* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download S2.Cell Signaling-Signaling and gene expresssion
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
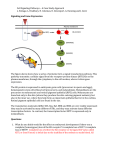
Cell Signaling Pathways – A Case Study Approach L. Emtage, L. Bradbury, N. Coleman, D. Davenport, A. Dunning and J. Grew Signaling and Gene Expression SCF Plasma membrane Kit Grb2 Sos (Ras GEF) (adapter) MI Ras GTP Ras (G protein) GDP RAF (MAPKKK) P MEK (MAPKK) P ERK (MAPK) P C T F BP M ITF P The figure above shows how a series of proteins form a signal transduction pathway. This pathway transmits a cellular signal from the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) Kit on the plasma membrane, through the cytoplasm, to the cell nucleus, where it alters gene expression. The Kit protein is expressed in embryonic germ cells (precursors to sperm and eggs), hematopoietic stem cells (blood cell precursors), and melanoblasts. Melanoblasts are the precursors to melanocytes and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells. Melanocytes are found not only in the skin (where they produce the skin coloring pigment melanin), but also in the inner ear, where they help form an important epithelial barrier in the cochlea. Retinal pigment epithelial cells are found in the eye. The transduction molecules GRB2, SOS, Ras, Raf, MEK and ERK are very widely expressed; they may be activated by many different RTKs, and they may activate many different transcription factors. In contrast, the transcription factor MITF is expressed only in melanoblasts. Questions 1. What do you think would be the effect on embryonic development if there was a complete (homozygous) loss of the Kit receptor? A complete loss of SCF? A complete loss of MITF? Cell Signaling Pathways – A Case Study Approach L. Emtage, L. Bradbury, N. Coleman, D. Davenport, A. Dunning and J. Grew 2. Individuals with Waardenburg syndrome Type 2A often have a white forelock and premature greying, unusual pigmentation of the iris, such as heterochromia iridis, and hearing loss. Waardenburg syndrome is a congenital disorder, caused by dominant loss-of-function mutations in a gene or genes in this pathway. Which gene or genes above could be mutated to give rise to Waardenburg syndrome 2A? Explain your answer. 3. Very pale pigmentation, such as found in Icelanders, is thought to be due to a polymorphism in SCF. If you were trying to identify the polymorphism responsible, would you sequence the coding region or the regulatory region of SCF first, and why?