. Absolute ages are very accurate; relative ages are not b. Relative ages are very accurate; absolute ages are not c. Absolute ages are in years; relative ages only tell whether one rock is older or younger than another d. The geologic landscape was created in a series of catastrophic Extinctions which are clearly dated 5. What does Phanerozoic mean in Greek? a. Old life b. Middle life c. Modern life d. Visible life e. Invisible life 6. If you wanted to date a rock that was at least 100 million years old, what radioisotope pair (parent and daughter isotopes would work better: Potassium-Argon or Carbon-14/Nitrogen-14? a. Potassium-Argon b. Carbon-14/Nitrogen-14 c. Neither d. Either e. Either, but oxygen-isotope stages are best 7. Why do we have such good dates on many fossil beds of the Western United States? a. Because we know how old the fossils are b. Because terrestrial sedimentary rocks such as those formed in rivers, contain many dinosaur species, which only existed before 65 million years ago c. Because fossil-rich beds contain many thin volcanic beds that erupted about every 600,000 years d. Because fossil-rich beds contain many thin volcanic beds containing minerals that can be dated using radiometric methods e. Both C and D are correct 8. How much of geologic time is encompassed by the Precambrian? In other words, what percentage of the Earth’s total lifespan took place before the worldwide explosion of large fossils? a. 25% b. 50% c. 70% d. 80% 9. What does the word ‘dendritic’ mean? a. Related to rivers b. Related to lakes c. Related to floodplains d. Tree-like e. Meandering 10. What are tributaries? a. The divides that define a drainage basin b. All of the rivers and streams that drain into the main trunk of a river c. Splays and avulsions that contribute to the formation of a delta d. Depositional bars on the outside bend of a river e. Both B and C 11. What happened to the fertility of the Nile Delta and Nile River floodplains after the Aswan Dam was built in 1970? a. It became less fertile because floods no longer delivered rich organic matter to the floodplain b. It became more fertile because floods no longer eroded rich soil from the floodplain c. It became less fertile because lower flow levels allowed encroachment of salty sea water d. It became more fertile because without annual flooding farmers could put fertilizer on the soil earlier in the growing season e. Both B and D are correct 12. What is headward erosion? a. Erosion to the baseline b. Erosion causing the headwaters to migrate farther upstream c. Erosion causing formation of avulsion channels d. Erosion within and incised channel e. All of the above 13. What is a floodplain? a. The main part of the channel that is eroded, i.e. plained, during floods b. The flat area of the river valley outside of the natural levees c. The portion of the river valley that is covered by water during floods d. All of the above e. Both C and D are correct 14. What is the difference between an alluvial fan and a delta? a. An alluvial fan is shaped like a kidney; a delta is shaped like a spleen b. An alluvial fan forms in a dry environment; a delta forms in a lake or the ocean c. Both only form during floods d. Sediment in an alluvial fan is dominated by desert silt and dust; Sediment in a delta is domnated by rocks and gravel e. Both B and D are correct 15. What is the greatest cause of costly, i.e. in terms of money, flood damage? a. Rich people have expensive boats in marinas that are destroyed during floods b. The fact that people build in floodplains c. The increasing occurrence of floods due to Global Warming d. The increased occurrence of hurricanes due to Global Warming e. Both C and D are correct 16. What is a point bar? a. A bar that is pointy shaped b. A sand bar formed in the delta at the mouth of a river c. A gravel bar formed in a braided stream d. A sand bar that forms on the inside corner of a meandering stream e. None of the above Quiz 7 What is permeability? a. A measurement of viscosity for a given hydrostatic pressure b. The percentage of the rock that has open space to hold water c. The capacity of a rock to transmit fluid d. The flow rate within an aquifer e. Both B and C are correct 2. What is the water table? a. The level in the ground below which the soil or rock is saturated 1. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. b. The level in the ground below the confining beds of an aquifer c. The level in the ground where potable water may first be found d. The level in the ground that feeds springs What is an artesian well? a. A confined aquifer b. An unconfined aquifer c. A well used by artisans d. A confined aquifer under pressure that will discharge above the local water table What type of rock/sediment most commonly forms aquifers in Montana? (See the lecture) a. Fractured volcanic rock b. Fractured and dissolved limestone caverns c. Porous sandstones d. Unconsolidated sediments, i.e. gravels and sands e. Rivers such as the Yellowstone In what type of rock are caves most likely to form? a. Fractured volcanic rocks b. Limestones c. Pumice and other porous volcanic rocks d. Sandstones How do stalactites and stalagmites form? a. They are mineralized replacements of buried fossils such as trees b. Hydrothermal hot springs precipitate the minerals as the hot water cools c. They are what is left over after the rest of the limestone forming the cave has dissolved d. Dissolved minerals, such as calcite, precipitate as the water dripping