* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Scope and Sequence for Classifying Matter
Van der Waals equation wikipedia , lookup
Plasma (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs paradox wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Strangeness production wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Bose–Einstein condensate wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Microplasma wikipedia , lookup
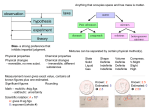
Scope and Sequence for Classifying Matter Science Technology -search for knowledge -“understanding” -how we use the knowledge – application -“using” Matter -has mass and takes up space -made up of atoms -name something you can see that isn’t made of matter – a shadow -If it isn’t matter then it is energy – chemistry concentrates more on matter and physics concentrates more on energy. We will do some of both but more chemistry. Atom -smallest particle of an element that has the properties of the element States of Matter -fill in chart from overhead – solid, liquid, gas -use Petri dishes with BBs to illustrate packing and mobility Plasma -ionized gas -electrons stripped from nucleus -occurs at very high temperatures -mixture of neutral atoms, free electrons, and charged ions -examples: sun, star, lightning through atmosphere States of Matter State Volume Shape Packing of particles Solid Liquid Gas Definite Definite Indefinite Definite Indefinite Indefinite Tight Loose Copyright © 2010, ASM International. All Rights Reserved. Particle mobility Least Most Boiling/ evaporation melting Solid Liquid Gas freezing condensation increasing energy Question for students: Where would plasma fit in the diagram? Types of Matter -Start w/ the Flinn “Nuts, Bolts, and Washers” Activity (See instructions and notes on Flinn Fax) -Notes: Element -one kind of atom Compound -2 or more elements chemically combined Mixture 2 or more substances physically combined -properties different from elements making it up -components can retain some of their properties -over 100 -elements combine in definite ratios -mixed in any ratio -represented by symbols -represented by formulas -no formula -examples: Sulfur – S Gold – Au Zinc – Zn -examples: water – H2O salt – NaCl carbon dioxide – CO2 -examples: salt water bronze kool-aid -basic building blocks -on periodic table -make up everything Copyright © 2010, ASM International. All Rights Reserved. fruit jello brass Types of Elements Metals Nonmetals Metalloids (semimetals) -left side -right side -on border between metals and nonmetals (stairstep line) -most numerous -fewest # of elements -solids -all 3 states -solids -lustrous -not lustrous (dull) -intermediate properties -conductors -tend not to be conductors -workable -brittle Ask students to provide examples of each Demo – Cu, Al, graphite, sulfur, silicon conductivity (use meter), luster, workability/brittleness Types of Structure Put BB board on overhead. Ask for a student volunteer to go to the board and circle 2 regions that have different types of structure. Discuss their differences. Crystalline -orderly arrangement of particles -repeating pattern -predictable Amorphous -random arrangement of particles -no repeating pattern -not predictable Use overhead to show a diagram of each. Have them copy it into their journal. Use a heat gun and HDPE jug to illustrate the differences between amorphous and crystalline Copyright © 2010, ASM International. All Rights Reserved.