* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Code Questions Answers 1. Write the reactions of glycolysis
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
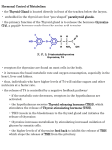
Code 1. Questions Write the reactions of glycolysis. Answers Aerobic glycolysis occurs in Cytosol. Reactions of aerobic glycolysis: 1. First glucose is irreversibly activated to glucose-6-phosphate in the cell. In liver one more specific enzyme also catalyses this reraction but at higher concentration of glucose. It is known as glucokinase (1 Mark) 2. 3. 4. 5. Glucose-6-phosphate is then isomerised to fructose -6-phosphate : (1 Mark) Fructose -6-phosphate is then irrerversibly phosphorylated to fructose 1,6 bisphosphate. Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate contains two phosphoric acid groups at C1 and C6 of fructose via phosphate ester bond. (01 Mark) Later fructose 1-6biphosphate molecule (six carbon sugar) is cleaved by aldolase enzyme to yield glyceraldyhyde -3-phosphate and dihydroxy acetone phosphate ( two 3 carbon sugars trioses) (01 Mark) Dihydroxy acetone phosphate formed in the above step is converted back to Glyceralehyde-3 phosphate . (01 Mark) 6. Now we have two molecules Glyceralehyde-3 phosphate molecules which get oxidized to 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate. This step utilizes inorganic phosphate (Pi). In 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate the phosphate group at carbon atom number 1 is high energy group. During the oxidation of glyceralhyde-3-phophate the reducing equivalents are transferred to the acceptor NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). The reduced NADH under aerobic conditions enter into mitochondria and produces 3 molecules of ATP through its passage into electron transport chain or respiratoiry chain. This type of formation of energy currency ATP through respiratory chain is called oxidative phosphorylation. (01 Mark) 3D16 – BL0032 Page 1 of 3 7. 8. In the next step the high energy compound 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate transfers its high energy to ADP to form ATP resulting in the formation of 3-Phosphoglycerate. This reaction is catalysed by phosphoglyceratekinase enzyme. This type of formation of energy currency ATP by high energy substrate is called as substrate level phosphorylation. (01 Mark) 3 phospoglycerate is then isomerised to 2 phosphoglycerate. (01 Mark) 9. 2 phosphoglycerate is then converted into one more high energy compound called as phosphoenolpyruvate. This reaction is catalysed by enolase enzyme . The activity of theis enzyme is completely inhibited by fluoride. Hence fluoride is used in the vacutainers during blood collection for glucose estimation. This prevents the utilization of glucose by RBCs. (01 Mark) 10. Later phosphoenolpyruvate is converted into pyruvate . 2. Explain formation and utilization of ketone bodies. Under aerobic conditions pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. Hence pyruvate is converted into acetyl CoA or oxaloacetate in the mitochondria. (01 Mark) Formation of ketone bodies. Inside the mitochondria HMG CoA is formed using 3 acetyl CoA as ………………………….. acetoacetate and free acetyl CoA. Acetoacetate is the parent ketone body. It is subsequently reduced by NADH dependent --------------------------------------------- This is known as ketoacidisis. Utilization of ketone bodies Acetoacetate and hydroybutyrate can be used as a source of energy in kidney and mucle. …………………………………………… oxidized in Kreb’s TCA cyle 3D16 – BL0032 Page 2 of 3 3. 4. Give detailed account on the sources, daily requirement, functions and deficiency symptoms of vitamin D. Explain in detail the regulation of serum calcium levels. Source – 2 marks Daily requirements – 2 marks Functions – 4 marks Deficiency symptoms – 2 marks Regulation of serum calcium level (Calcium homeostasis): Calcium homeostasis is a finely balanced process. The ionic calcium level is maintained by Vitamin D and hormones like Para thyroid hormone (PTH) and Calcitonin. (1 mark) Action of Vitamin D Increases the absorption of Ca (and phosphate) from the small intestine and causes removal of Ca from bone (bone resorption). Mechanism of calcium absorption from intestine through 1-25-dihydroxy Vitamin. D3: The mechanism of action of 1-25-dihydroxy Vit. D3 is typical of steroid hormone. It enters to the intestinal cell and binds to a cytoplasmic receptor. The Vitamin D3 receptor complex then moves to the nucleus where it interacts with DNA. This results in the synthesis of mRNA and this in turn forms a calcium binding protein. The calcium binding protein increases the absorption of Ca from intestine. (4 marks) Action of PTH on kidney and bone: 1) PTH increases the activity of 1-hydroxylase in kidney which increases the synthesis of 125-dihydroxy Vit. D3 and this in turn enhances the absorption of Ca from intestine. 2) It increases the reabsorption of calcium from glomerular filtrate in kidneys. 3) It causes the resorption of Calcium from bone. These 3 actions correct the hypocalcemia and bring it back to normal level. 4) PTH also causes excretion of phosphate in urine by inhibiting phosphate reabsorption in kidney. (3 marks) Action of calcitonin: This is a hormone from C cells of thyroid glands. Hypercalcemia stimulates its secretion. Calcitonin inhibits Calcium++ reabsorption from kidneys and resorption from bone. Thus it corrects hypercalcemia. (2 marks) 3D16 – BL0032 Page 3 of 3



![Poster ECE`14 PsedohipoPTH [Modo de compatibilidad]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007957322_1-13955f29e92676d795b568b8e6827da6-150x150.png)