* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hormonal Regulation of Growth, Development, and Metabolism
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Signs and symptoms of Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypoglycemia wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
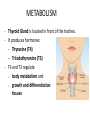
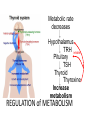
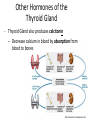
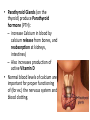
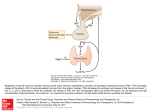
Hormonal Regulation of Growth, Development, and Metabolism Chapter 9.2 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Biology 12 (2011) METABOLISM • • • Thyroid Gland is located in front of the trachea. It produces hormones: – Thyroxine (T4) – Triiodothyronine (T3) T4 and T3 regulate – body metabolism and – growth and differentiation of tissues T4 and T3 • Tyrosine based hormones, dependent on iodine for production. • Lipophilic, travel through blood bound to a protein, thyroxine binding globulin (TBG) and cross the cell membrane easily to interact with nuclear receptors, thyroid hormone receptor. • T4 has a longer half-life than T3 and outnumbers T3 by 20:1 in the bloodstream, but T3 is 4 times as potent (more active). • Circulating T4 is converted to T3 by the removal of iodine. T4 is considered a precursor to T3. Effects of T4 and T3 • T4 and T3 help our body oxidize sugars and nutrients (proteins, fats) at a faster rate. – All the energy of glucose is transferred to heat and ATP, (no storing of glucose) and ATP is consumed during activity, therefore there is no weight gain. • Also increase cardiac output, heart rate, breathing rate, and production of RNA polymerases (so increased protein synthesis – as well as metabolism) Metabolic rate decreases Hypothalamus TRH inhibits Pituitary TSH Thyroid Thyroxine Increase metabolism REGULATION of METABOLISM REGULATION of METABOLISM • Metabolic rate decreases • hypothalamus sends thyroid releasing hormone (TRH) to the anterior pituitary • Anterior pituitary releases thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) • TSH acts on thyroid to stimulate release of thyroxine. • thyroxine raises metabolism by increasing sugar usage by body tissues • thyroxine levels feedback on hypothalamus and pituitary to inhibit further release of TRH /TSH Thryoid Disorders • Hypothyroidism: low thyroid secretions – glucose is not oxidized as quickly, and excess glucose is converted to glycogen and stored. – once glycogen stores are filled, excess sugar is stored as fat. http://www.holisticprimarycare.net/topics/topics-h-n/healthy-aging/94-the-clinical-picture-of-hypothyroidism Thyroid Disorders: Goiter Metabolic rate decreases Goiter • Lack of iodine for producing T4 and T3 • TSH produced continuously in effort to increase levels of T4 and T3 • NO Feedback because functional T4 and T3 not formed • Overstimulated thyroid enlarges Hypothalamus TRH Pituitary TSH Thyroid Other Hormones of the Thyroid Gland • Thyroid Gland also produces calcitonin – Decrease calcium in blood by absorption from blood to bones http://ncwcbio101.wordpress.com/ • Parathyroid Glands (on the thyroid) produce Parathyroid hormone (PTH): – increase Calcium in blood by calcium release from bones, and reabsorption at kidneys, intestines) – Also increases production of active Vitamin D • Normal blood levels of calcium are important for proper functioning of (for ex.) the nervous system and blood clotting. Other Metabolic Hormones • In addition to TSH, the Pituitary Gland also produces Growth hormone (somatotropin) • • Increase Protein synthesis, Breakdown of fats Abnomal levels lead to: dwarfism, gigantism, acromegaly Homework • Pg 403 #4, 6, 8, 10, 11