* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test 1
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
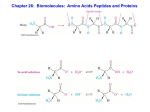
Name:_____________ Chemistry 460 Biochemistry First Hour Exam Remember- Show all work for partial credit 1. (10 points) Name as many organelles from a eukaryotic cell as you can and give a 1 sentence description of the organelles function. 1 point / organelle and 1 point / explanation Nucleus - membrane enclosed region that isolates the genetic material from the rest of the cell Mitochondria - organelle used to extract energy from chemical decomposition Chloroplast - organelle used to obtain energy and make C 6H12O6 and O2 from H2O and CO2 using light energy lysosome - organelle used to digest material endocytosed into the cell rough ER - membrane sac with ribosomes attached used to synthesis of proteins to be exported out of cell smooth ER - membrane sac distal from rough Er, proteins inside Er have now been synthesized and are now being processed, lipid synthesis. Golgi apparatus - used in final processing of secretory proteins Peroxisome - membrane bound organelle used to isolate chemical reaction involving peroxide Glyoxisome - plant equivalent of peroxisome Several other organelles accepted 2. (10 points) Some proteins contain added chemical groups or cofactors that give them added chemical reactivity. One such cofactor is NAD+ or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Our body cannot synthesize this cofactor so it must be obtained in our diet as the vitamin riboflavin. Below is the structure of NAD+. In this structure identify as many different chemical functional groups as you can: 2 points/group, 5 minimum OH on sugar alcohol C=ONH2 amide or amido aromatic rings with nitrogen to make nitrogen bases PO4H - phosphate groups O O between two PO4's - anhydride linkage NH2 primary amine C + O in sugar ring look like an ether O CH2 O N NH2 - H H HO P O HO O H P OH O- O CH2 H OH N O N H H H H OH OH NH2 N N 2 3. (10 points) I have said in class several times that because of its side chain pKa histidine can be used as an acid or a base at neutral pH. Assume you have a .05M solution of histidine, what are the molar concentration of both the acid (HA) and the base (A -) forms of this amino acid at pH 7.00. (Ignore the pKa’s of the main chain functional groups to simplify this problem.) Ignoring the main chain functional groups mean that you just have to worry about the side chain imidazole ring with a pKa of 6.00 I’ll call the acid from HisH+ and the base form His HisH+ + His = .05; His = .05 - HisH+ pH = pKa + log A -/HA = pKa + log Base/acid= pKa + log His/HisH+ 7.00 = 6.00 + log His/HisH+ 1.00 = log His/HisH+ 101 = His/HisH+ 10 = His/HisH+ 10(HisH+) = His = .05 - HisH+ 11HisH+ = .05 HisH+ = .05/11 = .00455 = HA = His H + His = .05-.0045 = .04545 = A- 3 4. (20 points) Fill in the following table: Name Isoleucine Tyrosine Lysine 3 letter abbreviation Ile Tyr Lys 1 letter abbreviation I Y K Structure OH CH3 NH3+ CH2 CH2 H NH3+ CH3 CH2 C COO- CH2 2 H CH2 NH3+ 11C COO- CH2 NH3+ H C COO- 15 H side chain pKa (if ionizable) - 10.07 10.53 General classification (nonpolar, polar, etc) Nonpolar aromatic, polar + Charged Base 5. (10 points) Calculate the pI of the peptide nh2-A-V-D-E-W-cooh pKa’a nh2 about 9 cooh about 3 COOH of D 3.65 COOH of E 4.25 So I will have a titration curve with 4 flat regions: 3.3.65,4.25 and 9 Note: I am using a high pKa of 3 for my cooh end because this is not an amino acid so the Charge effect from the nh3 end is minimal. At the lowest pH I will be fully protonated with 3 COOH and 1 NH3+ for a +1 charge I will therefor have a 0 charge at the end of my first flat region and will be at my pI the pI must then be at the average of my first two flat regions pI = (3+3.65)/2 = 3.325 Note your answer may be different depending on what you chose for the pKa of the cooh terminus 4 6A. (10 points)Suggest a chromatographic method to separate the above peptide (AVDEW) from the peptide AVRKW. Justify your choice of method. From problem 5 above we known that the pI of AVDEW is low, to at pH 7 the peptide will have a negative charge. The big difference is that the peptide AVRKW has two basic side chains instead of two acidic side chains, so I would guess that it is + charged at pH 7 instead. Thus ions exchange is the best method for separating these peptides. At ph 7 peptide AVDEW will stick to a + charged column (an anion excharger) but the peptide AVRKW will pass right through. Conversely if we used a cation exchanger (- charged column) AVRKW will stick, and AVDEW will pass through There is not a big enough difference in molecular weight for a gel column to work. 6B. (5 points) How could you tell when the above peptides eluted off the column? How could you tell? Both peptides have a tryptophan. The tryptophan gives them a UV absorbance, so all you have to do is to look at the absorbance of the solution around 280 nm. 6C. (10 points)Suggest a second chromatographic method you could use to separate the above peptides from the protein cytochomre c (104 amino acids), and justify your answer. Here we have a big difference in molecular weight so a gel permeation column work be ideal. Knowing that cytochrome c is an enzyme you might also suggest an affinity column based on a compound that is known to bind to cytochrome c. 7. (5 points) Define primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure in proteins. Primary structure: The covalent structure of a protein , ie the sequence of amino acids and the location of any disulfides. Secondary structure: local structures that occur between a few residues Tertiary structure: the overall structure of a single protein Quaternary structure: The structure of porinte complexes containing more than one protein. 5 8.(10 points) Lets say that a probe has just come back from Mars, and this probe captured a Martian life form that contained the following amino acid. Discuss the similarities of differences between this Martian amino acid and its nearest earth equivalent. H NH3+ C + CH2 NH3 COOI was trying to make this a D amino acid instead of an L amino acid. However, when I double checked my key, I discovered that this is also an L. Since this amino acid has a side chain with a primary amine I would call its nearest earth equivalent lysine. The biggest difference between this and lysine is that there are fewer C between the main chain and the charged base group so the pK may shift a little bit, and the NH3+ group much closer to the main chain so it can’t move around as much.