* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 3 Review
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
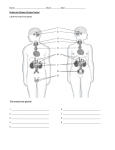
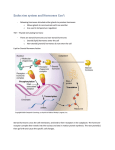
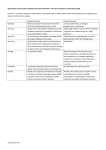
Exam 3 Review Immune and Endocrine Systems AN S 214 Supplemental Instruction 3/31/13 Immune System Outline • Cells of Immune System • Innate Defenses – Surface Barriers – Internal Defenses • Injury to Healing Flow Chart • Adaptive Defenses – Cell Mediated Immunity – Humoral Immunity – Forms of Immunity • Words to Know Cells of Immune System Innate Defenses • Surface Barriers – Skin • Acidity • Enzymes • Mucin • Defensins • Lipids • Keratin – Mucus Membranes • Internal Defenses – Natural Killer Cells (Police) • Large granular lymphocyte • Induce apoptosis • Non-specific – Fever – Inflammation • • • • • Heat Redness Swelling Pain Impairment of Function – Phagocytes Phagocyte Mobilization • Leukocytosis – Neutrophils enter blood from bone marrow • Margination – Neutrophils cling to capillary wall • Diapedesis – Neutrophils flatten and squeeze out of capillaries • Chemotaxis – Neutrophils follow chemical trail Mechanism of Phagocytes 1. Phagocyte adheres to pathogens or debris 2. Phagocyte forms pseudopods that eventually engulf the particles forming a phagosome 3. Lysosome fuses with the phagocytic vesicle, forming a phagolysosome 4. Lysosomal enzymes digest the particles, leaving a residual body 5. Exocytosis of the vesicle removes indigestible and residual material Injury to Healing Flow Chart Adaptive Defenses • Cell Mediated Immunity – T Cells • Humoral Immunity – B Cells • Specific • Systemic • Has memory Cell Mediated Immunity • CD4 + MHC II = Clones Helper T Cells – Activate immune response • Stimulate B cells • CD8 + MHC I = Clones Cytotoxic T Cells – Release perforin and granzymes Humoral Immunity • Antigen + Naïve B Cell = Clones Memory B Cells + Plasma B Cells • Plasma B Cells – Antibodies • • • • Precipitation Lysis by Complement Agglutination Neutralization • • • • • IgM IgA IgD IgG IgE Forms of Immunity • Primary – Mostly IgM, lag period, antibodies don’t last as long • Secondary – Mostly IgG, faster and larger response, antibodies last longer • • • • Active, Natural – Infection Active, Artificial – Vaccine Passive, Natural – Colostrum Passive, Artificial – Injection of antibodies Words to Know • Antigen – substance that can mobilize the adaptive defenses and provoke an immune response • Antigenic Determinant – part of the antigen that induces an immune response • Apoptosis – Cell death • Haptens – not immunogenic by themselves, immunogenic when attached to body proteins • Immunocompetence – (lymphocytes) able to recognize and bind to a specific antigen • Immunogenicity – ability to stimulate proliferation of specific lymphocytes and antibodies • Reactivity – ability to react with activated lymphocytes and antibodies released • Self-Tolerance – (lymphocytes) unresponsive to self antigens Endocrine System Outline • Types of Stimuli • Pituitary Hormones – Thyroid Hormone • • • • • Blood Glucose Levels Hormonal Abnormalities Blood Calcium Levels Blood Calcium Abnormalities Mechanisms of Hormone Action – Water-Soluble Hormones – Lipid-Soluble Hormones • Words to Know Types of Stimuli • Humoral Stimuli – Changing blood levels of ions and nutrients directly stimulates secretion of hormones • Neural Stimuli – Nerve fibers stimulate hormone release • Hormonal Stimuli – Hormones stimulate other endocrine organs to release their hormones Pituitary Hormones • Anterior Pituitary Hormones (Adenohypophysis) • Posterior Pituitary Hormones (Neurohypophysis) Hormone GH FSH LH PRL TSH ACTH Oxytocin ADH Secreted from Triggered by… (which Effects (cell type?) hormone?) Somatotrophs GHRH (stimulate) Direct: Fat and carbohydrate metabolism GHIH (somatostatin) (inhibit) Indirect: Stimulates the release of IGFs, which affects skeletal and extraskeletal Gonadotrophs GnRH Stimulates gamete production Gonadotrophs GnRH Stimulate gonadal hormone production Lactotrophs PRH (stimulate) Stimulates milk production PIH (dopamine) (inhibit) Thyrtrophs TRH Stimulates thyroid development Corticotrophs CRH Regulates to response to stress Stimulates the adrenal cortex to release corticosteroids Hypothalamus XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Stimulates milk ejection XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Stimulates uterine contractions Hypothalamus XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Inhibits urine production Thyroid Hormone A – Thyroglobulin synthesized/discharged into follicle lumen B – Iodide (I-)is actively transported in Not labeled – Iodide is oxidized to Iodine C – Iodine is attached to tyrosine in colloid D - Iodinated tyrosines are linked to form T3 & T4 E - Thyroglobulin colloid is combined with lysosome F - Enzymes cleave T3 & T4 from thyroglobulin colloid and hormones diffuse into blood • • • • • • Major metabolic hormone Maintenance of blood pressure Regulation of tissue growth Development of skeletal and nervous systems Reproductive capabilities T3 is ten times more active than T4 Blood Glucose Levels • Pancreas – Insulin • Decreases blood glucose levels – Glucagon • Increases blood glucose levels Hormone Abnormalities • Growth Hormone – Hypersecretion • In children results in gigantism • In adults results in acromegally – Hyposecretion • In children results in pituitary dwarfism • Insulin – Hypersecretion • Excessive insulin secretion results in hypoglycemia, disorientation, unconsciousness • Type II – Hyposecretion • Insufficient insulin results in polyuria, polydipsis, polyphagia • Type I • Thyroid Hormone – Hypersecretion • Grave’s disease – Hyposecretion • In Infants results in cretinism • In adults results in myxedema or endemic goiter if due to lack of iodine Blood Calcium Levels • Parathyroid Hormone – Produced by parathyroid gland – Increases blood calcium levels • Calcitrol (Activated Vitamin D) 1. 2. 3. UV radiation and epidermal keratinocytes convert steroid derivative to cholecalciferol – D3 Liver converts it to calcidiol Kidney converts that to calcitrol – Increases blood calcium levels • Calcitonin – Produced by parafollicular cells – Decreases blood calcium levels Blood Calcium Abnormalities • Hypercalcemia – Excess blood calcium • Hypocalcemia – Deficiency in blood calcium • Milk Fever Prevention – Stimulate cow’s calcium mobilization before calving – Feeding a transition diet 3 weeks before calving – Increase dietary calcium immediately after calving – Avoid fat cows at calving – Administering vitamin D injection 2-8 days before calving Mechanisms of Hormone Action • Target cell must have specific receptors to which the hormone binds – Water-soluble hormones – Lipid-soluble hormones Water-Soluble Hormones • Amino-acid based hormones 1. Hormone binds receptor (1st messenger) 2. Receptor activates G protein 3. G protein activates adenylate cyclase 4. Adenylate cyclase converts ATP to cAMP (2nd messenger) 5. cAMP activates protein kinases Lipid-Soluble Hormones • Steroid-based hormones and Thyroid Hormone 1. The steroid hormone diffuses through the plasma membrane and binds an intracellular receptors 2. The receptor-hormone complex enters the nucleus 3. The receptor-hormone complex binds a hormone response element (a specific DNA sequence) 4. Binding initiates transcription of the gene to mRNA 5. The mRNA directs protein synthesis Words to Know • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Antagonism – one or more hormones opposes the action of another hormone Autocrine – chemicals that exert effects on the same cells that secrete them Gluconeogenesis – synthesis of glucose from lactic acid and noncarbohydrates Glycogenolysis – breakdown of glycogen to glucose Half life – the time required for a hormone’s blood level to decrease by half Homeostasis – The tendency of an organism or a cell to regulate its internal conditions, usually by a system of feedback controls, so as to stabilize health and functioning, Hormones – long-distance chemical signals that travel in the blood or lymph Negative Feedback – feedback that reduces output of a system Paracrine – locally acting chemicals that affect cells other than those that secrete them Permissiveness – one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present Positive Feedback – feedback that enhances the output of a system Rickets – bones don’t mineralize properly Synergism – more than one hormone produces the same effects on a target sell Tropic Hormones – regulate the secretory action of other endocrine glands