* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Respiration copy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
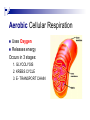
Cellular Respiration Biology What does this remind you of? Cellular Respiration n The process that releases energy by breaking down glucose n Occurs in ALL living cells n Chemical Formula for respiration C6H12O6 + O2 à CO2 + H2O + ATP n Glucose + Oxygen à Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP Aerobic Cellular Respiration Uses Oxygen n Releases energy Occurs in 3 stages: n 1. GLYCOLYSIS 2. KREBS CYCLE 3. E- TRANSPORT CHAIN Overview: Aerobic Respiration Step 1: Glycolysis n Occurs in the cytoplasm (fluid surrounding cell organelles) Glucose is converted (changed) into pyruvic acid (1 glucose = 2 pyruvic acids) ¨ 2 ATP molecules are produced ¨ Step 2: Krebs Cycle (aka Citric Acid Cycle) n Occurs in mitochondria n Pyruvic acid from glycolysis is broken down into CO2 n 1 molecule of ATP is produced for each pyruvic acid (total of 2) Electron Transport Chain n The Krebs Cycle generates high-energy electrons that are passed to the electron transport chain n Here they are used to change ADP to ATP n Water is formed Totals for Aerobic Respiration n Production of 36 ATP molecules n Heat is also released ¨ this is why you feel warm after you exercise Anaerobic Cellular Respiration n Does not use Oxygen n Releases energy n Occurs in 2 steps 1. Glycolysis 2. Lactic Acid Fermentation OR 2. Alcoholic Fermentation Lactic Acid Fermentation n Lactic Acid is produced n Sore muscles after a workout n How bacteria makes yogurt Alcoholic Fermentation n Ethyl alcohol is produced n How yeast makes bread Totals for Anaerobic Respiration n Anaerobic Cellular Respiration produces a total of 2 ATP molecules