* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth Outline
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
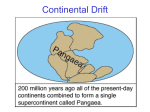
Name ________________ # ___ Changing Earth Study Guide I. Journey to the Center of the Earth (C14) a. The Earth has _________ layers. b. Write the number of the definition to each vocabulary word. crust ______ 1. solid because of extreme pressure, the hottest layer mantle ______ 2. made of rock, the part scientists know the most about outer core ______ 3. liquid rock, very, very hot inner core ______ 4. soft rock, like melted candy, this part sometimes reaches the Earth’s surface through volcanoes Label the layers of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics (C15) a. The theory of ______________ _______________states that the Earth’s crust is not a single piece, but is actually 12 large pieces called plates. b. Scientists believe that ___________cause the plates to move across the Earth’s surface. c. A _____________is a large crack in the Earth’s crust. This is where _________________ can occur. d. There are three different types of boundaries between plates. They are named based on how they move. _________________ boundaries – when two plates collide _________________ boundaries – two plates moving in opposite directions _________________ boundaries – two plates are sliding past each other III. Volcanoes (C16-17) a. A volcano is any opening in the Earth’s ___________ that allows hot __________, _____________ , and _________ __________to pass through into the______________________. b. What two things cause rock to melt? _____________ and __________ c. Melted rock found INSIDE the volcano is called _______________. d. When this melted rock reaches the surface, it is called ___________ . e. The opening in the Earth’s crust is called the ________________ __________. IV. Mountains, Volcanoes, and Earthquakes (C16-18) a. MOUNTAINS: The highest mountains form where ________________ plates collide. b. When continental and oceanic plates collide, the continental plate moves over the oceanic plate. The _______________Mountains were formed this way. c. Some mountains form where ________________from movement at the boundaries push rock upward. This pressure forms at the middle of the plates. d. Sometimes plates pull apart and leave big gaps. Magma can bubble to the surface and cause mountains to form under the ocean. e. VOLCANOES: When ___________collide, chains of volcanoes can form. f. Sometimes they form in the middle of plates when magma comes to the surface. g. EARTHQUAKES: caused by a ____________________________________ in the Earth’s crust. h. Plates can crush together, scrape past each other or bend along boundaries. i. The places where the crust moves are called______________ . j. An instrument called a ____________________is used to measure the magnitude of an earthquake. The numbers on the ____________ ________ describe the magnitude of the earthquake. V. Changes to the Earth’s Surface (C6-11) a. ____________________ are physical features on the Earth’s surface. They are constantly changing whether we realize it or not. b. ________________ is the process of changing rock into _____________. c. After the rock has been broken down into smaller pieces, _____________ takes place, which moves the sediment to a new location. d. Finally, the sediment is deposited in a new location. We call this process _________________. River deltas are formed when sediment builds up at the mouth of a river. e. The chief agents of weathering and erosion are _____________, ______________, and ______________ . f. __________ __________________is the downhill movement of rock and soil because of gravity. Some examples of FAST changes are ___________________, __________________, and ___________________. An example of a SLOW change is ______________ . VI. How the Earth’s Surface Has Changed (C22-25) a. The Theory of _____________________ _______________suggests that the Earth’s continents have moved over the years. It suggests that about 225 million years ago, the Earth was one big super continent called____________ . b. _____________ are traces and remains found in some rocks. c. Younger rock layers are found _______________________older rock layers. d. Take the Grand Canyon for instance, the oldest rock layers would be found at the ____________ of the canyon. e. Fossils are not actual remains of once living things, they are just traces left behind ________________________________________________________ .