* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroid gland
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
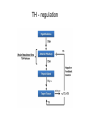
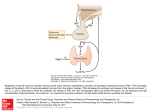
Thyroid-2 Regulation and Mechanism of Action lecture NO : 02 MBBS Dr Muhammad Ramzan Regulation of THs • Regulation of TH is important to: • Control the metabolic activities of all the body cells • Promotes the body growth especially CN development in children • Provide energy to satisfy the requirements of all body reactions • Maintain BMR for essential body systems like CVS; Respiratory.GIT and maintenance of body temperature Regulation of THs • TH are regulated through 2 path ways: • Neuro endocrine regulation / Hypothalamus- pituitary Thyroid axis or Indirect pathway • Pituitary - Thyroid axis/direct pathway • Negative feed back is the main mechanism Neuro endocrine pathway • Serum TH level is the key player in regulation of the TH • The deficiency of TH stimulates the hypothalamus to secrete Thyrotropin releasing hormone – TRH • TRH stimulates the Ant. Pituitary to secrete TSH that stimulates the thyroid gland to ↑TH (T4) • Opposite is true when serum TH level is high • Exposure to cold in children ↑ release of TRH –TSH and TH Pituitary- thyroid axis/ Direct pathway TH and TSH • It is the interaction B/W TH level and Pituitary gland • Deficiency of TH causes the stimulation of Pituitary to increase the secretion of TSH • TSH stimulates and ↑ the secretion of TH from Thyroid • Opposite is true when TH is high • Hypothalamus/TRH has no role in this regulation Regulation of TH – Both pathways TH - regulation TH – mechanism of action • TH hormones act through activation of genes similar to that of Steroids hormones • TH have nuclear receptors – Retinoid X receptors that bind with the TH to form hormone receptor complex(HRC) • HRC is translocated to the acceptor site at the nucleus Hormone Response Element HRE - the gene for TH • HRE is expressed for mRNA which translates enzymes/proteins that execute hormonal actions Transport of Thyroid hormones (TH) • TH are transported in free as well in bound form with plasma proteins • Only a small fraction of TH is available in free form and is biologically active • T3 is 10 times more active than T4 TH - Membrane transport and cytoplasmic de iodination • Thyroxin/T4 must be de iodinated to Free T3(FT3) in the cytoplasm by Deiodinase before its : • Translocation to the nucleus • TH cross the cell membrane via the carrier mediated transporters – Iodothyronine Transporters • This is active transport and ATP dependent Bound form of TH – the significance • Bound forms are attached to the Thyroxin Binding Globulin (TBG), Thyroxin Binding Pre albumen and Albumen • Bound forms are important in measuring the activity of gland TH - Mechanism of Action • TH cross the cell membrane by Iodothyronine transporters to reach the acceptor site in the nucleus • Thyroxin or T4 is de Iodinated first to T3 as active TH • Bind first with the Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and then with the Hormone Response Element (HRE) at DNA • Stimulates the TH genes (HRE) to transcribe mRNA that • finds its way to the cytoplasm TH - Mechanism of action cont. • mRNA translates the specific proteins/ enzymes that carry out hormone effects/actions on the : • Target cells throughout body • TH Promote the growth, metabolism and activities of other systems (CV,respiratory and body temperature) TH - Mechanism of action Mechanism of TH General actions of TH • Stimulate the genetic expression at HRE • Promote the synthesis of proteins and enzymes to promote growth, reproduction and repair • TH increases the metabolic rate of body cells, energy release and maintain the body temperature Metabolic actions of TH • TH have significant metabolic actions on the : • Protein metabolism • Fat metabolism • Carbohydrate metabolism and • Maintenance of Body temperature, BMR and heat Actions on Protein metabolism • Promotes genetic expression; DNA replication,DNA content, increases the no of cells for body growth and repair • TH promote protein synthesis, body growth and development of CNS especially in children • Prevents proteolysis protein Action on lipid metabolism • TH stimulates Lipid metabolism • Promotes lipolysis and ↑release of FAs from adipose tissues • Reduces adipose tissue mass/ Lipogenesis • Increases FA oxidation by ↑no of Mitochondria and activity • Plasma level of TG and CH is inversely proportional to the TH level Actions on carbohydrate metabolism • Thyroid hormones stimulate Carbohydrate metabolism: • Promotes the absorption of glucose from GIT • Increases glycolysis and glucose utilization and reduces blood glucose level - hypoglycemic • Promotes Glycogenolysis • Produces hyperglycemia : Prevents Insulin secretion and promotes insulin degradation