* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FORCES
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
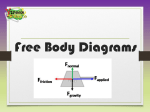
A push A pull A twist Using a spring balance The unit forces are measured in is the newton (after Sir Isaac Newton) The symbol for a newton is N We draw forces using an arrow The arrow shows the direction the force is acting in The size of the arrow shows how big or small the force is This shows a large force This shows a small force A. eg. eg. eg. eg. The SPEED of an object It can make something move It can speed something up It can slow something down It can make something stop moving hand twisting a door knob wind pushing on a sail girl pushing a rock a stone being pulled towards the earth by the force of gravity B The SHAPE of an object eg. a crashed car eg. a squashed pillow C The ENERGY of an object Eg. the stones gravitational potential energy changes to kinetic energy when the force of gravity acts on it This means that the force acts between objects that can TOUCH each other eg. a girl pushing a rock eg. the force of friction which acts when one surface is moving across other surface eg. wind pushing a windmill blade eg. a girl pulling on a fishing rod Eg. a bat hitting a ball This means that the force acts between objects that DO NOT TOUCH each other eg. magnetic force eg. gravitational force eg. electrostatic force If the forces on an object are BALANCED (even on all sides), the object will KEEP DOING WHAT IT IS ALREADY DOING This means it will keep stationary (still) OR keep moving at a STEADY (CONSTANT) SPEED 1. ie. the motion will not CHANGE 2. If the forces on an object are UNBALANCED (not even on all sides) the object will CHANGE WHAT IT IS DOING This means it will Start moving if it was stationary OR If it was already moving the object will Move faster Slow down Turn a corner ie. the motion will CHANGE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the MOTION (or lack of motion) of the object to decide whether the forces are balanced or not Decide what forces are acting on the object Draw the force arrows around the object, begin arrow at the centre of the picture and label them Make sure the arrow head is facing away from the picture Draw large arrows for large forces and small arrows for small forces Draw the force of gravity pulling downwards on all objects on or above the earths surface Make things change their SHAPE Eg. crushing a can in a can crusher. The unbalanced force is downwards Make things change their DIRECTION Eg. a bus turning a corner. The unbalanced force is towards the inside of the turn When 2 different massesare dropped from the same height they; Travel downwards at the same speed Have the same acceleration (they speed up the same amount) Are pulled downwards equally because the force of gravity on each mass is the SAME The masses hit the ground at the same time. (remember coin/feather and Galileo’s cannon balls)