from the ceiling evaporates What mineral typically forms petrified wood? a. Forms of silica such as chert or chalcedony b. Limestone c. Muscovite d. Pyrite What are the two types of glaciers? a. Temporary and Permanent b. Flowing and Non-flowing c. Continental and Valley (Mountain) d. High latitude and low latitude e. Continental and Lacustrine What is a surging glacier? a. A glacier that is growing in size very rapidly b. A glacier that moves very rapidly downhill c. A glacier that erodes the underlying surface much more rapidly than most glaciers d. A glacier that is melting very rapidly e. Both A and B are correct What features are characteristic of glacial erosion? a. moraines, arêtes, V-shaped valleys, hanging valleys, till, kettles, glacial erratics, loess b. cirques, arêtes, U-shaped valleys, hanging valleys, striations c. Moraines, U-shaped valleys, till, drumlins, eskers, varves, striations, loess 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. d. moraines, till, drumlins, eskers, varves, glacial erratics, loess What features are characteristic of glacial deposition? a. moraines, arêtes, V-shaped valleys, hanging valleys, till, kettles, glacial erratics, loess b. cirques, arêtes, U-shaped valleys, hanging valleys, striations c. Moraines, U-shaped valleys, till, drumlins, eskers, varves, striations, loess d. moraines, till, drumlins, eskers, varves, glacial erratics, loess How do Ice Ages affect sea levels? a. Sea level rises because the weather is cooler and wetter b. Sea level drops because the weather is colder and drier c. Sea level rises because ice sheets calve Ice bergs from surging glaciers which then melt d. Sea level drops because water is tied up in ice sheets instead of in the ocean When was the Pleistocene Epoch? a. Before 540 million years ago b. From 65 million years ago to the present c. From about 1.8 Million years ago to 10,000 years before the present d. From 10,000 years ago to the present What produced the giant ripple marks and deposits of sediment seen in the Scablands? a. An large and ancient river formed from thousands of years of melting of the Laurentide Ice Sheet b. It is an ancient beach from when Pacific was farther inland during the last major transgression c. A massive and short lasting flood produced when the ice damming glacial Lake Missoula melted d. Lake (pluvial) deposits from glacial Lake Missoula e. Winds at the end of the last Ice Age that formed large dunes of loess What are Milankovitch Cycles? a. Cyclical variations in the Earth’s orbital parameters b. Cyclical variations in the Earth’s surface temperature c. Cyclical variations in the Earth’s concentrations of greenhouse gases d. Cyclical variations in the Earth’s Glacial/Interglacial conditions e. Both A and D are correct Quiz 8 1. Where does most tectonic activity occur? a. At the boundaries between crustal plates b. In mountain ranges c. At hot spots d. At seamounts and volcanoes 2. What is the source of the Earth’s internal heat generation? a. Gravitational friction b. Solar energy c. Friction at the boundary between the spinning outer core and the mantle d. Decay of radioactive elements within the Earth 3. What was the paleontological evidence for continental drift? a. All of the continents had the same plants and animals b. The climates of het continents were similar near the Equator c. Distinctly different fossils were found on all continents d. Similar fossils were found on continents which are now separated, e.g. a fern (Glossopteris), a fresh-water reptile (Mesosaurus and a mammal-like reptile (Lystrosaurus) 4. What two lines of paleomagnetic data support the idea of seafloor spreading? a. Polar wander and the electromagnetic field of the Earth b. Polar wander and the symmetric pattern of magnetic reversals on the ocean floor c. The dynamo generated by the spinning, liquid Outer Core and pattern of magnetic reversals d. Magnetic anomalies and Mantle Convection 5. Approximately how old is the oldest sediment found on the ocean floor? a. No older than 10 million years old b. No older than 65 million years old c. No older than 100 million years old d. No older than 200 million years old 6. What are the three types of plate boundaries? a. Normal, Reverse and Transform b. Continental, Oceanic and Hot Spot c. Felsic, Intermediate and Mafic d.Divergent, Convergent and Transform 7. What is a subduction zone? a. A zone where one plate slips below another b. A convergent zone that produces a deep trench c. A convergent zone that melts rock at depth and produces a linear volcanic mountain range inland d. All of the above e. None of the above 8. Of what are the fold belts of the Appalachian Mtns of eastern N. America a surface expression? a. An accreted spreading ridge, i.e., an Ophiolite Suite b. An ancient convergent plate boundary c. An ancient passive margin d. An ancient strike-slip fault, like The San Andreas Fault 9. On what major island does the Mid-Atlantic Ridge appear above the surface of the ocean? a. Iceland b. Greenland c. Antarctica d. Baffin Island e. Great Britain 10. What is happening to lithospheric plates at divergent plate boundaries? a. Plates are colliding b. Plates are slipping beneath one another c. Plates are moving apart d. Mantle convection brings magma to the surface, where it cools; creating new lithospheric crust e. Both C and D are correct 11. What causes subsidence of oceanic crust? a. Oceanic crust cools and sinks as it grows older b. Oceanic crust cools and expands as it grows older c. Oceanic heats up and sinks as it grows older d. Oceanic crust is eroded by circulation of hot seawater and hydrothermal alteration 12. What is a ‘black smoker’? a. Underwater volcanic vents that spew ash on the ocean floor b. Active geysers in the ocean that produce underwater terraces composed of c. Vents for hot, mineral-laden waters near ridge spreading zones d. A species of Tube worm that lives on hydrothermal waters near spreading zones 13. What are the four major layers seen in oceanic lithosphere? a. Sedimentary, Metamorphic and Igneous Rocks, on top of newly formed Basaltic Crust b. Ocean sediments, Pillow Basalts, Sheeted Dikes, and Gabbro c. Ocean Sediments, Biogenic Oozes, Andesitic Volcanism and Limestones d. Granites, Basalts, Schists and Limestones 14. What are ophiolites? a. Mantle, Moho and Crust b. The sequence of rocks that forms oceanic crust c. Rocks created in subduction zones d. Biogenic oozes characteristic of sediments at Ridge Spreading Zones 15. What is meant by ‘hydrothermal alteration’? a. Precipitation of evaporites at high temperature in Rifting Margins b. Local metamorphism due tensional forces c. Regional alteration of rocks due to subduction d. Chemical and mineral alteration of rocks due to the flow Quiz 9 1. What are the three types of convergent boundaries? a. local, regional and global b. convergent, divergent and continental c. convergent, divergent and transform d. oceanic-oceanic, oceanic-continental and continental-continental 2. Continental collision is always marked by ______________ which causes __________. a. subduction zones; formation of sutured margins and uplifted mountains b. strong horizontal compression; folding and thrust faulting c. strong horizontal extension, folding and thrust faulting d. a mix of horizontal compression and transform faulting; production of oceanic crust 3. Why (or rather, how) is magma generated in subduction zones? a. dehydration of the subducted oceanic crust causes partial melting of the overlying mantle b. radiation in the Earth’s interior melts the subducted slab c. frictional heating melts the subducted crust d. mantle plumes melt country rock as the magma migrates to the surface 4. What types of magmas are formed in subduction zones? a. Basaltic and Ultramafic magmas b. Andesitic and Rhyolitic magmas c. Ophiolite Suites d. Metamorphic and Granitic magmas e. Both A and C are correct 5. What are plutons? a. a sequence of rocks formed in oceanic divergent zones b. regional metamorphic suites found in convergent zones c. large magma bodies that cool beneath the Earth’s surface d. large buried magma bodies found in magmatic arcs of many convergent zones e. both C and D are correct 6. What type of metamorphism occurs near the trench? a. High Temperature; Low Pressure b. Low Temperature; Low Pressure c. High Temperature; High Pressure d. Low Temperature; High Pressure 7. a 8. What are the four major structural and topographic features in a subduction zone? a. clastic belt, fold and thrust belt, former magmatic arc, ophiolite b. orogenic, catagenic, diagenetic and syngenetic belts c. convergent, divergent, transform and hydrothermal belts d. swell, forearc, magmatic arc and backarc 9. What are examples of mountain ranges formed by oceanic-continental collision? a. The Himalayas, Tibetan Plateau and the Urals b. The Andes, the Cascades, the Rocky Mountains c. Hawaiian Islands, Yellowstone Caldera, Kamchatka Peninsula, Aleutian Archipelago d. Iceland, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, and the Tonga Islands 10. Of what is the ‘Mesozoic history of western North America a good example’? a. regional and local metamorphism b. accretion of numerous exotic terranes c. extension of a continental back arc basin d. compression of a continental-continental boundary e. compression of an oceanic-continental boundary 11. What accounts for the fact that volcanic eruptions at convergent plate boundaries are violent? a. Because the magmas generated are rich in silica (felsic) and thus viscous, i.e. thick b. Because the magmas generated are rich in water and gases, which build up pressure in the magma c. Because the magmas generated are silica-deficient (mafic), and thus viscous, i.e. thick d. Because the magmas generated are poor in water, and thus viscous, i.e. thick e. Both A and B are correct 12. What are ‘accreted terranes’? a. a group of rocks sharing a common age, structure, stratigraphy and origin, sutured to the continental margin b. a group of crustal blocks composed of ancient seafloor, island arcs, deep-marine sediments and fragments of continents c. a group of crustal blocks forming the margins of the continents d. all of the above e. none of the above 13. What are mantle plumes and what do they form? a. long columns of hot, less dense rock, rising from deep in the mantle and mid-ocean ridge spreading zones b. long columns of hot, less dense rock, rising from deep in the mantle and forming hot spots, volcanism and broad crustal swells c. IGNORE THIS QUESTION d. 14. What does a plume that develops beneath the continent form? a. a regional batholith b. an island chain such as the Hawaiian-Emperor chain c. regional uplift, basalt flows from fissures and Rhyolitic volcanoes and calderas d. horizontal compression, resulting in folding and thrust faulting 15. How old is the oldest volcanism in the Snake River Plain? a. 600,000 years old b. 1.2 million years old c. 12 million years old d. 16 million years old e. 65 million years old